Abstract
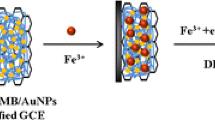
The article describes the synthesis of bismuth nanosheets (BiNSs) in the presence of a small quantity of graphene oxide (GO) which is helpful for the formation of two-dimensional BiNSs and improves dispersity. The material, when placed on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE), is shown to enable catalytic stripping voltammetric determination of total dissolved iron without the need for adding a complexing agent. The average thickness and length of the BiNSs are 3 to 4 nm and 100 to 200 nm, respectively. The unique nanostructure of the BiNSs, the ability of Bi to form alloys with metal, and the current amplification of the catalytic system make the modified GCE an excellent choice for electrochemical determination of Fe(III). Under the optimal conditions, the electrode has a linear response to Fe(III) in the 0.01 to 20 μM concentrations range, with a lower detection limit of 2.3 nM. The electrode was successfully applied to the sensitive determination of Fe(III) in coastal waters.

Bismuth nanosheets were prepared by graphene oxide-assisted synthesis and utilized for catalytic stripping voltammetric determination of trace Fe(III) in coastal waters.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
D’Autréaux B, Tucker NP, Dixon R, Spiro S (2005) A non-haem iron centre in the transcription factor N or R senses nitric oxide. Nature 437:769–7725
Liu X, Theil EC (2005) Ferritins: dynamic management of biological iron and oxygen chemistry. Acc Chem Res 38:167–175
Sean R, Lynch MD (2005) The impact of iron fortification on nutritional anaemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 18:333–346
Sunda GW, Huntsman SA (1995) Iron uptake and growth limitation in oceanic and coastal phytoplankton. Mar Chem 50:189–206
Coale KH, Johnson KS, Fitzwater SE, Gordon RM, Kudela R (1996) A massive phytoplankton bloom induced by an ecosystem-scale iron fertilization experiment in the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Nature 383:495–501
Wells ML, Trick CG (2004) Controlling iron availability to phytoplankton in iron-replete coastal waters. Mar Chem 86:1–13
Freschi GP, Freschi CD, Neto JG (2008) Evaluation of different rhodium modifiers and coatings on the simultaneous determination of As, Bi, Pb, Sb, Se and of Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn in milk by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchim Acta 161:129–135
Jong J, Schoemann V, Lannuzel D, Tison JL, Mattielli N (2008) High-accuracy determination of iron in seawater by isotope dilution multiple collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ID-MC-ICP-MS) using nitrilotriacetic acid chelating resin for pre-concentration and matrix separation. Anal Chim Acta 623:126–139
Yang C, Hu Z, Yang J, Gao H (2012) Novel phenyl-iminodiacetic acid grafted multiwalled carbon nanotubes for solid phase extraction of iron, copper and lead ions from aqueous medium. Microchim Acta 176:359–366
Asan A, Andac M, Isildak I, Tinkilic N (2008) Flow injection spectrophotometric determination of iron(III) using diphenylamine-4-sulfonic acid sodium salt. Chem Pap 62:345–349
Cha KW, Park KW (1998) Determination of iron(III) with salicylic acid by the fluorescence quenching method. Talanta 46:1567–1571
Lu G, Yao X, Wu X, Zhang T (2001) Determination of the total iron by chitosan-modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchim J 69:81–87
Lu M, Compton RG (2013) Voltammetric determination of iron(III) in water. Electroanalysis 25:1123–1129
Mashhadizadeh MH, Shosei IS, Monadi N (2004) A novel ion selective membrane potentiometric sensor for direct determination of Fe(III) in the presence of Fe(II). Talanta 64:1048–1052
Van den Berg CMG (2006) Chemical speciation of iron in seawater by cathodic stripping voltammetry with dihydroxynaphthalene. Anal Chem 78:156–163
Croot PL, Johansson M (2000) Determination of iron speciation by cathodic stripping voltammetry in seawater using the competing ligand 2-(2-Thiazolylazo)-p-cresol (TAC). Electroanalysis 12:565–576
