Abstract
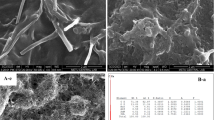
Glassy carbon electrodes were modified with silica materials such as silica nanoparticles, mesoporous silica nanoparticles and mesoporous silica thin films with the aim to introduce scaffolds suitable for the immobilization of enzymes. Xanthine oxidase was selected as a model enzyme, and xanthine as the target analyte. A comparison of the modified electrodes showed the biosensor prepared with mesoporous silica nanoparticles to perform best. By using the respective biosensor, xanthine can be amperometrically determined (via measurement of enzymatically formed hydrogen peroxide) at a working voltage of 0.7 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) with a 0.28 μM detection limit. The biosensor was evaluated in terms of potential interferences, reproducibility and stability, and applied to the determination of fish freshness via sensing of xanthine.

A sensitive xanthine biosensor was built by modifying glassy carbon electrodes with mesoporous silica nanoparticles and xanthine oxidase. The silica nanochannels improve the bioelectrode performances to selectively detect the analyte over a wide range of concentrations (0.28–212 μM).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma HF, Chen TT, Luo Y, Kong FY, Fan DH, Fang HL, Wang W (2015) Electrochemical determination of dopamine using octahedral SnO2 nanocrystals bound to reduced graphene oxide nanosheets. Microchim Acta 182:2001–2007
Wang Y, Wu T, Bi CY (2015) Simultaneous determination of acetaminophen, theophylline and caffeine using a glassy carbon disk electrode modified with a composite consisting of poly(Alizarin Violet 3B), multiwalled carbon nanotubes and graphene. Microchim Acta 183:731–739
Yu G, Zhao Q, Wu W, Wei X, Lu Q (2016) A facile and practical biosensor for choline based on manganese dioxide nanoparticles synthesized in–situ at the surface of electrode by one–step electrodeposition. Talanta 146:707–713
Coll C, Bernardos A, Martínez–Máñez R, Sancenón F (2013) Gated silica mesoporous supports for controlled release and signaling applications. Acc Chem Res 46:339–349
Tang L, Cheng J (2013) Nonporous silica nanoparticles for nanomedicine application. Nano Today 8:290–312
Walcarius A (2015) Mesoporous materials–based electrochemical sensors. Electroanalysis 27:1303–1340
Saadaoui M, Fernández I, Sánchez A, Díez P, Campuzano S, Raouafi N, Pingarrón JM, Villalonga R (2015) Mesoporous silica thin film mechanized with a DNAzyme–based molecular switch for electrochemical biosensing. Electrochem Commun 58:57–61
Balakrishnan V, Azwana H, Abdul Razak K, Shamsuddin S (2013) In vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity of colloidal amorphous silica nanoparticles designed for drug delivery on human cell lines. J Nanomater:729306. doi:10.1155/2013/729306
Pham H, Nguyen QP (2014) Effect of silica nanoparticles on clay swelling and aqueous stability of nanoparticle dispersions. J Nanoparticle Res 16:2137–2142
Bottini M, Annibale FD, Magrini A, Cerignoli F, Arimura Y, Dawson MI, Bergamaschi E, Rosato N, Bergamaschi A, Mustelin T (2007) Quantum dot–doped silica nanoparticles as probes for targeting of T–lymphocytes. Int J Nanomedicine 2:227–233
Mao L, Yamamoto K (2000) Amperometric on–line sensor for continuous measurement of hypoxanthine based on osmium–polyvinylpyridine gel polymer and xanthine oxidase bienzyme modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal Chim Acta 415:143–150
Boulieu R, Bory C, Baltassat P, Gonnet C (1983) Hypoxanthine and xanthine levels determined by high–performance liquid chromatography in plasma, erythrocyte, and urine samples from healthy subjects: the problem of hypoxanthine level evolution as a function of time. Anal Biochem 129:398–404
Shihabi ZK, Hinsdale ME, Bleyer AJ (1995) Xanthine analysis in biological fluids by capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr B 669:163–169
Suzuki T, Takahashi E (1975) Metabolism of xanthine and hypoxanthine in tea plants (Theasinensis L.). Biochem J 146:79–85
