Abstract
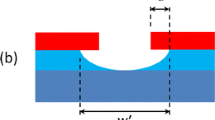
The emergent technology of using nanopores for stochastic sensing of biomolecules introduces a demand for the development of simple fabrication methodologies of nanopores in solid state membranes. This process becomes particularly challenging when membranes of composite layer architecture are involved. To overcome this challenge we have employed a focused electron beam induced chemical etching process. We present here the fabrication of nanopores in silicon-on-insulator based membranes in a single step process. In this process, chemical etching of the membrane materials by XeF2 gas is locally accelerated by an electron beam, resulting in local etching, with a top membrane oxide layer preventing delocalized etching of the silicon underneath. Nanopores with a funnel or conical, 3-dimensional (3D) shape can be fabricated, depending on the duration of exposure to XeF2, and their diameter is dominated by the time of exposure to the electron beam. The demonstrated ability to form high-aspect ratio nanopores in comparably thick, multi-layered silicon based membranes allows for an easy integration into current silicon process technology and hence is attractive for implementation in biosensing lab-on-chip fabrication technologies.

Nanopore drilling in silicon-on-insulator membranes is accomplished by focused electron beam induced chemical etching.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Howorka S, Siwy Z (2009) Nanopore analytics: sensing of single molecules. Chem Soc Rev 38:2360–2384
Branton D, Deamer DW, Marziali A, Bayley H, Benner SA, Butler T, Di Ventra M, Garaj S, Hibbs A, Huang XH, Jovanovich SB, Krstic PS, Lindsay S, Ling XSS, Mastrangelo CH, Meller A, Oliver JS, Pershin YV, Ramsey JM, Riehn R, Soni GV, Tabard-Cossa V, Wanunu M, Wiggin M, Schloss JA (2008) The potential and challenges of nanopore sequencing. Nat Biotechnol 26:1146–1153
Movileanu L (2009) Interrogating single proteins through nanopores: challenges and opportunities. Trends Biotechnol 27:333–341
Ashkenasy N, Sanchez-Quesada J, Bayley H, Ghadiri MR (2005) Recognizing a single base in an individual DNA strand: a step toward DNA sequencing in nanopores. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:1401–1404
Howorka S, Cheley S, Bayley H (2001) Sequence-specific detection of individual DNA strands using engineered nanopores. Nat Biotechnol 19:636–639
Dekker C (2007) Solid-state nanopores. Nat Nanotechnol 2:209–215
Rhee M, Burns MA (2007) Nanopore sequencing technology: nanopore preparations. Trends Biotechnol 25:174–181
Gierak J (2009) Focused ion beam technology and ultimate applications. Semicond Sci Technol 24:043001
Fologea D, Ledden B, McNabb DS, Li JL (2007) Electrical characterization of protein molecules by a solid-state nanopore. Appl Phys Lett 91
Han AP, Schurmann G, Mondin G, Bitterli RA, Hegelbach NG, de Rooij NF, Staufer U (2006) Sensing protein molecules using nanofabricated pores. Appl Phys Lett 88
Yusko EC, Johnson JM, Majd S, Prangkio P, Rollings RC, Li J, Yang J, Mayer M (2011) Controlling protein translocation through nanopores with bio-inspired fluid walls. Nat Nanotechnol 6:253–260
Wei R, Gatterdam V, Wieneke R, Tampe R, Rant U (2012) Stochastic sensing of proteins with receptor-modified solid-state nanopores. Nat Nanotechnol 7:257–263
Liebes-Peer Y, Rapaport H, Ashkenasy N (2014) Amplification of single molecule translocation signal using β-strand peptide functionalized nanopores. ACS Nano 8:6822–6832
Drozdov M, Kauffmann Y, Carter WC, Kaplan WD (2010) Shape-controlled nanopores in single crystals. Nanotechnology 21:475301–475307
Wu MY, Smeets RMM, Zandbergen M, Ziese U, Krapf D, Batson PE, Dekker NH, Dekker C, Zandbergen HW (2009) Control of shape and material composition of solid-state nanopores. Nano Lett 9:479–484
Wanunu M (2012) Nanopores: a journey towards DNA sequencing. Phys Life Rev 9:125–158
Siwy Z, Heins E, Harrell CC, Kohli P, Martin CR (2004) Conical-nanotube ion-current rectifiers: the role of surface charge. J Am Chem Soc 126:10850–10851
Kim MJ, Wanunu M, Bell DC, Meller A (2006) Rapid fabrication of uniformly sized nanopores and nanopore arrays for parallel DNA analysis. Adv Mater 18:3149–3153
Venkatesan BM, Shah AB, Zuo JM, Bashir R (2010) DNA sensing using nanocrystalline surface-enhanced Al2O3 nanopore sensors. Adv Funct Mater 20:1266–1275
