Abstract
The authors have developed a rapid and reliable method for the capillary electrochromatographic determination of cephalosporin antibiotics in environmental waters. An open-tubular capillary column was modified with the complex [Cu(mal)(bpy)], a copper(II) complex with malic acid and 4,4′-bipyridyl, by an amide coupling method to act as the stationary phase. The simultaneous determination of the cephalosporins formulations, namely cefapirin (CP), ceftiofur (EFT) and cefixime (CFM) in environmental water samples was accomplished in buffer of pH 5.0 by applying a voltage of 8 kV and with DAD detection. Detection limits typically are 0.1 μg⋅mL−1.The method was applied to the analysis of cephalosporins in spiked water samples from Kunming Lake to give recoveries betwen 88 and 106%.

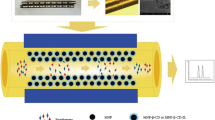
A metal-organic framework (MOF) was synthesized from copper(II), malic acid and 4,4′-bipyridyl and used as stationary phase of capillary electrochromatography (CEC) by covalent immobilization on the capillary inner walls. Compared to an uncoated fused-silica capillary, improved separation of cephalosporin antibiotics can be accomplished.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Shaboury SR, Saleh GA, Mohamed FA, Rageh AH (2007) Analysis of cephalosporin antibiotics. J Pharm Biomed Anal 45:1–9
Jin HE, Jin SE, Maeng HJ (2014) Recent bioanalytical methods for quantification of third-generation cephalosporins using HPLC and LC-MS(/MS) and their applications in pharmacokinetic studies. Biomed Chromatogr 28:1565–1587
Holstege DM, Puschner B, Whitehead G, Galey FD (2002) Screening and mass spectral confirmation of β-lactam antibiotic residues in milk using LC-MS/MS. J Agr Food Chem 50(2):406–411
McWhinney BC, Wallis SC, Hillister T, Roberts JA, Lipman J, Ungerer JPJ (2010) Analysis of 12 beta-lactam antibiotics in human plasma by HPLC with ultraviolet detection. J Chromatogr B 878(22):2039–2043
Chen XW, Ye NS (2016) Graphene oxide-reinforced hollow fiber solid-phase microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of cephalosporins in milk samples. Food Anal Methods 9(9):2452–2462
Yu X, Tang X, Zuo J, Zhang M, Chen L, Li Z (2016) Distribution and persistence of cephalosporins in cephalosporin producing wastewater using SPE and UPLC-MS/MS method. Sci Total Environ 569-570:23–30
Hancu G, Kelemen H, Rusu A, Gyéresi Á (2013) Development of a capillary electrophoresis method for the simultaneous determination of cephalosporins. J Serb Chem Soc 78(9):1413–1423
Quesada-Molina C, Olmo-Iruela M, Garcia-Campana AM (2012) Analysis of cephalosporin residues in environmental waters by capillary zone electrophoresis with off-line and on-line preconcentration. Anal Methods 4:2341–2347
Zhang K, Liang L, Huang M, Hu Y, Li G (2014) Determination of iodate in iodized salt and water samples by shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Microchim Acta 181(11–12):1301–1308
Matysik F (2008) Advances in amperometric and conductometric detection in capillary and chip-based electrophoresis. Microchim Acta 160(1–2):1–14
Garcia-Canas V, Gonzalez R, Cifuentes A (2002) Highly reproducible capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE) of DNA fragments using uncoated columns. Detection of genetically modified maize by PCR-CGE. J Sep Sci 25(9):577–583
Zhu Z, Lu JJ, Liu S (2012) Protein separation by capillary gel electrophoresis: a review. Anal Chim Acta 709:21–31
Wen Y, Li J, Liu J, Lu W, Ma J, Chen L (2013) Dual cloud point extraction coupled with hydrodynamic-electrokinetic two-step injection followed by micellar electrokinetic chromatography for simultaneous determination of trace phenolic estrogens in water samples. Anal Bional Chem 405(17):5843–5852
Ward TJ, Ward KD (2012) Chiral separations: a review of current topics and trends. Anal Chem 84(2):626–635
Zhang Y, Deng P, Chen N, Liu P, Yang Z (2010) Preparation and evaluation of tandem stationary phases for μ-HPLC and capillary electrochromatography. Microchim Acta 170(1–2):1–7
Ou J, Lin H, Zhang Z, Huang G, Dong J, Zou H (2013) Recent advances in preparation and application of hybrid organic-silica monolithic capillary columns. Electrophoresis 34(1SI):126–140
Ye NS, Li J (2014) Determination of dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine by open-tubular capillary electrochromatography using graphene oxide molecularly imprinted polymers as the stationary phase. J Sep Sci 37:2239–2247
Hu W, Hong T, Gao X, Ji Y (2014) Applications of nanoparticle-modified stationary phases in capillary electrochromatography. TrAC Trend Anal Chem 61:29–39
Xie S, Zhang M, Fei Z, Yuan L (2014) Experimental comparison of chiral metal-organic framework used as stationary phase in chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1363:137–143
Ma JC, Ye NS, Li J (2016) Covalent bonding of homochiral metal-organic framework in capillaries for stereoisomer separation by capillary electrochromatography. Electrophoresis 37(4):601–608
Ye NS, Ma JC, An JX, Li J, Cai ZM, Zong H (2016) Separation of amino acid enantiomers by a capillary modified with a metal-organic framework. RSC Adv 6(47):41587–41593
Tarongoy EM, Haddad PR, Boysen RI, Hearn MT, Quirino JP (2016) Open tubular-capillary electrochromatography: developments and applications from 2013 to 2015. Electrophoresis 37(1):66–85
