Abstract
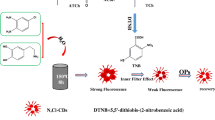
A new water soluble fluorescent coronene probe (CTCA) was synthesized and is shown to display strong fluorescence (with excitation/emission maxima at 313/450 nm) in aqueous solution. Dopamine was oxidized under air to form polydopamine (PDA) which quenches the fluorescence of CTCA. The enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is known catalyze the hydrolysis of acetylthiocholine to produce thiocholine. Thiocholine inhibits the polymerization of DA, and this leads to recovery in CTCA fluorescence. These findings form the basis for a new method for detection of AChE activity. The assay has a detection limit as low as 0.05 mU·mL−1 of AChE. It is highly selective, and other enzymes do no noticeably interfere. It was applied to the determination of AChE activity in (spiked) human serum, and of AChE inhibitors in (spiked) lake water samples.

Controlled synthesis of polydopamine for the highly sensitive and selective sensing of AChE activity is reported for the first time.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inestrosa NC, Alvarez A, Perez CA, Moreno RD, Vicente M, Linker C et al (1996) Acetylcholinesterase accelerates assembly of amyloid-β-peptides into Alzheimer's fibrils: possible role of the peripheral site of the enzyme. Neuron 16:881–891
Ballard CG (2002) Advances in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: benefits of dual cholinesterase inhibition. Eur Neurol 47:64–70
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Wang M, Gu XG, Zhang GX, Zhang DQ, Zhu DB (2009) Continuous colorimetric assay for acetylcholinesterase and inhibitor screening with gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 25:2504–2507
Maeda H, Matsuno H, Ushida M, Katayama K, Saeki K, Itoh N (2005) 2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonyl fluoresceins as fluorescent alternatives to Ellman's reagent in thiol-quantification enzyme assays. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:2922–2925
Feng FD, Tang YL, Wang S, Li YL, Zhu DB (2007) Continuous fluorometric assays for acetylcholinesterase activity and inhibition with conjugated polyelectrolytes. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:7882–7886
Gill R, Bahshi L, Freeman R, Willner I (2008) Optical detection of glucose and acetylcholine esterase inhibitors by H2O2-sensitive CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:1676–1679
Yi YH, Zhu GB, Liu C, Huang Y, Zhang YY, Li HT et al (2013) A label-free silicon quantum dots-based photoluminescence sensor for ultrasensitive detection of pesticides. Anal Chem 85:11464–11470
Zhang YD, Cai YA, Qi ZL, Lu L, Qian YX (2013) DNA-templated silver nanoclusters for fluorescence turn-on assay of acetylcholinesterase activity. Anal Chem 85:8455–8461
Sabelle S, Renard PY, Pecorella K, de Suzzoni-Dezard S, Creminon C, Grassi J et al (2002) Design and synthesis of chemiluminescent probes for the detection of cholinesterase activity. J Am Chem Soc 124:4874–4880
Du D, Tao Y, Zhang WY, Liu DL, Li HB (2011) Oxidative desorption of thiocholine assembled on core-shell Fe3O4/AuNPs magnetic nanocomposites for highly sensitive determination of acetylcholinesterase activity: an exposure biomarker of organophosphates. Biosens Bioelectron 26:4231–4235
Wang M, Gu XG, Zhang GX, Zhang DQ, Zhu DB (2009) Convenient and continuous fluorometric assay method for acetylcholinesterase and inhibitor screening based on the aggregation-induced emission. Anal Chem 81:4444–4449
Chen J, Liao DL, Wang Y, Zhou HP, Li WY, Yu C (2013) Real-time fluorometric assay for acetylcholinesterase activity and inhibitor screening through the pyrene probe monomer-excimer transition. Org Lett 15:2132–2135
Liao DL, Chen J, Zhou HP, Wang Y, Li YX, Yu C (2013) In situ formation of metal coordination polymer: a strategy for fluorescence turn-on assay of acetylcholinesterase activity and inhibitor screening. Anal Chem 85:2667–2672
Lei CY, Wang Z, Nie Z, Deng HH, Hu HP, Huang Y et al (2015) Resurfaced fluorescent protein as a sensing platform for label-free detection of copper(II) ion and acetylcholinesterase activity. Anal Chem 87:1974–1980
Rohr U, Schlichting P, Böhm A, Gross M, Meerholz K, Bräuchle C et al (1998) Liquid crystalline coronene derivatives with extraordinary fluorescence properties. Angew Chem Int Ed 37:1434–1437
Alibert-Fouet S, Seguy I, Bobo JF, Destruel P, Bock H (2007) Liquid-crystalline and electron-deficient coronene oligocarboxylic esters and imides by twofold benzogenic Diels-Alder reactions on perylenes. Chem-Eur J 13:1746–1753
Kulkarni C, Munirathinam R, George SJ (2013) Self-assembly of coronene bisimides: mechanistic insight and chiral amplification. Chem-Eur J 19:11270–11278
Hirayama S, Sakai H, Araki Y, Tanaka M, Imakawa M, Wada T et al (2014) Systematic control of the excited-state dynamics and carrier-transport properties of functionalized benzo[ghi]perylene and coronene derivatives. Chem-Eur J 20:9081–9093
Zhang CH, Shi K, Cai K, Xie JJ, Lei T, Yan QF et al (2015) Cyano- and chloro-substituted coronene diimides as solution-processable electron-transporting semiconductors. Chem Commun 51:7144–7147
Mogera U, Sagade AA, George SJ, Kulkarni GU (2014) Ultrafast response humidity sensor using supramolecular nanofibre and its application in monitoring breath humidity and flow. Sci Rep 4:4103
Hong S, Na YS, Choi S, Song IT, Kim WY, Lee H (2012) Non-covalent self-assembly and covalent polymerization co-contribute to polydopamine formation. Adv Funct Mater 22:4711–4717
