Abstract
The authors describe a multiphase density gradient centrifugation method for the separation and purification of hybrid nanoparticles (NPs). The method was applied to the purification of NPs consisting of magnetite gold NPs of type Fe3O4@Au and coated with 1-dodecylthiol. A density gradient has been established by forming cushions of a multicomponent solution composed of (a) a nonlinear gradient of sucrose in the of 5–50 % concentration range, (b) a constant concentration of ficoll (a neutral, highly branched, high-mass, hydrophilic polysaccharide; 30 % w/w), and (c) a constant concentration of percoll (colloidal silica particles coated with polyvinylpyrrolidone; 15 % w/w). The final separation profiles are adjusted via dynamic differential centrifugation at 4480×g for 30 min. The mixture of NPs to be separated is added and centrifuged at 2520×g for 40 min. This will separate the NPs into five fractions together with other secondary components. The fractions were characterized by FTIR, XPS, and SEM-EDX techniques. Finally, a continuous flow system with resonance light scattering detection was established and coupled to the separation system in order to monitor the separated fractions.

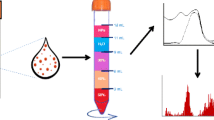
Multilayer density gradient centrifugation (MDGC) system coupled to a continuous flow system (CFS) equipped with a resonance light scattering detector (RSLD). AuNPs (gold nanoparticles); AuNPs-C12SH (1-dodecylthiol AuNPs); Fe3O4NPs (magnetic nanoparticles) and Fe3O4@AuNPs (magnetic-gold nanoparticles).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei GT, Liu FK, Wang CR (1999) Shape separation of nanometer gold particles by size-exclusion chromatography. Anal Chem 71:2085–2091. doi:10.1021/ac990044u
Hanauer M, Pierrat S, Zins I, Lotz A, Sönnichsen C (2007) Separation of nanoparticles by gel electrophoresis according to size and shape. Nano Lett 7:2881–2885. doi:10.1021/nl071615y
Sweeney SF, Woehrle GH, Hutchisom JE (2006) Rapid purification and size separation of gold nanoparticles via diafiltration. J Am Chem Soc 128:3190–3197. doi:10.1021/ja0558241
Palencia M, Rivas BL, Valle H (2014) Size separation of silver nanoparticles by dead-end ultrafiltration: description of fouling mechanism by pore blocking model. J Membr Sci 455:7–14. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2013.12.051
Shiundu PM, Munguti SM, Stephen M, Ratanathanawongs W, Kim S (2003) Retention behavior of metal particle dispersions in aqueous and nonaqueous carriers in thermal field-flow fractionation. J Chromatogr A 983:163–176. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(02)01694-1
Kim ST, Kang DY, Lee S, Kim WS, Lee JT, Cho HS, Kim SH (2007) Separation and quantitation of silver nanoparticles using sedimentation field-flow fractionation. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 30:2533–2544. doi:10.1080/10826070701540092
Steinigeweg D, Schütz M, Salehi M, Schlücker S (2011) Fast and cost-effective purification of gold nanoparticles in the 20–250 nm size range by continuous density gradient centrifugation. Small 17:2443–2448. doi:10.1002/smll.201100663
Xiong B, Cheng J, Qiao Y, Zhou R, He Y, Yeung ES (2011) Separation of nanorods by density gradient centrifugation. J Chromatogr A 1218:3823–3829. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2011.04.038
Dong S, Wang Y, Liang A, Li X, Zhang Q. Separation of gold nanorods by viscosity gradient centrifugation. Microchim Acta. doi: 10.1007/s00604-015-1709-z
Sánchez-López V, Fernández-Romero JM, Gómez-Hens A (2009) Evaluation of liposome populations using a sucrose density gradient centrifugation approach coupled to a continuous flow system. Anal Chim Acta 645:79–85. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2009.04.045
Román-Pizarro V, Fernández-Romero JM, Gómez-Hens A (2014) Fluorometric determination of alkaline phosphatase activity in food using magnetoliposomes as on-flow micro-container devices. J Agric Food Chem 62:1819–1825. doi:10.1021/jf5004804
Chang Y, Hsieh PH, Chao CCK (2009) The efficiency of percoll and ficoll density gradient media in the isolation of marrow derived human mesenchymal stem cells with osteogenic potential. Chang Gung Med J 32:264–275
Akbulut O, Mace CR, Martinez RV, Kumar AA, Nie Z, Patton MR, Whitesides GM (2012) Separation of nanoparticles in aqueous multiphase systems through centrifugation. Nano Lett 12:4060–4064. doi:10.1021/nl301452x
Cui YR, Hong C, Zhou YL, Li Y, Gao XM, Zhang XX (2011) Synthesis of orientedly bioconjugated core/shell Fe3O4@Au magnetic nanoparticles for cell separation. Talanta 85:1246–1252. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2011.05.010
Turkevich J, Stevenson PC, Hillier J (1951) A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss Faraday Soc 55:55–75. doi:10.1039/df9511100055
Román-Pizarro V, Fernández-Romero JM, Gómez-Hens A (2012) Gold nanoparticle-biotinilated liposome hybrids as analytical reagents for biotin determination using a competitive assay and resonance light scattering detection. Talanta 99:538–543. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2012.06.029
Rudakovskaya PG, Beloglazkina EK, Majouga AG, Zyk NV (2010) Synthesis and characterization of terpyridine-type ligand-protected gold-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Mendeleev Commun 20:158–160. doi:10.1016/j.mencom.2010.05.012
Acknowledgments
Authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Spanish MICINN (Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación) (Grant No. CTQ-2012-32941/BQU) and the FEDER program. Authors also wish to acknowledge to the UCO Research Support Central Service (UCO/SCAI) for the availability of the supporting techniques for NPs characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Écija-Arenas, Á., Román-Pizarro, V., Fernández-Romero, J.M. et al. Separation and purification of hydrophobic magnetite-gold hybrid nanoparticles by multiphase density gradient centrifugation. Microchim Acta 183, 2005–2012 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1838-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1838-z