Abstract
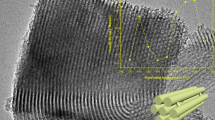
We describe uniform and high-temperature-stable mesoporous TiO2 beads functionalized with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs-TiO2) for use in conductometric sensing of gases and organic vapors. The size of the interconnected main mesopores of the TiO2 beads ranges from 8 to 15 nm, and the AuNPs have diameters between 8 and 10 nm. The mesoporous TiO2 beads are formed during calcination while the structure-directing template agent is removed. Monodispersed AuNPs are formed by reduction in-situ and are placed inside the mesoporous TiO2 framework. This prevents aggregation of the AuNPs even at 500 °C. The materials were characterized by UV–vis spectroscopy, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, nitrogen adsorption-desorption, and X-ray diffraction. Comb-type gold electrodes were then fabricated on an alumina substrate and are shown to display excellent properties in terms of sensing ammonia, ethanol, methanol or acetone. The sensitivity (defined as the ratio of resistivities under vapor and air) of a typical AuNPs(0.5 %)-TiO2 gas sensor for ethanol reached up to 5.65 at above 600 ppm at 75 °C. Response time and recovery times (t90 ≤ 20 s) are faster than (or comparable to) other metal-doped TiO2 sensors, and working temperatures are much lower. An interesting observation was made in that the changes in the conductivity of the sensor change with temperature. The sensor prepared with AuNPs(0.5 %)-TiO2 is of the p-type (in its response to ammonia gas) at 45 °C, but becomes n-type at 20 °C. Obviously, rather slight changes in temperature lead to a complete change in the direction of the conductometric signal change. This may provide a new aspect in terms of selective and highly sensitive detection of ammonia at ambient and slightly elevated temperatures.

We describe uniform and high-temperature-stable mesoporous TiO2 beads functionalized with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs-TiO2) for use in conductometric sensing of gases and organic vapors. Interestingly, the changes in the conductivity of typical sensors were opposite with the increasing of temperature.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rahman MM, Khan SB, Jamal A, Faisal M, Asiri AM (2012) Highly sensitive methanol chemical sensor based on undoped silver oxide nanoparticles prepared by a solution method. Microchim Acta 178:99–106
Li J, Kuang D, Feng Y, Zhang F, Liu M (2012) Glucose biosensor based on glucose oxidase immobilized on a nanofilm composed of mesoporous hydroxyapatite, titanium dioxide, and modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 176:73–80
Li W, Wu ZX, Wang JX, Elzatahry A, Zhao DY (2014) A perspective on mesoporous TiO2 materials. Chem Mater 26:287–298
Varghese OK, Gong D, Paulose M, Ong K, Grimes C (2003) Hydrogen sensing using titania nanotubes. Sensors Actuators B: Chem 93:338–344
Varghese OK, Gong D, Paulose M, Ong K, Grimes C (2003) Extreme changes in the electrical resistance of titania nanotubes with hydrogen exposure. Adv Mater 15:624–627
Buso BD, Post M, Cantalini C, Mulvaney P, Martucci A (2008) Gold nanoparticle-doped TiO2 semiconductor thin films: Gas sensing properties. Adv Funct Mater 18:3834–3849
Zeng W, Liu TM, Herzog A, Liu DJ (2010) Formaldehyde gas sensing property and mechanism of TiO2–Ag nanocomposite. J Phys B 45:4235–4239
Wang L, Lou Z, Fei T, Zhang T (2012) Templating synthesis of ZnO hollow nanospheres loaded with Au nanoparticles and their enhanced gas sensing properties. J Mater Chem 22:4767–4771
Lei T, Zhang SP, Li D, Zhang W, Huang S, Xie CS (2014) The influence of Au and Pt electrodes on the stability of TiO2 under UV light activation for sensing formaldehyde in moisture circumstances. Sensors Actuators B: Chem 199:15–21
Daniel EC, Astruc D (2003) Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev 104:293–346
Macwan DP, Dave PN, Chaturvedi S (2011) A review on nano-TiO2 sol–gel type syntheses and its applications. J Mater Sci 46:3669–3686
Wang GY, Zhang WX, Cui YC, Jiang DZ, Wu TH (2001) Effect of H2O on catalytic performance of MOx and Au/MOx catalysts for CO oxidation. Chin J Catal 22:408–410
