Abstract
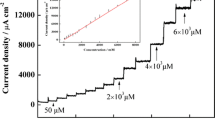
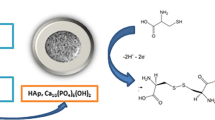
A conducting polymer composite was prepared from nano-sized hydroxyaptite (nHAp) doped into poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) and then electrodeposited on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE). The nHAp carries carboxy groups and therefore is negatively charged at moderate pH value. When doped into PEDOT (PEDOT-nHAp), it forms a uniform and stable film that exhibits low electrochemical impedance, a large specific surface, and high activity toward the electrochemical oxidation of nitrite. Under optimized conditions and at a relatively low working potential of 0.78 V (vs. SCE), the modified GCE exhibited a linear amperometric response in the 0.25 μM to 1.05 mM nitrite concentration range, and the limit of detection is as low as 83 nM.

A highly sensitive nitrite sensor was developed based on conducting polymer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) doped with carboxyl group functionalized hydroxyapatite nanoparticles, which exhibited a large surface area and good conductivity and stability.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zanin H, Saito E, Marciano FR, Ceragioli HJ, Granato AEC, Porcionatto M, Lobo AO (2013) Fast preparation of nano-hydroxyapatite/superhydrophilic reduced graphene oxide composites for bioactive applications. J Mater Chem B 1:4947–4955
Nathanael AJ, Hong SI, Mangalaraj D, Ponpandian N, Chen PC (2012) Template-free growth of novel hydroxyapatite nanorings: formation mechanism and their enhanced functional properties. Cryst Growth Des 12:3565–3574
Rezwan K, Chen QZ, Blaker JJ, Boccaccini AR (2006) Biodegradable and bioactive porous polymer/inorganic composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 27:3413–3431
Hassan MN, Mahmoud MM, El-Fattah AA, Kandil S (2016) Microwave-assisted preparation of nano-hydroxyapatite for bone substitutes. Ceram Int 42:3725–3744
Zahmakiran M, Tonbul Y, Özkar S (2010) Ruthenium (0) nanoclusters supported on hydroxyapatite: highly active, reusable and green catalyst in the hydrogenation of aromatics under mild conditions with an unprecedented catalytic lifetime. Chem Commun 46:4788–4790
Zahouily M, Abrouki Y, Bahlaouan B, Rayadh A, Sebti S (2003) Hydroxyapatite: new efficient catalyst for the Michael addition. Catal Commun 4:521–524
Tran RT, Wang L, Zhang C, Huang M, Tang W, Zhang C, Zhang Z, Jin D, Banik B, Brown JL, Xie Z, Bai X, Yang J (2014) Fiber-optic raster scanning two-photon endomicroscope using a tubular piezoelectric actuator. J Biomed Mater Res A 102:2521–2523
Akazawa T, Kobayashi M, Yoshida M, Matsushima K, Minoshima H, Sugimura H, Kanno T, Horiuchi J (1999) Improved liquid chromatographic separation of different proteins by designing functional surfaces of cattle bone-originated apatite. J Chromatogr A 862:217–220
Li Y, Liu X, Zeng X, Liu Y, X. Liu, Wei W, Luo S (2009) Simultaneous determination of ultra-trace lead and cadmium at a hydroxyapatite-modified carbon ionic liquid electrode by square-wave stripping voltammetry. Sens Actuators B Chem 139:604–610
Wei G, Ma PX (2004) Structure and properties of nano-hydroxyapatite/polymer composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 25:4749–4757
Wang HS, Wang GX, Pan QX (2005) Electrochemical study of the interactions of DNA with redox-active molecules based on the immobilization of dsDNA on the sol-gel derived nano porous hydroxyapatite-polyvinyl alcohol hybrid material coating. Electroanal 17:1854–1860
Yang L, Wei W, Gao X, Xia J, Tao H (2005) A new antibody immobilization strategy based on electrodeposition of nanometer-sized hydroxyapatite for label-free capacitive immunosensor. Talanta 68:40–46
Pan D, Wang Y, Chen Z, Yin T, Qin W (2009) Fabrication and characterization of carbon nanotube-hydroxyapatite nanocomposite: application to anodic stripping voltammetric determination of cadmium. Electroanal 21:944–952
Lee SC, Choi HW, Lee HJ, Kim KJ, Chang JH, Kim SY, Choi J, Oh KS, Jeong YK (2007) In-situ synthesis of reactive hydroxyapatite nano-crystals for a novel approach of surface grafting polymerization. J Mater Chem 17:174–180
Hu YY, Liu XP, Ma X, Rawal A, Prozorov T, Akinc M, Mallapragada SK, Schmidt-Rohr K (2011) Biomimetic self-assembling copolymer−hydroxyapatite nanocomposites with the nanocrystal size controlled by citrate. Chem Mater 23:2481–2490
Montero-Ocampo C, Villegas D, Veleva L (2005) Controlled potential electrodeposition of calcium phosphate on Ti6Al4V. J Electrochem Soc 152:C692–C696
Zhang JM, Lin CJ, Feng ZD, Tian ZW (1998) Mechanistic study on electrochemical codeposition of mixed zinc–erbium oxide films on the cathodic surface. J Electroanal Chem 452:235–240
Argum AA, Cirpan A, Reynolds JR (2003) The first truly all-polymer electrochromic devices. Adv Mater 15:1338–1341