Obata H, Van den Berg CMG (2001) Determination of picomolar levels of iron in seawater using catalytic cathodic stripping voltammetry. Anal Chem 73:2522–2528
Gledhill M, Van den Berg CMG (1994) Determination of complexation of iron(III) with natural organic complexing ligands in seawater using cathodic stripping voltammetry. Mar Chem 47:41–54
Wang J (2005) Stripping analysis at bismuth electrodes: a review. Electroanalysis 17:1341–1346
Wang ZQ, Liu G, Zhang LN, Wang H (2012) A bismuth modified hybrid binder carbon paste electrode for electrochemical stripping detection of trace heavy metals in soil. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:12326–12339
Pauliukaite R, Hočevar SB, Ogorevc B, Wang J (2004) Characterization and applications of a bismuth bulk electrode. Electroanalysis 16:719–723
Torma F, Kádár M, Tóth K, Tatár E (2008) Nafion/2,2-bipyridyl-modified bismuth film electrode for anodic stripping voltammetry. Anal Chim Acta 619:173–182
Li Y, Sun G, Zhang Y, Ge C, Bao N, Wang Y (2014) A glassy carbon electrode modified with bismuth nanotubes in a silsesquioxane framework for sensing of trace lead and cadmium by stripping voltammetry. Microchim Acta 181:751–757
Lee GJ, Lee HM, Rhee CK (2007) Bismuth nano-powder electrode for trace analysis of heavy metals using anodic stripping voltammetry. Electrochem Commun 9:2514–2518
Bobrowski A, Nowak K, Zarebski J (2005) Application of a bismuth film electrode to the voltammetric determination of trace iron using a Fe(III)–TEA–BrO3 − catalytic system. Anal Bioanal Chem 382:1691–1697
Segura R, Toral M, Arancibia V (2008) Determination of iron in water samples by adsorptive stripping voltammetry with a bismuth film electrode in the presence of 1-(2-piridylazo)-2-naphthol. Talanta 75:973–977
Lin M, Pan D, Hu X, Li F, Han H (2015) A tin-bismuth alloy electrode for the cathodic stripping voltammetric determination of iron in coastal waters. Anal Methods 7:5169–5174
Ugo P, Moretto LM, De Boni A, Scopece P, Mazzocchin GA (2002) Iron (II) andiron (III) determination by potentiometry and ion-exchange voltammetry ationomer-coated electrodes. Anal Chim Acta 474:147–160
Gholivand MB, Geravandi B, Parvin MH (2011) Anodic stripping voltammetric determination of iron(II) at a carbon paste electrode modified with dithiodianiline (DTDA) and gold nanoparticles (GNP). Electroanalysis 23:1345–1351
Anguiano DI, Garcia MG, Ruiz C, Torres J, Alonso-Lemus I, Alvarez-Contreras L, Verde-Gomez Y, Bustos E (2012) Electrochemical detection of iron in a lixiviant solution of polluted soil using a modified glassy carbon electrode. Int J Electrochem 739408:6
Lin M, Han H, Pan D, Zhang H, Su Z (2015) Voltammetric determination of total dissolved iron in coastal waters using a glassy carbon electrode modified with reduced graphene oxide, Methylene Blue and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:805–813
Lin M, Pan D, Hu X, Han H, Li F (2015) Titanium carbide nanoparticles/ion-exchange polymer-based sensor for catalytic stripping determination of trace iron in coastal waters. Sensors Actuators B 219:164–170
Zarebski J (1977) Alkaline triethanoloamine-bromate solutions as supporting electrolytes for the determination of iron in trace amounts by differential pulse polarography. Chem Anal 22:1049–1051
Peng B, Shen YP, Gao ZT, Zhou M, Ma YJ, Zhao SG (2015) Determination of total iron in water and food by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with microvolume UV-vis spectrophotometry. Food Chem 176:188–293
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41276093), the Youth Innovation Promotion Association (2011170) and Outstanding Young Scientists of CAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 213 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Pan, D., Lin, M. et al. Graphene oxide-assisted synthesis of bismuth nanosheets for catalytic stripping voltammetric determination of iron in coastal waters. Microchim Acta 183, 855–861 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1733-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1733-z