Abstract
The article describes the use of a designed histidine (His)-tagged arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) peptide as a linker to bind integrin to captured cancer cells, and how to amplify the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) signal after binding of NiO nanoparticles (NiO-NPs) via the His-tag on the peptide. Specifically, breast cancer cells were captured via the interaction between human mucin (MUC-1) and a gold surface modified with a MUC-selective aptamer. The resulting cytosensor exhibits specificity and high sensitivity which is due to the enhancement of the SPR signal by NiO-NPs. The breast cancer cell line MCF-7 can be easily distinguished from normal islet beta cells by using this biosensor. Implementation of the His-tagged RGD peptide modified with NiO-NPs resulted in 20-fold enhancement of the SPR signal at the limit of detection. Hence, the actual limit of detection is lowered to 136 cells per mL. In our perception, this cytosensor has a large clinical potential in that it may also be used to detect various other kinds of tumor cells.

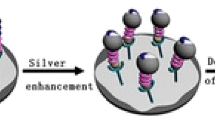
Histidine-tagged arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptide carried by NiO interacts with the integrin of cancer cells and amplifies the SPR signal resulting from interaction between human mucin (MUC-1) and a gold surface modified with a MUC-selective aptamer. As little as 136 cells·mL−1 are detectable.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lacroix M (2006) Significance, detection and markers of disseminated breast cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer 13:1033–1067
Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van’t Veer LJ (2005) Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer 5:591–602
Koepke JA (2006) Molecular marker test standardization. Cancer 69:1578–1581
Molina R, Gion M (1998) Use of blood tumor markers in the detection of recurrent breast cancer. Breast 7:187–189
BrooksPC CRA, Cheresh DA (1994) Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science 264:569–571
Hood J, Cheresh D (2002) Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration. Nat Rev Cancer 2:91–100
Pierschbacher MD, Ruoslahti E (1984) The cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature 309:30–33
Baron R, Zayats M, Willner I (2005) Dopamine-, l-DOPA-, adrenaline-, and noradrenaline-induced growth of Au nanoparticles: assays for the detection of neurotransmitters and of tyrosinase activity. Anal Chem 77:1566–1571
Sha MY, Xu HX, Natan MJ, Cromer R (2008) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering tags for rapid and homogeneous detection of circulating tumor cells in the presence of human whole blood. J Am Chem Soc 130:17214–17215
Acharya G, Chang CL, Doorneweerd DD, Vlashi E, Henne WA, Hartmann LC, Low PS, Savran CA (2007) Immunomagnetic diffractometry for detection of diagnostic serum markers. J Am Chem Soc 129:15824–15829
Bailey RC, Kwong GA, Radu CG, Witte ON, Heath JR (2007) DNA-encoded antibody libraries: a unified platform for multiplexed cell sorting and detection of genes and proteins. J Am Chem Soc 129:1959–1967
Zhou M, Shah R, Shen RL, Rubin MA (2003) Basal cell cocktail (34[beta] E12 + p63) improves the detection of prostate basal cells. Am J Surg Pathol 27:365–371
Liu L, Zhu X, Zhang D, Huang J, Li G (2007) An electrochemical method to detect folate receptor positive tumor cells. Electrochem Commun 9:2547–2550
Hayden O, Bindeus R, Dickert FL (2003) Mass-sensitive detection of cells, viruses and enzymes with artificial receptors. Sens. Actuators B 93:316–319
He F, Shen Q, Jiang H, Zhou J, Cheng J, Guo D, Li Q, Wang X, Fu D, Chen B (2009) Rapid identification and high sensitive detection of cancer cells on the gold nanoparticle interface by combined contact angle and electrochemical measurements. Talanta 77:1009–1014
Liu Q, Yu J, Xiao L, Tang JCO, Zhang Y, Wang P, Yang M (2009) Impedance studies of bio-behavior and chemosensitivity of cancer cells by micro-electrode arrays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 24:1305–1310
Andreescu S, Sakik OA (2005) Advanced electrochemical sensors for cell cancer monitoring. Methods 37:84–93
Li T, Fan Q, Liu T, Zhu XL, Zhao J, Li G (2010) Detection of breast cancer cells specially and accurately by an electrochemical method. Biosens. Bioelectron. 25:2686–2689