Kim YH, Sachse C, Machala ML, May C, Müller-Meskamp L, Leo K (2011) Highly conductive PEDOT:PSS electrode with optimized solvent and thermal post-treatment for ITO-free organic solar cells. Adv Funct Mater 21:1076–1081
Mathiyarasu J, Senthilkumar S, Phani KLN, Yegnaraman V (2008) PEDOT-au nanocomposite film for electrochemical sensing. Mater Lett 62:571–573
Roncali J, Blanchard P, Frere P (2005) 3, 4-Ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) as a versatile building block for advanced functional π-conjugated systems. J Mater Chem 15:1589–1610
Luo X, Weaver CL, Tan S, Cui XT (2013) Pure graphene oxide doped conducting polymer nanocomposite for bio-interfacing. J Mater Chem B 1:1340–1348
Wang W, Xu G, Cui XT, Sheng G, Luo X (2014) Enhanced catalytic and dopamine sensing properties of electrochemically reduced conducting polymer nanocomposite doped with pure graphene oxide. Biosens Bioelectron 58:153–156
Cui M, Song Z, Wu Y, Guo B, Fan X, Luo X (2016) A highly sensitive biosensor for tumor maker alpha fetoprotein based on poly (ethylene glycol) doped conducting polymer PEDOT. Biosens Bioelectron 79:736–741
Xu G, Li B, Luo X (2013) Carbon nanotube doped poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for the electrocatalytic oxidation and detection of hydroquinone. Sens Actuators B Chem 176:69–74
Zhu ZT, Mabeck JT, Zhu CC, Cady NC, Batt CA, Malliaras GG (2004) A simple poly (3, 4-ethylene dioxythiophene)/poly (styrene sulfonic acid) transistor for glucose sensing at neutral pH. Chem Commun:1556–1557
Lawal AT, Wallace GG (2014) Vapour phase polymerisation of conducting and non-conducting polymers: a review. Talanta 119:133–143
Mativetsky JM, Tarver J, Yang X, Koel BE, Loo YL (2014) Structural origin of anisotropic transport in electrically conducting dichloroacetic acid-treated polymers. Org Electron 15:631–638
Rhee SH, Tanaka J (1999) Effect of citric acid on the nucleation of hydroxyapatite in a simulated body fluid. Biomaterials 20:2155–2160
Spanos N, Patis A, Kanellopoulou D, Andritsos N, Koutsoukos PG (2007) Precipitation of calcium phosphate from simulated milk ultrafiltrate solutions. CrystGrowth Des 7:25–29
Jiang WG, Pan HH, Cai YR, Tao JH, Liu P, Xu XR, Tang RK (2008) Atomic force microscopy reveals hydroxyapatite-citrate interfacial structure at the atomic level. Langmuir 24:12446–12451
Kamyabi MA, Aghajanloo F (2008) Electrocatalytic oxidation and determination of nitrite on carbon paste electrode modified with oxovanadium(IV)-4-methyl salophen. J Electroanal Chem 614:157–165
Huang SS, Liu L, Mei LP, Zhou JY, Guo FY, Wang AJ, Feng JJ (2016) Electrochemical sensor for nitrite using a glassy carbon electrode modified with gold-copper nanochain networks. Microchim Acta 183:791–797
Mehmeti E, Stanković DM, Hajrizi A, Kalcher K (2016) The use of graphene nanoribbons as efficient electrochemical sensing material for nitrite determination. Talanta 159:34–39
Lin P, Chai F, Zhang R, Xu G, Fan X, Luo X (2016) Electrochemical synthesis of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with gold nanoparticles, and its application to nitrite sensing. Microchim Acta 183:1235–1241
Dai J, Deng D, Yuan Y, Zhang J, Deng F, He S (2016) Amperometric nitrite sensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and poly (toluidine blue). Microchim Acta 183:1553–1561
Xu G, Liang S, Fan J, Sheng G, Luo X (2016) Amperometric sensing of nitrite using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a multilayer consisting of carboxylated nanocrystalline cellulose and poly (diallyldimethyl ammonium) ions in a PEDOT host. Microchim Acta 183:2031–2037
Marlinda AR, Pandikumar A, Yusoff N, Huang NM, Lim HN (2015) Electrochemical sensing of nitrite using a glassy carbon electrode modified with reduced functionalized graphene oxide decorated with flower-like zinc oxide. Microchim Acta 182:1113–1122
Rabti A, Aoun SB, Raouafi N (2016) A sensitive nitrite sensor using an electrode consisting of reduced graphene oxide functionalized with ferrocene. Microchim Acta 183:3111–3117
Zhuang Z, Lin H, Zhang X, Qiu F, Yang H (2016) A glassy carbon electrode modified with carbon dots and gold nanoparticles for enhanced electrocatalytic oxidation and detection of nitrite. Microchim Acta 183:2807–2814
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21422504 and 21275087), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China (JQ201406), the Taishan Scholar Program of Shandong Province of China and the Domestic Visiting Scholar Program of Shandong Province of China for Young Backbone Teachers of Colleges and Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 484 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Han, R., Feng, X. et al. A glassy carbon electrode modified with poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with nano-sized hydroxyapatite for amperometric determination of nitrite. Microchim Acta 184, 1721–1727 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2180-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2180-9