Abstract
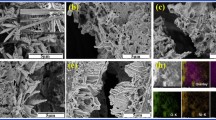
The authors describe vertically aligned gold nanotube arrays (Au-NTAs) and gold nanowire arrays (Au-NWAs) that were directly grown in alumina oxide templates by galvanostatic deposition. The morphology of the gold arrays can be controlled by adjusting the pH value of the plating bath. Scanning electron microscopy shows the nanoarrays to be highly ordered (with an average length of around 2 μm), and the opening width of the gold nanotube arrays to be uniform (with diameters of around 50 nm). The electrocatalytic activities of the Au-NTAs and Au-NWAs deposited on a glassy carbon electrode toward glucose oxidation were compared by cyclic voltammetry and amperometry at pH 7.2. The Au-NTAs yield higher amperometric currents. The respective glucose sensor, when operated at a working potential of 0.25 V (vs. SCE), exhibits a linear range that extends from 5 μM to 16.4 mM concentrations of glucose, a sensitivity of 44.2 μA mM−1 cm−2, and a detection limit of 2.1 μM (at an S/N ratio of 3). The excellent sensing performance is attributed to the large surface area and the fast electron transfer rate for the one-dimensional gold nanoarrays.

Arrays of gold nanotubes and of gold nanowires were deposited on a glassy carbon electrode and applied to the determination of glucose at pH 7.2 with a detection limit as low as 2.1 µM.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuchibhatla SVNT, Karakoti AS, Bera D, Seal S (2007) One dimensional nanostructured materials. Prog Mater Sci 52:699–913
Barth S, Hernandez-Ramirez F, Holmes JD, Romano-Rodriguez A (2010) Synthesis and applications of one-dimensional semiconductors. Prog Mater Sci 55:563–627
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Su L, Zhang Z, Huo D, Hou C, Lei Y (2014) CuO nanowires based sensitive and selective non-enzymatic glucose detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 191:86–93
Wen Z, Zhu L, Zhang Z, Ye Z (2015) Fabrication of gas sensor based on mesoporous rhombus-shaped ZnO rod arrays. Sensors Actuators B Chem 208:112–121
Wang XH, Yang Z, Sun XL, Li XW, Wang DS, Wang P, He D (2011) NiO nanocone array electrode with high capacity and rate capability for Li-ion batteries. J Mater Chem 21:9988–9990
Cao G, Liu D (2008) Template-based synthesis of nanorod, nanowire, and nanotube arrays. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 136:45–64
Li Y, Niu X, Tang J, Lan M, Zhao H (2014) A comparative study of nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors based on Pt-Pd nanotube and nanowire arrays. Electrochim Acta 130:1–8
Yang G, Yang X, Yang C, Yang Y (2011) A reagentless amperometric immunosensor for human chorionic gonadotrophin based on a gold nanotube arrays electrode. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 389:195–200
Piao Y, Lim H, Chang JY, Lee W-Y, Kim H (2005) Nanostructured materials prepared by use of ordered porous alumina membranes. Electrochim Acta 50:2997–3013
Zhang X, Dong D, Li D, Williams T, Wang H, Webley PA (2009) Direct electrodeposition of Pt nanotube arrays and their enhanced electrocatalytic activities. Electrochem Commun 11:190–193
Jamal M, Xu J, Razeeb KM (2010) Disposable biosensor based on immobilisation of glutamate oxidase on Pt nanoparticles modified Au nanowire array electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 26:1420–1424
Dong J, Ren L, Zhang Y, Cui X, Hu P, Xu J (2015) Direct electrodeposition of cable-like CuO@Cu nanowires array for non-enzymatic sensing. Talanta 132:719–726
Jamal M, Hasan M, Mathewson A, Razeeb KM (2013) Disposable sensor based on enzyme-free Ni nanowire array electrode to detect glutamate. Biosens Bioelectron 40:213–218
Wang G, He X, Wang L, Gu A, Huang Y, Fang B, Geng B, Zhang X (2012) Non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing of glucose. Microchim Acta 180:161–186
Cherevko S, Chung CH (2009) Gold nanowire array electrode for non-enzymatic voltammetric and amperometric glucose detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 142:216–223