Liu YL, Ai KL, Lu LH (2014) Polydopamine and its derivative materials: synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem Rev 114:5057–5115
Wei Q, Zhang FL, Li J, Li BJ, Zhao CS (2010) Oxidant-induced dopamine polymerization for multifunctional coatings. Polym Chem-Uk 1:1430–1433
Ruan CP, Ai KL, Li XB, Lu LH (2014) A superhydrophobic sponge with excellent absorbency and flame retardancy. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:5556–5560
Zhong XY, Yang K, Dong ZL, Yi X, Wang Y, Ge CC et al (2015) Polydopamine as a biocompatible multifunctional nanocarrier for combined radioisotope therapy and chemotherapy of cancer. Adv Funct Mater 25:7327–7336
Liu YL, Ai KL, Liu JH, Deng M, He YY, Lu LH (2013) Dopamine-melanin colloidal nanospheres: an efficient near-infrared photothermal therapeutic agent for in vivo cancer therapy. Adv Mater 25:1353–1359
Qiang WB, Hu HT, Sun L, Li H, Xu DK (2015) Aptamer/polydopamine nanospheres nanocomplex for in situ molecular sensing in living cells. Anal Chem 87:12190–12196
Qiang WB, Li W, Li XQ, Chen X, Xu DK (2014) Bioinspired polydopamine nanospheres: a superquencher for fluorescence sensing of biomolecules. Chem Sci 5:3018–3024
Wang D, Chen C, Ke XB, Kang N, Shen YQ, Liu YL et al (2015) Bioinspired near-infrared-excited sensing platform for in vitro antioxidant capacity assay based on upconversion nanoparticles and a dopamine-melanin hybrid system. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7:3030–3040
Ma SS, Qi YX, Jiang XQ, Chen JQ, Zhou QY, Shi GY et al (2016) Selective and sensitive monitoring of cerebral antioxidants based on the dye-labeled DNA/polydopamine conjugates. Anal Chem 88:11647–11653
Rao KV, George SJ (2010) Synthesis and controllable self-assembly of a novel coronene bisimide amphiphile. Org Lett 12:2656–2659
Chen J, Jiao HP, Li WY, Liao DL, Zhou HP, Yu C (2013) Real-time fluorescence turn-on detection of alkaline phosphatase activity with a novel perylene probe. Chem-Asian J 8:276–281
Yang MD, Zhou HP, Li YX, Zhang QF, Li JM, Zhang CY et al (2017) Peroxidase activity of the coronene bisimide supramolecular architecture and its applications in colorimetric sensing of H2O2 and glucose. J Mater Chem B 5:6572–6578
Zhang YY, Zhang CY, Chen J, Li YX, Yang MD, Zhou HP et al (2017) A real-time fluorescence turn-on assay for acetylcholinesterase activity based on the controlled release of a perylene probe from MnO2 nanosheets. J Mater Chem C 5:4691–4694
Chang JF, Li HY, Hou T, Li F (2016) Paper-based fluorescent sensor for rapid naked-eye detection of acetylcholinesterase activity and organophosphorus pesticides with high sensitivity and selectivity. Biosens Bioelectron 86:971–977
Qian ZS, Chai LJ, Tang C, Huang YY, Chen JR, Feng H (2016) A fluorometric assay for acetylcholinesterase activity and inhibitor screening with carbon quantum dots. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 222:879–886
Yan X, Song Y, Wu XL, Zhu CZ, Su XG, Du D et al (2017) Oxidase-mimicking activity of ultrathin MnO2 nanosheets in colorimetric assay of acetylcholinesterase activity. Nano 9:2317–2323
Ni PJ, Sun YJ, Dai HC, Jiang S, Lu WD, Wang YL et al (2016) Colorimetric determination of the activity of acetylcholinesterase and its inhibitors by exploiting the iodide-catalyzed oxidation of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine by hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 183:2589–2595
Ni PJ, Sun YJ, Dai HC, Lu WD, Jiang S, Wang YL et al (2017) Prussian blue nanocubes peroxidase mimetic-based colorimetric assay for screening acetylcholinesterase activity and its inhibitor. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 240:1314–1320
Hou T, Zhang LF, Sun XZ, Li F (2016) Biphasic photoelectrochemical sensing strategy based on in situ formation of CdS quantum dots for highly sensitive detection of acetylcholinesterase activity and inhibition. Biosens Bioelectron 75:359–364
Wang XZ, Hou T, Dong SS, Liu XJ, Li F (2016) Fluorescence biosensing strategy based on mercury ion-mediated DNA conformational switch and nicking enzyme-assisted cycling amplification for highly sensitive detection of carbamate pesticide. Biosens Bioelectron 77:644–649
Trettnak W, Reininger F, Zinterl E, Wolfbeis OS (1993) Fiberoptic remote detection of pesticides and related inhibitors of the enzyme acetylcholine esterase. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 11:87–93
Virel A, Saa L, Pavlov V (2009) Modulated growth of nanoparticles. Application for sensing nerve gases. Anal Chem 81:268–272
Ju KJ, Feng JX, Feng JJ, Zhang QL, Xu TQ, Wei J et al (2015) Biosensor for pesticide triazophos based on its inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and using a glassy carbon electrode modified with coral-like gold nanostructures supported on reduced graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 182:2427–2434
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51761145102, 21561162004), and the Science and Technology Development Project of Jilin Province (International Collaboration Program, 20160414040GH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 4787 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Zhou, H., Zhang, Y. et al. Controlled synthesis of polydopamine: A new strategy for highly sensitive fluorescence turn-on detection of acetylcholinesterase activity. Microchim Acta 185, 132 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2678-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2678-9