Abstract
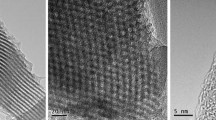
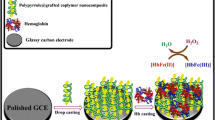
Highly dispersed gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were introduced into a hierarchically porous zeolite of the MFI type that contains mesopores and an inherently microporous structure. These represent a novel matrix for the immobilization of biomolecules. The composites were characterized by FTIR, X-ray diffraction, UV–vis spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, nitrogen sorption measurements, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The crystallinity and morphology of the zeolite is not compromised by incorporating the AuNPs with their size of 3–20 nm. A sensor for hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) was fabricated by incorporating hemoglobin into the matrix and placing it on the surface of a glassy carbon electrode. The resulting biosensor exhibits excellent bioelectrocatalytic capability for the reduction of H2O2. The amperometric response at −0.4 V linearly depends on H2O2 in the 1.0 μM to 18 mM concentration range. The detection limit is 0.8 μM (at an S/N of 3). Its good sensitivity, stability and reproducibility make the modified hierarchically porous zeolite a promising new matrix material for protein immobilization and the construction of biosensors.

Amperometric responses of Hb/Au-MFIOH/GCE upon successive additions of different concentrations of H2O2 to 0.1 M pH 7.0 phosphate buffer solution at applied potential of −0.4 V.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck JS, Vartuli JC, Roth WJ, Leonowicz ME, Kresge CT (1992) A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J Am Chem Soc 114(27):10834–10843
Mohammad H, Nasrin S, Morteza E, Peyman S (2012) Mesoporous silica-based materials for use in electrochemical enzyme nanobiosensors. Trends Anal Chem 33(3):117–129
Walcarius A (2008) Electroanalytical applications of microporous zeolites and mesoporous (organo) silicas: recent trends. Electroanalysis 20(7):711–738
Dai ZH, Bao JC, Yang XD, Ju HX (2008) A bienzyme channeling glucose sensor with a wide concentration range based on co-entrapment of enzymes in SBA-15 mesopores. Biosens Bioelectron 23(7):1070–1076
Lin JH, He CY, Zhang SS (2009) Immunoassay channels for α-fetoprotein based on encapsulation of biorecognition molecules into SBA-15 mesopores. Anal Chim Acta 643(1):90–94
Cai YY, Li H, Du B, Yang MH, Li Y (2011) Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunoassay for BRCA1 using BMIM ·BF4-coated SBA-15 as labels and functionalized graphene as enhancer. Biomaterials 32(8):2117–2123
Holm MS, Taarning E, Egeblad K, Christensen CH (2011) Catalysis with hierarchical zeolites. Catal Today 168(1):3–16
Olson DH, Kokotailo GT, Lawton SL, Meier WM (1981) Crystal structure and structure-related properties of ZSM-5. J Phys Chem 85(15):2238–2243
Groen J, Bach T, Ziese U (2005) Creation of hollow zeolite architectures by controlled desilication of Al-zoned ZSM-5 crystals. J Am Chem Soc 127(31):10792–10793
Verboekend D, Pérez-Ramírez J (2011) Design of hierarchical zeolite catalysts by desilication. Catal Sci Technol 1(6):879–890
Peng S, Gao Q, Wang Q, Shi JL (2004) Layered structural heme protein magadiite nanocomposites with high enzyme-like peroxidase activity. Chem Mater 16(13):2675–2684
Zeng XD, Wei WZ, Li XF, Zeng JX, Wu L (2007) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin entrapped in semi-interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel based on polyacrylamide and chitosan. Bioelectrochemistry 71(2):135–141
Dai ZH, Liu SQ, Ju HX, Chen HY (2004) Direct electron transfer and enzymatic activity of hemoglobin in a hexagonal mesoporous silica matrix. Biosens Bioelectron 19(8):861–867
Li JX, Xiong ZY, Zhou LH, Han X, Liu HL (2010) Effects of pore structure of mesoporous silicas on the electrochemical properties of hemoglobin. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 130(1):333–337
Zhang L, Zhang Q, Li JH (2007) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin immobilized in bimodal mesoporous silica and chitosan inorganic–organic hybrid film. Electrochem Commun 9(7):1530–1535
Xian YZ, Xian Y, Zhou LH, Wu FH, Jin LT (2007) Encapsulation hemoglobin in ordered mesoporous silicas: influence factors for immobilization and bioelectrochemistry. Electrochem Commun 9(1):142–148