Martín A, Pescaglini A, Schopf C, Scardaci V, Coull R, Byrne L, Iacopino D (2014) Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering of 4-Aminobenzenethiol on Au Nanorod Ordered Arrays. J Phys Chem C 118:13260–13267
Galbiati S, Morin A, Pauc N (2014) Supportless Platinum nanotubes Array by atomic layer deposition as PEM Fuel cell electrode. Electrochim Acta 125:107–116
Mei H, Wu W, Yu B, Li Y, Wu H, Wang S, Xia Q (2015) Non-enzymatic sensing of glucose at neutral pH values using a glassy carbon electrode modified with carbon supported Co@Pt core-shell nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:1869–1875
Zhao L, Wu G, Cai Z, Zhao T, Yao Q, Chen X (2015) Ultrasensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensing at near-neutral pH values via anodic stripping voltammetry using a glassy carbon electrode modified with Pt3Pd nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 182:2055–2060
Chen X, Tian X, Zhao L, Huang Z, Oyama M (2013) Nonenzymatic sensing of glucose at neutral pH values using a glassy carbon electrode modified with graphene nanosheets and Pt-Pd bimetallic nanocubes. Microchim Acta 181:783–789
Bridges CR, DiCarmine PM, Fokina A, Huesmann D, Seferos DS (2013) Synthesis of gold nanotubes with variable wall thicknesses. J Mater Chem A 1:1127–1133
Zhang X, Li D, Bourgeois L, Wang H, Webley PA (2009) Direct electrodeposition of porous gold nanowire arrays for biosensing applications. ChemPhysChem 10:436–441
Sun W, Ivey DG (1999) Development of an electroplating solution for codepositing Au–Sn alloys. Mater Sci Eng B 65:111–122
Green TA (2007) Gold electrodeposition for microelectronic, optoelectronic and microsystem applications. Gold Bull 40:105–114
Wang YZ, Zhong H, Li XM, Jia FF, Shi YX, Zhang WG, Cheng ZP, Zhang LL, Wang JK (2013) Perovskite LaTiO(3)-Ag0.2 nanomaterials for nonenzymatic glucose sensor with high performance. Biosens Bioelectron 48:56–60
Cheng TM, Huang TK, Lin HK, Tung SP, Chen YL, Lee CY, Chiu HT (2010) (110)-exposed gold nanocoral electrode as low onset potential selective glucose sensor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:2773–2780
Shi Q, Diao G, Mu S (2014) The electrocatalytic oxidation of glucose on the bimetallic Au-Ag particles-modified reduced graphene oxide electrodes in alkaline solutions. Electrochim Acta 133:335–346
Zhou Y-G, Yang S, Qian Q-Y, Xia X-H (2009) Gold nanoparticles integrated in a nanotube array for electrochemical detection of glucose. Electrochem Commun 11:216–219
Xia Y, Huang W, Zheng J, Niu Z, Li Z (2011) Nonenzymatic amperometric response of glucose on a nanoporous gold film electrode fabricated by a rapid and simple electrochemical method. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3555–3561
Prehn R, Cortina-Puig M, Muñoz FX (2012) A non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on the use of gold micropillar Array electrodes. J Electrochem Soc 159:F134
Yang L, Zhang Y, Chu M, Deng W, Tan Y, Ma M, Su X, Xie Q, Yao S (2014) Facile fabrication of network film electrodes with ultrathin Au nanowires for nonenzymatic glucose sensing and glucose/O2 fuel cell. Biosens Bioelectron 52:105–110
Shu H, Cao L, Chang G, He H, Zhang Y, He Y (2014) Direct electrodeposition of gold nanostructures onto glassy carbon electrodes for non-enzymatic detection of glucose. Electrochim Acta 132:524–532
Wang J, Cao X, Wang X, Yang S, Wang R (2014) Electrochemical oxidation and determination of glucose in Alkaline Media based on Au (111)-like nanoparticle Array on indium tin oxide electrode. Electrochim Acta 138:174–186
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the supports of National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 61371021 and 61527818). The authors also acknowledge the support of the Shanghai Education Commission (Peak Discipline Construction).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 305 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, T., Dong, J. & Xu, J. Direct electrodeposition of highly ordered gold nanotube arrays for use in non-enzymatic amperometric sensing of glucose. Microchim Acta 183, 1925–1932 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1835-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1835-2