Merchant CA, Healy K, Wanunu M, Ray V, Peterman N, Bartel J, Fischbein MD, Venta K, Luo Z, Johnson ATC, Drndic M (2010) DNA translocation through graphene nanopores. Nano Lett 10:2915–2921
Wu MY, Krapf D, Zandbergen M, Zandbergen H, Batson PE (2005) Formation of nanopores in a sin/sio2 membrane with an electron beam. Appl Phys Lett 87(113106):113101–113103
Polonsky S, Rossnagel S, Stolovitzky G (2007) Nanopore in metal-dielectric sandwich for DNA position control. Appl Phys Lett 91:153103-153101-153103
Gracheva ME, Xiong A, Aksimentiev A, Schulten K, Timp G, Leburton JP (2006) Simulation of the electric response of DNA translocation through a semiconductor nanopore–capacitor. Nanotechnology 17:622–633
Petrossian L, Wilk SJ, Joshi P, Hihath S, Goodnick SM, Thornton TJ (2007) Fabrication of cylindrical nanopores and nanopore arrays in silicon-on-insulator substrates. J Microelectromech Syst 16:1419–1428
Chang H, Venkatesan B, Iqbal S, Andreadakis G, Kosari F, Vasmatzis G, Peroulis D, Bashir R (2006) DNA counterion current and saturation examined by a MEMS-based solid state nanopore sensor. Biomed Microdevices 8:263–269
Egerton RF, Li P, Malac M (2004) Radiation damage in the TEM and SEM. Micron 35:399–409
Iqbal SM, Akin D, Bashir R (2007) Solid-state nanopore channels with DNA selectivity. Nat Nanotechnol 2:243–248
Buchholz K, Tinazli A, Kleefen A, Dorfner D, Pedone D, Rant U, Tampe R, Abstreiter G, Tornow M (2008) Silicon-on-insulator based nanopore cavity arrays for lipid membrane investigation. Nanotechnology 19(445305):445301–445306
Liebes Y, Hadad B, Ashkenasy N (2011) Effects of electrons in focused electron beam induced nanopore etching. Nanotechnology 22:285303
Yemini M, Hadad B, Liebes Y, Goldner A, Ashkenasy N (2009) A novel methodology for controlled fabrication of nanopores by focused electron beam induced etching. Nanotechnology 20:245302
Spinney PS, Howitt DG, Smith RL, Collins SD (2010) Nanopore formation by low-energy focused electron beam machining. Nanotechnology 21:375301–375307
Sökmen Ü, Stranz A, Fündling S, Wehmann H-H, Bandalo V, Bora A, Tornow M, Waag A, Peiner E (2009) Capabilities of ICP-RIE cryogenic dry etching of silicon: Review of exemplary microstructures. J Micromech Microeng 19:105005
Dang ZY, Motapothula M, Ow YS, Venkatesan T, Breese MBH, Rana MA, Osman A (2011) Fabrication of large-area ultra-thin single crystal silicon membranes. Appl Phys Lett 99:223105-223101-223103
Ziebart V, Paul O, Baltes H (1999) Strongly buckled square micromachined membranes. J Microelectromech Syst 8:423–432
Randolph SJ, Fowlkes JD, Rack PD (2005) Focused electron-beam-induced etching of silicon dioxide. J Appl Phys 98:034902
Randolph SJ, Fowlkes JD, Rack PD (2006) Focused, nanoscale electron-beam-induced deposition and etching. Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci 31:55–89
Storm AJ, Chen JH, Ling XS, Zandbergen HW, Dekker C (2005) Electron-beam-induced deformations of SiO2 nanostructures. J Appl Phys 98(014307):014301–014308
Siwy ZS (2006) Ion-current rectification in nanopores and nanotubes with broken symmetry. Adv Funct Mater 16:735–746
Chang H, Iqbal SM, Stach EA, King AH, Zaluzec NJ, Bashir R (2006) Fabrication and characterization of solid-state nanopores using a field emission scanning electron microscope. Appl Phys Lett 88:3
Storm AJ, Chen JH, Ling XS, Zandbergen HW, Dekker C (2003) Fabrication of solid-state nanopores with single-nanometre precision. Nat Mater 2:537–540
Sexton LT, Horne LP, Martin CR (2007) Developing synthetic conical nanopores for biosensing applications. Mol Biosyst 3:667–685
Acknowledgments
This work was partially financially supported by the BMBF under grant 0312031E, by the NTH School for Contacts in Nanosystems, and by a German-Israeli Project Cooperation (DIP) under grants AS 424/1-1 and TO 266/8-1. The authors thank Drs. V. Ezersky and E. Roth for assistance in TEM imaging and fruitful discussions, B. Hadad for technical assistance in e-beam writer operation, and Mr. M. Karsten and Mr. W. Weiß for technical help. YLP is a recipient of a Negev doctoral scholarship and the Shimona Geresh prize.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liebes-Peer, Y., Bandalo, V., Sökmen, Ü. et al. Fabrication of nanopores in multi-layered silicon-based membranes using focused electron beam induced etching with XeF2 gas. Microchim Acta 183, 987–994 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1557-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1557-x