Abstract
The authors describe a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) deposited on multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MIP/MWCNTs) for separation and preconcentration of L-cysteine (L-Cys). The MIP was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction and FT-IR and via adsorption kinetics and adsorption isotherms. The MIP is shown to be a viable sorbent for L-Cys which subsequently is quantified by spectrophotometry through formation of a charge transfer complex with the DDQ reagent. The experimental parameters affecting separation efficiency and spectrophotometric determination were optimized. Under optimum conditions and at an analytical wavelength of 478 nm, the calibration plot is linear in the 4.0 to 180 ng mL−1 concentration range, and the limit of detection (at an S/N ratio of 3) is 2.3 ng mL−1. The intra-day and inter-day precision are in the range from 2.4 to 3.6%. The method was successfully applied to determination of L-Cys in spiked human serum and water samples where it gave recoveries ranging from 96.6 to 102.4%.

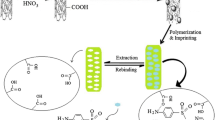
Schematic of the preparation of a molecularly imprinted polymer coated on the multiwalled carbon nanotube (MIP/MWCNT) by functionalization of MCNTs with methacrylic acid and subsequent polymerization. The MIP/MWCNTs were successfully applied for extraction and spectrophotometric determination of L-Cys by charge transfer (CT) complexation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ensafi AA, Rezaei B, Nouroozi S (2009) Flow injection Spectrofluorimetric determination of Cystine and cysteine. J Braz Chem Soc 20(2):288–293
Ahmad M, Pan C, Zhu J (2010) Electrochemical determination of L-cysteine by an elbow shaped, Sb-doped ZnO nano wire-modified electrode. J Mater Chem 20(34):7169–7174
Kaniowska E, Chwatko G, Głowacki R, Kubalczyk P, Bald E (1998) Urinary excretion measurement of cysteine and homocysteine in the form of their S-pyridinium derivatives by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J Chromatogr A 798(1–2):27–35
Jin W, Chen H (2000) A new method of determination of diffusion coefficients using capillary zone electrophoresis (peak-height method). Chromatographia 52(1):17–21
Kubec R, Svobodova M, Valisec J (2001) Gas-chromatographic determination of Smethylcysteine sulfoxide in cruciferous vegetables. Eur Food Res Technol 213(4–5):386–388
Huang S, Wang L, Huang C, Hu B, Su W, Xiao Q (2016) Graphene quantum dot coupled with gold nanoparticle based “off-on” fluorescent probe for sensitive and selective detection of L-cysteine. Microchim Acta 183(6):1855–1864
Devasenathipathy R, Mani SM, Chen SM, Kohilarani K, Ramaraj S (2015) Determination of L- cysteine at iron tetrasulfonated phthalocyanine decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes film modified electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 10:682–690
Blasco F, Medina-Hernandez MJ, Sagrado S (1997) Use of pH gradients incontinuous-flow systems and multivariate regression techniques applied to the determination of methionine and cysteine in pharmaceuticals. Anal Chim Acta 348(1–3):151–159
Dong Y, Su YM, Chen P, Sun H (2015) Chemiluminescence of carbon dots induced by diperiodato-nicklate (IV) in alkaline solution and its application to a quenchometric flow-injection assays of paracetamol, L-cysteine and glutathione. Microchim Acta 182(5-6):1071–1077
Wen X, Yang Q, Yan Z, Deng Q (2011) Chemical analysis of food: techniques and applications. Microchem J 97(2):249–254
Pohl P, Stecka H, Jamroz P (2012) Solid phase extraction with flame atomic absorption spectrometry for determination of traces of Ca, K, mg and Na in quality control of white sugar. Food Chem 130(2):441–446
Ozdemi N, Soylak M, Elci L, Dogan M (2004) Speciation analysis of inorganic Sb(III) and Sb(V) ions by using mini column filled with Amberlite XAD-8 resin. Anal Chim Acta 505(1):37–41
Martín-Esteban A (2001) Molecularly imprinted polymers: new molecular recognition materials for selective solid-phase extraction of organic compounds. Fresenius J Anal Chem 370(7):795–802