Konova P, Naydenov A, Venkov C, Mehandjiev D, Andreeva D, Tabakova T (2004) Activity and deactivation of Au/TiO2 catalyst in CO oxidation. J Mol Catal A Chem 213:235–240
Subramanian V, Wolf EE, Kamat PV (2003) Influence of metal/metal Ion concentration on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2-Au composite nanoparticles. Langmuir 19:469–474
Li H, Bian Z, Zhu J, Huo Y, Li H, Lu Y (2007) Mesoporous Au/TiO2 nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J Am Chem Soc 129:4538–4539
Chen D, Cao L, Huang F, Imperia P, Cheng YB, Caruso RA (2010) Synthesis of monodisperse mesoporous titania beads with controllable diameter, high surface areas, and variable pore diameters (14–23 nm). J Am Chem Soc 132:4438–4444
Buso BD, Pacifico J, Martucci A, Mulvaney P (2007) Gold-nanoparticle-doped TiO2 semiconductor thin films: optical characterization. Adv Funct Mater 17:347–354
Zhou W, Sun F, Pan K, Tian G, Jiang B, Ren Z, Tian C, Fu H (2011) Well-ordered large-pore mesoporous anatase TiO2 with remarkably high thermal stability and improved crystallinity: preparation, characterization, and photocatalytic performance. Adv Funct Mater 21:1922–1930
Pérez MD, Otal E, Bilmes SA, Soler-Illia G, Crepaldi EL, Grosso D, Sanchez C (2004) Growth of gold nanoparticle arrays in TiO2 mesoporous matrixes. Langmuir 20:6879–6886
He P, Shen L, Liu R, Luo Z, Li Z (2011) Direct detection of β-agonists by Use of gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assays. Anal Chem 83:6988–6995
Lopez-Sanchez JA, Dimitratos D, Hammond C, Brett GL, Kesavan L, White S, Miedziak P, Tiruvalam R, Jenkins RL, Carley AF, Knight D, Kiely CJ, Hutchings GJ (2011) Facile removal of stabilizer-ligands from supported gold nanoparticles. Nat Chem 3:551–556
Yu Y, Cao CY, Chen Z, Liu H, Li P, Dou ZF, Song WG (2013) Synthesis and characterisation of a lanthanide-capped dodecavanadate cage. Chem Commun 49:3116–3118
Wagner T, Haffer S, Weinberger C, Klaus D, Tiemann M (2013) Mesoporous materials as gas sensors. Chem Soc Rev 42:4036–4053
Hu P, Du G, Zhou W, Cui J, Lin J, Liu H, Liu D, Wang J, Chen S (2010) Colorimetric detection of Pb2+ using glutathione functionalized gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:3263–3269
Barsan N, Koziej D, Weimar U (2007) Metal oxide-based gas sensor research: How to? Sensors Actuators B: Chem 121:18–35
Sze SM, Ng KK (1981) Physics of semiconductor devices. John Wiley and sons, New York, pp 160–180
Kong J, Franklin NR, Zhou C, Chapline M, Peng S, Cho K, Dai HJ (2000) Nanotube molecular wires as chemical sensors. Science 287:622–625
Hossein-Babaei F, Keshmiri M, Kakavand M, Troczynski T (2005) A resistive gas sensor based on undoped p-type anatase. Sensors Actuators B: Chem 110:28–35
Mabrook M, Hawkins P (2001) A rapidly-responding sensor for benzene, methanol and ethanol vapours based on films of titanium dioxide dispersed in a polymer operating at room temperature. Sensors Actuators B Chem 75:197–202
Hossein-Babaei F, Rahbarpour S (2011) Separate assessment of chemoresistivity and Schottky-type gas sensitivity in M-metal oxide-M’ structures. Sensors Actuators B: Chem 160:174–180
Tang J, White M, Stucky GD, McFarland EW (2003) Electrochemical fabrication of large-area Au/TiO2 junctions. Electrochem Commun 5:497–501
Boccuzzi F, Chiorino A, Tsubota S, Haruta M (1996) FTIR study of carbon monoxide oxidation and scrambling at room temperature over gold supported on ZnO and TiO2. 2. J Phys Chem 100:3635–3631
Xi B, Verma LK, Li J, Bhatia CS, Danner AJ, Yang H, Zeng HC (2012) TiO2 thin films prepared via adsorptive self-assembly for self-cleaning applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:1093–1102
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21471120), the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2014CFB782).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wei Xiong and Huanhuan Liu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 4344 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, W., Liu, H. & Liu, S. Conductometric sensor for ammonia and ethanol using gold nanoparticle-doped mesoporous TiO2 . Microchim Acta 182, 2345–2352 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1577-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1577-6