Abstract
The authors describe a nanocomposite prepared from gold nanoparticles, branched polyethylenimine and carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes (AuNP/b-PEI/c-MWCNTs), and its application to a highly sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for the soluble CD40 ligand (sCD40L), a biomarker of acute coronary syndrome (ACS). It is known that c-MWCNTs possess a remarkably good electrochemical conductivity that can improve the sensitivity of an immunosensor, but their tendency towards aggregation is an obstacle. The use of b-PEI can substantially decrease the tendency towards aggregation. AuNPs with their large specific surface and good electrical conductivity were used to load the antibody. The nanocomposite was characterized by transmission electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and cyclic voltammetry. When using hexacyanoferrate as an electrochemical probe (best detected at 0.18 V vs. SCE), the electrode displays a linear response in the 10 fg mL−1 to 100 pg mL−1 sCD40L concentration range, and a lower detection limit of 3 fg mL−1. The electrode is regenerable. It was applied to the determination of sCD40L in spiked serum samples, and the results agreed well with an ELISA.

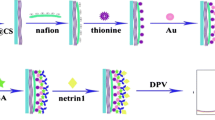
Schematic of a highly sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of soluble CD40 ligand (sCD40L), a biomarker for the acute coronary syndrome (ACS). It is based on the use of a nanocomposite consisting of gold nanoparticles, branched polyethylenimine and carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes (AuNPs/b-PEI/c-MWCNTs).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang X, Zhu P, Pi F, Jiang H, Shao J, Zhang Y, Sun X (2016) A sensitive and simple macrophage-based electrochemical biosensor for evaluating lipopolysaccharide cytotoxicity of pathogenic bacteria. Biosens Bioelectron 81:349–357
Fang Y, Umasankar Y, Ramasamy RP (2016) A novel bi-enzyme electrochemical biosensor for selective and sensitive determination of methyl salicylate. Biosens Bioelectron 81(64):3–19
Ahuja T, Mir IA, Kumar D, Rajesh (2007) Biomolecular immobilization on conducting polymers for biosensing applications. Biomaterials 28(5):791–805
Paul KB, Singh V, Vanjari SRK, Singh SG (2017) One step biofunctionalized electrospun multiwalled carbon nanotubes embedded zinc oxide nanowire interface for highly sensitive detection of carcinoma antigen-125. Biosens Bioelectron 88:144–152
Sabela MI, Mpanza T, Kanchi S, Sharma D, Bisetty K (2016) Electrochemical sensing platform amplified with a nanobiocomposite of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase enzyme for the detection of capsaicin. Biosens Bioelectron 83:45–53
Tsai YC, Chen SY, Liaw HW (2007) Immobilization of lactate dehydrogenase within multiwalled carbon nanotube-chitosan nanocomposite for application to lactate biosensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 125(2):474–481
Kaur N, Thakur H, Kumar R, Prabhakar N (2016) An electrochemical sensor modified with poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-wrapped multi-walled carbon nanotubes for enzyme inhibition-based determination of organophosphates. Microchim Acta 183(7):2307–2315
Xia C, Li Y, Yuan G, Guo Y, Yu C (2015) Immunoassay for serum amyloid A using a glassy carbon electrode modified with carboxy-polypyrrole, multiwalled carbon nanotubes, ionic liquid and chitosan. Microchim Acta 182(7):1395–1402
Chen S, Yuan R, Chai Y, Min L, Li W, Yang X (2009) Electrochemical sensing platform based on tris(2,2′-bipyridyl)cobalt(III) and multiwall carbon nanotubes–Nafion composite for immunoassay of carcinoma antigen-125. Electrochim Acta 54(28):7242–7247
Gopalan AI, Muthuchamy N, Komathi S, Lee KP (2015) A novel multicomponent redox polymer nanobead based high performance non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 84:53–63
Wang X, Li S, Zhang P, Lv F, Liu L, Li L, Wang S (2015) An optical nanoruler based on a conjugated polymer− silver nanoprism pair for label-free protein detection. Adv Mater 27(39):6040–6045
Hajian R, Mehrayin Z, Mohagheghian M, Zafari M, Hosseini P, Shams N (2015) Fabrication of an electrochemical sensor based on carbon nanotubes modified with gold nanoparticles for determination of valrubicin as a chemotherapy drug: valrubicin-DNA interaction. Mater Sci Eng C 49:769–775
Li X, Liu X, Wang W, Li L, Lu X (2014) High loading Pt nanoparticles on functionalization of carbon nanotubes for fabricating nonenzyme hydrogen peroxide sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 59(13):221–226
Jiang Z, Liangming W, Chonghao P, Yanjie S, Zhi Y, Liying Z, Hao W, Yafei Z (2013) A non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on the composite of cubic Cu nanoparticles and arc-synthesized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Biosens Bioelectron 47C(17):86–91
Varo N, Lemos JAD, Libby P, Morrow DA, Murphy SA, Nuzzo R, Gibson CM, Cannon CP, Braunwald E, Schönbeck U (2004) Soluble CD40L: risk prediction after acute coronary syndromes. ACC Curr J Rev 13(1):12
Schönbeck U, Varo N, Libby P, Buring J, Ridker PM (2001) Soluble CD40L and cardiovascular risk in women. Circulation 104(19):2266–2268