Zhang J, Lei JP, Pan R, Xue YD, Ju HX (2010) Highly sensitive electrocatalytic biosensing of hypoxanthine based on functionalization of graphene sheets with water–soluble conducting graft copolymer. Biosens Bioelectron 26:371–376
Zhang YY, Deng SY, Lei JP, QN X, HX J (2011) Carbon nanospheres enhanced electrochemiluminescence of CdS quantum dots for biosensing of hypoxanthine. Talanta 85:2154–2158
Devi R, Yadav S, Pundir CS (2012) Au–colloids–polypyrrole nanocomposite film based xanthine biosensor. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 394:38–45
Nakatani HS, Santos LV, Pelegrine CP, Gomes M, Matsushita M, Souza NE (2005) Biosensor based on xanthine oxidase for monitoring hypoxanthine in fish meat. Am J Biochem Biotechnol 1:85–89
Devi R, Narang J, Yadav S, Pundir CS (2012) Amperometric determination of xanthine in tea, coffee, and fish meat with graphite rod bound xanthine oxidase. J Anal Chem 67:273–277
Xue H, Mu S (1995) Bioelectrochemical response of the polypyrrole xanthine oxidase electrode. J Electroanal Chem 39:241–247
Liu Y, Lo N, Tao W, Yao S (2004) Amperometric study of au–colloid function on xanthine biosensor based on xanthine oxidase immobilized in polypyrrole layer. Electroanalysis 16:1271–1278
Shi X, Gu W, Li B, Chen N, Zhao K, Xian Y (2014) Enzymatic biosensors based on the use of metal oxide nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 181:1–22
Gao Y, Shen C, Di J, Tu Y (2009) Fabrication of amperometric xanthine biosensors based on direct chemistry of xanthine oxidase. Mater Sci Eng C 29:2213–2216
Dan S, Yan–Na W, Huai–Guo X, Serge C, Shou–Nian D (2009) Xanthine oxidase/laponite nanoparticles immobilized on glassy carbon electrode: direct electron transfer and multielectrocatalysis. Biosens Bioelectron 24:3556–3561
Stöber W, Fink A (1968) Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 26:62–69
Zhao Y, Trewyn BG, Slowing II, VS–Y L (2009) Mesoporous silica nanoparticle–based double drug delivery system for glucose–responsive controlled release of insulin and cyclic AMP. J Am Chem Soc 131:8398–8400
Walcarius A, Sibottier E, Etienne M, Ghanbaja J (2007) Electrochemically assisted self–assembly of mesoporous silica thin films. Nat Mater 6:602–608
Devi R, Yadav S, Nehra R, Yadav S, Pundir CS (2013) Electrochemical biosensor based on gold coated iron nanoparticles/chitosan composite bound xanthine oxidase for detection of xanthine in fish meat. J Food Eng 115:207–214
Muamer D, Esma C, Emre C, Mehmet S (2015) Construction of novel xanthine biosensor by using polymeric mediator/MWCNT nanocomposite layer for fish freshness detection. Food Chem 181:277–283
Villalonga R, Matos M, Cao R (2007) Construction of an amperometric biosensor for xanthine via supramolecular associations. Electrochem Commun 9:454–458
Coughlan MP, Rajagopalan KV, Handler P (1969) The role of molybdenum in xanthine oxidase and related enzymes. Reactivity with cyanide, arsenite, and methanol. J Biol Chem 244:2658–2663
Edmondson D, Massey V, Palmer G, Beacham LM (1972) The resolution of active and inactive xanthine oxidase by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem 247:1597–1604
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to acknowledge the financial support to this work from the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research (MHESR) and the University of Tunis El–Manar for the mobility grant (Bourse d’Alternance) awarded to MS. RV acknowledge to Ramón & Cajal contract from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation. Financial support from the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación CTQ2011–24355, CTQ2012–34238 and Comunidad de Madrid S2013/MIT–3029, Program NANOAVANSENS are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 443 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saadaoui, M., Sánchez, A., Díez, P. et al. Amperometric xanthine biosensors using glassy carbon electrodes modified with electrografted porous silica nanomaterials loaded with xanthine oxidase. Microchim Acta 183, 2023–2030 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1840-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1840-5