Wang J (2012) Electrochemical biosensing based on noble metal nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 177(3–4):245–270
Cheng XW, Meng QY, Chen JY, Long YC (2012) A facile route to synthesize mesoporous ZSM-5 zeolite incorporating high ZnO loading in mesopores. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 153:198–203
Lee B, Ma Z, Zhang ZT, Park C, Dai S (2009) Influences of synthesis conditions and mesoporous structures on the gold nanoparticles supported on mesoporous silica hosts. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 122(1):160–167
Hao YJ, Chong YZ, Li SR, Yang HQ (2012) Controlled synthesis of Au nanoparticles in the nanocages of SBA-16: improved activity and enhanced recyclability for the oxidative esterification of alcohols. J Phys Chem C 116(11):6512–6519
Storhoff JJ, Lazarides AA, Mucic RC, Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL (2000) What controls the optical properties of DNA-linked gold nanoparticle assemblies? J Am Chem Soc 122(19):4640–4650
Olson DH, Haag WO, Lago RM (1980) Chemical and physical properties of the ZSM-5 substitutional series. J Catal 61(2):390–396
Jiang Q, Wu ZY, Wang YM, Cao Y, Zhou CF, Zhu JH (2006) Fabrication of photoluminescent ZnO/SBA-15 through directly dispersing zinc nitrate into the as-prepared mesoporous silica occluded with template. J Mater Chem 16(16):1536–1542
Bond GC, Louis C (2006) Catalysis by gold. Imperial College Press, London
Laviron E (1979) General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Electrochem 101(1):19–28
Wang SF, Chen T, Zhang ZL, Shen XC, Lu ZX (2005) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of heme proteins entrapped in agarose hydrogel films in room-temperature ionic liquids. Langmuir 21(20):9260–9266
Chen X, Hu N, Zeng Y, Rusling JF, Yang J (1999) Ordered electrochemically active films of hemoglobin, didodecyldimethylammonium ions, and clay. Langmuir 15(20):7022–7030
Nassar AEF, Willis WS, Rusling JF (1995) Electron transfer from electrodes to myoglobin: facilitated in surfactant films and blocked by adsorbed biomacromolecules. Anal Chem 67(14):2386–2392
Wang YH, Yu CM, Pan ZQ, Wang YF, Guo JW (2013) A gold electrode modified with hemoglobin and the chitosan@ Fe3O4 nanocomposite particles for direct electrochemistry of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 180:659–667
Dong SY, Li N, Zhang PH, Li YS, Chen Z (2012) Fabrication of hemoglobin/ionic liquid modified carbon paste electrode based on the electrodeposition of gold nanoparticles/CdS quantum dots and its electrochemical application. Electroanalysis 24(7):1554–1560
Chen B, Wang H, Zhang HY, He ZX, Zhou YZ (2012) A novel hydrogen peroxide sensor based on hemoglobin immobilized PAn–SiO2/DTAB composite film. J Mol Liq 171:23–28
Sun W, Qin P, Zhao RJ, Jiao K (2010) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin on gold nanoparticle decorated carbon ionic liquid electrode. Talanta 80:2177–2181
Wei NN, Xin X, Du JY, Li JL (2011) A novel hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on the immobilization of hemoglobin on three-dimensionally ordered macroporous (3DOM) gold-nanoparticle-doped titanium dioxide (GTD) film. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3602–3607
Xu J, Liu C, Teng Y (2010) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hydrogen peroxide using hemoglobin immobilized in hollow zirconium dioxide spheres and sodium alginate films. Microchim Acta 169(1–2):181–186
Xu J, Liu C, Wu Z (2011) Direct electrochemistry and enhanced electrocatalytic activity of hemoglobin entrapped in graphene and ZnO nanosphere composite film. Microchim Acta 172(3–4):425–430
Acknowledgments
This work is financed by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21001027 and 61071040) and Shanghai Nature Science Foundation (Grant:13ZR1411900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 557 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, L., Dong, J., Cheng, X. et al. Hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin immobilized on gold nanoparticles in a hierarchically porous zeolite. Microchim Acta 180, 1333–1340 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1064-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1064-x