Chen H, Gal YS, Kim SH, Choi HJ, Oh MC, Lee J, Koh K (2008) Potassium ion sensing using a self-assembled calix[4]crown monolayer by surface Plasmon resonance. Sens. Actuators, B 133:577–581
Rich RL, Myszka DG (2005) Survey of the year 2004 commercial optical biosensor literature. J Mol Recognit 18:431–478
Shankaran DR, Gobi KV, Miura N (2007) Recent advancements in surface Plasmon resonance immunosensors for detection of small molecules of biomedical, food and environmental interest. Sens. Actuators, B 121:158–177
Whelan RJ, Wohland T, Neumann L, Huang B, Kobilka BK, Zare RN (2002) Analysis of biomolecular interactions using a miniaturized surface Plasmon resonance sensor. Anal Chem 74:4570–4579
Robelek R, Wegener J (2010) Label-free and time-resolved measurements of cell volume changes by surface Plasmon resonance (SPR) spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 25:1221–1224
Chen H, Hou Y, Ye Z, Wang H, Koh K, Shen Z, Shu Y (2007) Label-free surface Plasmon resonance cytosensor for breast cancercell detection based on Nano-conjugation of monodisperse magnetic nanoparticle and folic acid. Sens. Actuators, B 201:433–438
Lei P, Tang H, Ding S, Ding X, Zhu D, Shen B, Cheng Q, Yan Y (2015) Determination of the inva gene of salmonella using surface Plasmon resonance along with streptavidin aptamer amplification. Microchim Acta 182:289–296
Chen H, Mei Q, Hou Y, Koh K, Lee J, Chen B, Fang L, Zhao X (2013) Building a sensitive immunosensing platform based on oriented immobilization of histidine-tagged antibody on NiO-decorated SWNTs. Sens. Actuators, B 181:38–43
Ganesana M, Istarnboulie G, Marty JL, Noguer T, Andreescu S (2011) Site-specific immobilization of a (his)6-tagged acetylcholinesterase on nickel nanoparticles for highly sensitive toxicity biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 30:43–48
Lo Y-S, Nam DH, So H-M, Chang H, Kim J, Kim Y, Lee J-O (2009) Oriented immobilization of antibody fragmentson Ni-decorated single-walled carbon nanotube devices. AcsNano 3:3649–3655
Shi X, Gu W, Li B, Chen N, Zhao K, Xian Y (2014) Enzymatic biosensors based on the use of metal oxide nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 181:1–22
Uchida M, Flenniken ML, Allen M, Willits DA, Crowley BE, Brumfield S, Willis AF, Jackiw L, Jutila M, Young MJ, Douglas T (2006) Targeting of cancer cells with ferrimagnetic ferritin cage nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 128:16626–16633
Toriello N. M, Douglas E. S, Mathies R. A (2005) Microfluidic device for electric field-driven single-cell capture and activation. Anal Chem 77: 6935–6941.
Chen H, Qi F, Zhou H, Jia S, Gao Y, Koh K, Yin Y (2015) Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles as a means of signal enhancement in surface Plasmon resonance spectroscopy for thrombin detection,. Sen Actuators, B 212:505–511
Zhu X, Yang J, Liu M, Wu Y, Shen Z, Li G (2013) Sensitive detection of human breast cancer cells based on aptamer–cell–aptamer sandwich architecture. Anal Chim Acta 764:59–63
Yan M, Sun G, Liu F, Lu J, Yu J, Song X (2013) An aptasensor for sensitive detection of human breast cancer cells by using porous GO/Au composites and porous PtFe alloy as effective sensing platform and signal amplification labels. Anal Chim Acta 798:33–39
Wei W, Li D, Pan X, Liu S (2012) Electrochemiluminescent detection of mucin 1 protein and MCF-7 cancer cells based on the resonance energy transfer. Analyst 137:2101–2106
Hua X, Zhou Z, Yuan L, Liu S (2013) Selective collection and detection of MCF-7 breast cancer cells using aptamer-functionalized magnetic beads and quantum dots based Nano-bio-probes. Anal Chim Acta 788:135–140
Zhao J, Zhang L, Chen C, Jiang J, Yu R (2012) A novel sensing platform using aptamer and RNA polymerase-based amplification for detection of cancer cells. Anal Chim Acta 745:106–111
Song Y, Chen Y, Feng L, Ren J, Qu X (2011) Selective and quantitative cancer cell detection using target-directed functionalized graphene and its synergetic peroxidase-like activity. Chem Commun 47:4436–4438
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61275085, 31100560).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, S., Li, P., Koh, K. et al. A cytosensor based on NiO nanoparticle-enhanced surface plasmon resonance for detection of the breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Microchim Acta 183, 683–688 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1700-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1700-8