Gokulakrishnan K, Deepa R, Mohan V, Gross MD (2006) Soluble P-selectin and CD40L levels in subjects with prediabetes, diabetes mellitus, and metabolic syndrome--the Chennai urban rural epidemiology study. Metab Clin Exp 55(2):237–242
Bilir B, Soysal-Atile N, Ekiz BB, Yilmaz I, Bali I, Altintas N, Baykiz D, Aydin M, Guldiken S (2016) Evaluation of SCUBE-1 and sCD40L biomarkers in patients with hypothyroidism due to Hashimoto's thyroiditis: a single-blind, controlled clinical study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20(3):407–413
Wang H, Zhu L, Cheng J, Cai J, Li Y, Ma X, Wei R (2015) CD40 ligand induces expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 and E-selectin in orbital fibroblasts from patients with Graves' orbitopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 253(4):1–10
Li R, Chen WC, Pang XQ, Tian WY, Wang WP, Zhang XG (2012) Combined effect of sCD40L and PI3K siRNA on transplanted tumours growth and microenvironment in nude mice with gastric cancer. Mol Biol Rep 39(9):8755–8761
Pan LH, Kuo SH, Lin TY, Lin CW, Fang PY, Yang HW (2016) An electrochemical biosensor to simultaneously detect VEGF and PSA for early prostate cancer diagnosis based on graphene oxide/ssDNA/PLLA nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 89:598–605
Choudhary M, Kumar V, Singh A, Singh M, Kaur S, Reddy G, Pasricha R, Singh S, Arora K (2013) Graphene oxide based label free ultrasensitive immunosensor for lung cancer biomarker, hTERT. J Bioenerg Biomembr 4(4):1–9
Yu X, Hua T, Liu X, Yan Z, Xu P, Du P (2014) Nickel-based thin film on multiwalled carbon nanotubes as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for water splitting. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(17):15395–15402
Navale S, Khuspe G, Chougule M, Patil V (2014) Camphor sulfonic acid doped PPy/α-Fe 2 O 3 hybrid nanocomposites as NO 2 sensors. RSC Adv 4(53):27998–28004
Mahanta D, Manna U, Madras G, Patil S (2010) Multilayer self-assembly of TiO2 nanoparticles and polyaniline-grafted-chitosan copolymer (CPANI) for photocatalysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3(1):84–92
Chen H-Y, Shen H-P, Wu C-H, Chiu W-Y, Chen W-C, Tai H-J (2013) Core–shell composite latexes derived from PEDOT: PSS dispersion and the preparation of conductive, flexible and transparent films. J Mater Chem C 1(34):5351–5358
Oh JW, Yoon YW, Heo J, Yu J, Kim H, Kim TH (2016) Electrochemical detection of nanomolar dopamine in the presence of neurophysiological concentration of ascorbic acid and uric acid using charge-coated carbon nanotubes via facile and green preparation. Talanta 147:453–459
Chen RJ, Zhang Y, Wang D, Dai H (2001) Noncovalent sidewall functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes for protein immobilization. J Am Chem Soc 123(16):3838–3839
Wu H, Shi H, Zhang H, Wang X, Yang Y, Yu C, Hao C, Du J, Hu H, Yang S (2014) Prostate stem cell antigen antibody-conjugated multiwalled carbon nanotubes for targeted ultrasound imaging and drug delivery. Biomaterials 35(20):5369–5380
Müller CI, Lambert C (2011) Electrochemical and optical characterization of triarylamine functionalized gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 27(8):5029–5039
Lu X, Li Y, Zhang X, Du J, Zhou X, Xue Z, Liu X (2012) A simple and an efficient strategy to synthesize multi-component nanocomposites for biosensor applications. Anal Chim Acta 711:40–45
Gururajan P, Gurumurthy P, Nayar P, Babu S, Sarasabharati A, Victor D, Cherian K (2009) Increased serum concentrations of soluble CD40 ligand as a prognostic marker in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Indian J Clin Biochem 24(3):229–233
Zhao Y, He J, Yuan G, Xia C, Li Y, Yu C (2015) Rapidly accomplished femtomole soluble CD40 ligand detection in human serum: a “green” homobifunctional agent coupled with reduced graphene oxide-tetraethylene pentamine as platform. RSC Adv 5(107):88392–88400
Yuan G, Yu C, Xia C, Gao L, Xu W, Li W, He J (2015) A simultaneous electrochemical multianalyte immunoassay of high sensitivity C-reactive protein and soluble CD40 ligand based on reduced graphene oxide-tetraethylene pentamine that directly adsorb metal ions as labels. Biosens Bioelectron 72:237–246
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the financial support from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 81370403), Chongqing foundation and advanced research project (No. CSTC2015jcyjBX0053), and Chongqing medical university scientific research cultivating fund (No.201414).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Junlin He and Jing Wu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3524 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., He, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Reusable voltammetric immunosensor for sCD40L, a biomarker for the acute coronary syndrome, using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of gold nanoparticles, branched polyethylenimine and carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 184, 1837–1845 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2192-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2192-5