Abstract
We report on a giant magnetoresistance (GMR) based immunosensor for the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) labeled with superparamagnetic microparticles (Dynabeads). The GMR sensor contains 200 GMR strips and was fabricated by micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) technology. This system can detect Dynabeads in concentrations down to 10 ng⋅mL−1. Sandwich immunoassays were employed on the surface of a gold film modified with a self-assembled monolayer and using biotinylated secondary antibody against CEA and streptavidinylated Dynabeads. With DC magnetic fields in the range of 40 to 90 Oe, CEA can be detected with a detection limit as low as 10 pg⋅mL−1. Samples spiked with different concentrations of CEA can be distinguished clearly, and the method is deemed to be well suited for clinical use.

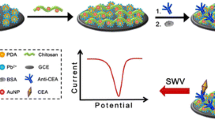
Make use of antigen-antibody immune reaction, Dynabeads that conjugated with polyclonal CEA antibodies were captured onto the surface of Au film which immobilize of monoclonal CEA antibodies. Under the dc magnetic field magnetizing, the superparamagnetism Dynabeads induced a weak magnetic field that can be detected by the nearby GMR sensor, which reveals the presence of CEA. GMR: giant magneto-resistance CEA: carcinoembryonic antigens.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aytur T, Foley J, Anwar M, Boser B, Harris E, Beatty PR (2006) A novel magnetic bead bioassay platform using a microchip-based sensor for infectious disease diagnosis. J Immunol Methods 314:21–29
Oster J, Parker J, Brassard L à (2001) Polyvinyl-alcohol-based magnetic beads for rapid and efficient separation of specific or unspecific nucleic acid sequences. J Magn Magn Mater 225:145–150
Krogh TN, Berg T, Højrup P (1999) Protein analysis using enzymes immobilized to paramagnetic beads. Anal Biochem 274:153–162
Janssen XJ, Schellekens AJ, van Ommering K, van Ijzendoorn LJ, Prins MW (2009) Controlled torque on superparamagnetic beads for functional biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 24:1937–1941
Porter J, Robinson J, Pickup R, Edwards C (1998) An evaluation of lectin-mediated magnetic bead cell sorting for the targeted separation of enteric bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 84:722–732
Neurauter AA, Bonyhadi M, Lien E, Nokleby L, Ruud E, Camacho S, Aarvak T (2007) Cell isolation and expansion using dynabeads ((R)). Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 106:41–73
Pividor MI, Alegret S (2010) Micro and nanoparticles in biosensing systems for food safety and environmental monitoring. An example of converging technologies. Microchim Acta 170:227–242
Duffy MJ, van Dalen A, Haglund C, Hansson L, Klapdor R, Lamerz R, Nilsson O, Sturgeon C, Topolcan O (2003) Clinical utility of biochemical markers in colorectal cancer: European group on tumour markers (EGTM) guidelines. Eur J Cancer 39:718–727
Chon H, Lee S, Son SW, Chil Hwan O, Choo J (2009) Highly sensitive immunoassay of lung cancer marker carcinoembryonic antigen using surface-enhanced Raman scattering of hollow gold nanospheres. Anal Chme 81:3029–3034
Han J, Zhuo Y, Chai YQ, Mao L, Yuan YL, Yuan R (2011) Highly conducting gold nanoparticles–graphene nanohybrid films for ultrasensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Talanta 85:130–135
Liu MY, Jia CP, Jin QH, Lou XH, Yao SH, Xiang JQ, Zhao JL (2010) Novel colorimetric enzyme immunoassay for the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Talanta 81:1625–1629
Thomson DM, Krupey J, Freedman SO, Gold P (1969) The radioimmunoassay of circulating carcinoembryonic antigen of the human digestive system. Proc Natl Acad Sci 64:161–167
Lin JH, Yan F, Ju HX (2004) Noncompetitive enzyme immunoassay for carcinoembryonic antigen by flow injection chemiluminescence. Clin Chim Acta 341:109–115
Yan F, Zhou JN, Lin JH, Ju HX, Hu XY (2005) Flow injection immunoassay for carcinoembryonic antigen combined with time-resolved fluorometric detection. J Immunol Methods 305:120–127
Feng DX, Lu XC, Dong X, Ling YY, Zhang YZ (2013) Label-free electrochemical immunosensor for the carcinoembryonic antigen using a glassy carbon electrode modified with electrodeposited Prussian blue, a graphene and carbon nanotube assembly and an antibody immobilized on gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 180:767–774
Darain F, Park S-U, Shim Y-B (2003) Disposable amperometric immunosensor system for rabbit IgG using a conducting polymer modified screen-printed electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 18:773–780