Lasakova M, Jandera P (2009) Molecularly imprinted polymers and their application in solid phase extraction. J Sep Sci 32(5–6):799–812
Cheong WJ, Yang SH, Ali F (2013) Molecular imprinted polymers for separation science: a review of reviews. J Sep Sci 36(3):609–628
Lin Z, Cheng W, Li Y, Liu Z, Chen X, Huang C (2012) Novel superparamagnetic surface molecularly imprinted nanoparticle adopting dummy template: an efficient solid-phase extraction adsorbent for bisphenol. Anal Chim Acta 720:71–76
Aswini KK, Vinu Mohan AM, Biju VM (2014) Molecularly imprinted polymer based electrochemical detection of L-cysteine at carbon paste electrode. Mater Sci Eng C 37:321–326
Cai X, Li J, Zhang Z, Wang G, Song X, You J, Chen L (2014) Chemodosimeter-based fluorescent detection of L-cysteine after extracted by molecularly imprinted polymers. Talanta 120:297–303
Xie CG, Zhang ZP, Wang DP, Guan GJ, Gao DM, Liu JH (2006) Surface molecular self-assembly strategy for TNT imprinting of polymer nanowire/nanotube arrays. Anal Chem 78(83):39–46
Yang H-H, Zhang S-Q, Tan F, Zhuang Z-X, Wang X-R (2005) Surface molecularly imprinted nanowires for biorecognition. J Am Chem Soc 127(5):1378–1379
Tan CJ, Chua HG, Ker KH, Tong YW (2008) Preparation of bovine serum albumin surface-imprinted submicrometer particles with magnetic susceptibility through core shell miniemulsion polymerization. Anal Chem 80(3):683–692
Hu TP, Zhang YM, Zheng LH, Fan GZ (2010) Molecular recognition and adsorption performance of benzothiophene imprinted polymer on silica gel surface. J Fuel Chem Technol 38(6):722–729
Dai H, Xiao DL, He H, Li H, Yuan DH, Zhang C (2015) Synthesis and analytical applications of molecularly imprinted polymers on the surface of carbon nanotubes: a review. Microchim Acta 182(5–6):893–908
Xu Z, Zhou W, Xu PP, Pan JM, Wu XY, Yan YS (2011) A molecularly imprinted polymer based on TiO2 as sacrificial support for selective recognition of dibenzothiophene. J Chem Eng 172(1):191–198
Niu M, Pham-Huy C, He H (2016) Core-shell nanoparticles coated with molecularly imprinted polymers: a review. Microchim Acta 183(10):2677–2695
Ki C, Chang J (2006) Preparation of a molecularly imprinted polymeric nanocapsule with potential use in delivery applications. Macromolecules 39(9):3415–3419
Janiak DS, Ayyub OB, Kofinas P (2009) Effects of charge density on the recognition properties of molecularly imprinted polymeric hydrogels. Macromolecules 42(5):1703–1709
Hua Z, Chen Z, Li Y, Zhao M (2008) Thermo sensitive and salt-sensitive molecularly imprinted hydrogel for bovine serum albumin. Langmuir 24(12):5773–5780
Yang YZ, Liu XG, Guo MC, Li S, Liu WF, Xu BS (2011) Molecularly imprinted polymer on carbon microsphere surfaces for adsorbing dibenzothiophene. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 377(1–3):379–385
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I Solids J Amer Chem Soc 38(11):2221–2295
Negi D, Chanu T (2008) Surface-modified CdS nanoparticles as a fluorescent probe for the selective detection of cysteine. Nanotechnology 19(46):465503–465508
Wang Y, Wang J, Yang F, Yang X (2010) Spectrophotometric determination of cysteine with gold nanoparticles stabilized with single-stranded oligo nucleotides. Anal Sci 26(5):545–549
Wei X, Qi L, Tan J, Liu R, Wang F (2010) A colorimetric sensor for determination of cysteine by carboxymethyl cellulose-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 671(1):80–84
Pan N, Li-Ying W, Wu LL, Peng CF, Xie ZJ (2016) Colorimetric determination of cysteine by exploiting its inhibitory action on the peroxidase-like activity of au@Pt core-shell nanohybrids. Microchim Acta 184(1):65–72
Gaitonde MK (1967) A spectrophotometric method for the direct determination of cysteine in the presence of other naturally occurring amino acids. Biochem J 104(2):627–633
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 92 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemi, M., Nazari, Z. & Bigdelifam, D. A molecularly imprinted polymer based on multiwalled carbon nanotubes for separation and spectrophotometric determination of L-cysteine. Microchim Acta 184, 2523–2532 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2236-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2236-x