Furukawa H, Cordova KE, O'Keeffe M, Yaghi OM (2013) The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science 341(6149):1230444
Liu J, Chen L, Cui H, Zhang J, Zhang L, Su CY (2014) Applications of metal-organic frameworks in heterogeneous supramolecular catalysis. Chem Soc Rev 43(16):6011–6061
Zeng M, Tan Y, He Y, Yin Z, Chen Q, Kurmoo M (2013) A porous 4-fold-interpenetrated chiral framework exhibiting vapochromism, single-crystal-to-single-crystal solvent exchange, gas sorption, and a poisoning effect. Inorg Chem 52(5):2353–2360
Wen Y, Chen L, Li J, Liu D, Chen L (2014) Recent advances in solid-phase sorbents for sample preparation prior to chromatographic analysis. TRAC-Trend Anal Chem 59:26–41
Geier SJ, Mason JA, Bloch ED, Queen WL, Hudson MR, Brown CM, Long JR (2013) Selective adsorption of ethylene over ethane and propylene over propane in the metal-organic frameworks M2(dobdc) (M = Mg, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Zn). Chem Sci 4(5):2054–2061
Ge D, Lee HK (2012) Sonication-assisted emulsification microextraction combined with vortex-assisted porous membrane-protected micro-solid-phase extraction using mixed zeoliticimidazolate frameworks 8 as sorbent. J Chromatogr A 1263:1–6
Jia YQ, Su H, Wang ZH, Wong YE, Chen XF, Wang ML, Chan TD (2016) Metal-organic framework@microporous organic network as adsorbent for solid-phase microextraction. Anal Chem 88:9364–9367
Rocio-Bautista P, Pacheco-Fernandez I, Pasan J, Pino V (2016) Are metal-organic frameworks able to provide a new generation of solid-phase microextraction coatings?-a review. Anal Chim Acta 939:26–41
Cui X, Gu Z, Jiang D, Li Y, Wang H, Yan X (2009) In situ hydrothermal growth of metal-organic framework 199 films on stainless steel fibers for solid-phase microextraction of gaseous benzene homologues. Anal Chem 81(23):9771–9777
Yusuf K, Agel A, AL Othman Z (2014) Metal-organic frameworks in chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1348:1–16
Gu Z, Yang C, Chang N, Yan X (2012) Metal-organic frameworks for analytical chemistry: from sample collection to chromatographic separation. Acc Chem Res 45(5):734–745
Pan C, Wang W, Zhang H, Xu L, Chen X (2015) In situ synthesis of homochiral metal-organic framework in capillary column for capillary electrochromatography enantioseparation. J Chromatogr A 1388:207–216
Ghorbani-Kalhor E (2016) A metal-organic framework nanocomposite made from functionalized magnetite nanoparticles and HKUST-1 (MOF-199) for preconcentration of Cd(II), Pb(II), and Ni(II). Microchim Acta 183(9):2639–2647
Wu Q, Cheng S, Wang C, Li X, Li Z, Hao C (2016) Magnetic porous carbon derived from a zinc-cobalt metal-organic framework: a adsorbent for magnetic solid phase extraction of flunitrazepam. Microchim Acta 183(11):3009–3017
Zhou Q, Zhu L, Xia X, Tang H (2016) The water – resistant zeolite imidazolate framework 67 is a viable solid phase sorbent for fluoroquinolones while efficiently excluding macromolecules. Microchim Acta 183(6):1839–1846
Rocío-Bautista P, Pino V, Ayala JH, Pasán J, Ruiz-Pérez C, Afonso AM (2016) A magnetic-based dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction method using the metal-organic framework HKUST-1 and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection for determining polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in waters and fruit tea infusions. J Chromatogr A 1436:42–50
Münch AS, Mertens FORL (2015) The Lewis acidic and basic character of the internal HKUST-1 surface determined by inverse gas chromatography. CrystEngComm 17(2):438–447
Bao T, Zhang J, Zhang W, Chen Z (2015) Growth of metal–organic framework HKUST-1 in capillary using liquid-phase epitaxy for open-tubular capillary electrochromatography and capillary liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1381:239–246
Wu Y, Sun H (2013) Effective separation and simultaneous determination of cefamandole and probenecid in body fluids by capillary zone electrophoresis with salicylic acid as an internal standard. Anal Methods 5(21):6017–6022
Tůma P, Jaček M, Fejfarová V, Polák J (2016) Electrophoretic stacking for sensitive determination of antibiotic ceftazidime in human blood and microdialysates from diabetic foot. Anal Chim Acta 942:139–145
Hancu G, Kelemen H, Rusu A, Gyéresi Á (2013) Development of a capillary electrophoresis method for the simultaneous determination of cephalosporins. J Serb Chem Soc 78(9):1413–1423
Siddiqui MR, Alothman ZA, Wabaidur SM, Khan MA, Alam MS, Ali MS (2015) High performance liquid chromatographic method for the quantitative analysis of cefuroxime in pharmaceutical preparations. J Chi Chem Soc 60(2):2869–2871
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (2162008), the Importation and Development of High-Caliber Talents Project of Beijing Municipal Institutions (CIT&TCD 201504083).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 124 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., An, J., Li, J. et al. A capillary coated with a metal-organic framework for the capillary electrochromatographic determination of cephalosporins. Microchim Acta 184, 1345–1351 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2131-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2131-5