Li FQ, Kodzius R, Gooneratne CP, Foulds IG, Kosel J (2014) Magneto-mechanical trapping systems for biological target detection. Microchim Acta 181:1743–1748
Besse P-A, Boero G, Demierre M, Pott V, Popovic R (2002) Detection of a single magnetic microbead using a miniaturized silicon hall sensor. Appl Phys Lett 80:4199–4201
Lei J, Wang T, Lei C, Zhou Y (2013) Detection of dynabeads using a micro-electro-mechanical-systems fluxgate sensor. Appl Phys Lett 102:022413
Schotter J, Kamp PB, Becker A, Pühler A, Reiss G, Brückl H (2004) Comparison of a prototype magnetoresistive biosensor to standard fluorescent DNA detection, biosens. Bioelectron 19(10):1149–1156
Baselt DR, Lee GU, Natesan M, Metzger SW, Sheehan PE, Colton RJ (1998) A biosensor based on magnetoresistance technology, biosens. Bioelectron 13:731–739
Edelstein RL, Tamanaha CR, Sheehan PE, Miller MM, Baselt DR, Whitman LJ, Colton RJ (2000) The BARC biosensor applied to the detection of biological warfare agents biosens. Bioelectron 14:805–813
Miller MM, Sheehan PE, Edelstein RL, Tamanaha CR, Zhong L, Bounnak S, Whitman LJ, Colton RJ (2001) A DNA array sensor utilizing magnetic microbeads and magnetoelectronic detection. J Magn Magn Mater 225(1–2):138–144
Graham DL, Ferreira HA, Freitas PP, Cabral JMS (2003) High sensitivity detection of molecular recognition using magnetically labelled biomolecules and magnetoresistive sensors. Biosens Bioelectron 18(4):483–488
Schotter J, Kamp PB, Becker A, Puhler A, Brinkmann D, Schepper W, Bruckl H, Reiss G (2002) A biochip based on magnetoresistive sensors. IEEE Trans Magn 38:3365–3367
Ferreira HA, Graham DL, Freitas PP, Cabral JMS (2003) Biodetection using magnetically labeled biomolecules and arrays of spin valve sensors. J Appl Phys 93:7281–7286
Mujika M, Arana S, Castañoa E, Tijero M, Vilares R, Ruano-López JM, Cruz A, Sainz L, Berganza J (2009) Magnetoresistive immunosensor for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 including a microfluidic network. Biosens Bioelectron 24:1253–1258
Xu L, Yu H, Akhras MS, Han SJ, Osterfeld S, White RL, Pourmand N, Wang SX (2008) Giant magnetoresistive biochip for DNA detection and HPV genotyping. Biosens Bioelectron 24:99–103
Rife JC, Miller MM, Sheehan PE, Tamanaha CR, Tondra M, Whitman LJ (2003) Design/performance of GMR sensors for detection of magnetic microbeads. Sensors Actuators A 107(3):209–218
Reiss G, Brückl H, Hütten A, Schotter J, Brzeska M, Panhorst M, Sudfeld D, Becker A, Kamp PB, Pühler A, Wojczykowski K, Jutzi P (2005) Magnetoresistive sensors and magnetic nanoparticles for biotechnology. J Mater Res 20(12):3294–3304
Li G, Wang SX (2004) Model and experiment of detecting multiple magnetic nanoparticles as biomolecular labels by spin valve sensors. IEEE Trans Magn 40:3000–3002
Wang SX, Bae SY, Li G, Sun S, White RL, Kemp JT, Webb CD (2005) Towards a magnetic microarray for sensitive diagnostics. J Magn Magn Mater 293:731–736
Jokerst JV, Raamanathan A, Christodoulides N, Floriano PN, Pollard AA, Simmons GW, Wong J, Gage C, Furmaga WB, Redding SW, McDevitt JT (2009) Nano-bio-chips for high performance multiplexed protein detection: determinations of cancer biomarkers in serum and saliva using quantum dot bioconjugate labels. Biosens Bioelectron 24:3622–3629
Liu N, Feng F, Liu ZM, Ma ZF (2015) Porous platinum nanoparticles and PdPt nanocages for use in an ultrasensitive immunoelectrode for the simultaneous determination of the tumor markers CEA and AFP. Microchim Acta 182:1143–1151
Yang XM, Zhuo Y, Zhu SS, Luo YW, Feng YJ, Xu Y (2015) Selectively assaying CEA based on a creative strategy of gold nanoparticles enhancing silver nanoclusters' fluorescence. Biosens Bioelectron 64:345–351
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61273065), National Science and Technology Support Program (2012BAK08B05) and National Key Laboratory Research Fund (9140C790403110C7905), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (13ZR1420800), Support fund of Joint research center for advanced aerospace technology of Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology-Shanghai Jiao Tong University, the Analytical and Testing Center in Shanghai Jiao Tong University, the Center for Advanced Electronic Materials and Devices in Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 57 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Xc., Lei, C., Guo, L. et al. Giant magneto-resistance based immunoassay for the tumor marker carcinoembryonic antigen. Microchim Acta 183, 1107–1114 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1686-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1686-2