Abstract
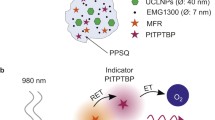
We report on a strategy to model both the size (d) and the polydispersity (PdI) of magnetic oxygen-sensitive nanoparticles with a typical size of 200 nm in order to increase the surface area. The strategy is based on experimental design and Response Surface Methodology. Nanoparticles were prepared by miniemulsion solvent evaporation of solutions of poly(styrene-co-maleic anhydride). Features of this strategy include (1) a quick selection of the most important variables that govern d and PdI; (2) a better understanding of the parameters that affect the performance of the polymer; and (3) optimized conditions for the synthesis of nanoparticles of targeted d and PdI. The results were used to produce nanoparticles in sizes that range from 100 to 300 nm and with small polydispersity. The addition of a platinum porphyrin complex that acts as a luminescent probe for oxygen and of magnetite (Fe3O4) to the polymeric particles, did not affect d and PdI, thus demonstrating that this strategy simplifies their synthesis. The resulting luminescent and magnetic sensor nanoparticles respond to dissolved oxygen with sensitivity (Stern-Volmer constant) of around 35 bar−1.

ᇵ



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amao Y (2003) Probes and polymers for optical sensing of oxygen. Microchim Acta 143(1):1–12. doi:10.1007/s00604-003-0037-x
Marín-Suárez M, Curchod BFE, Tavernelli I, Rothlisberger U, Scopelliti R, Jung I, Di Censo D, Grätzel M, Fernández-Sánchez JF, Fernández-Gutiérrez A, Nazeeruddin MK, Baranoff E (2012) Nanocomposites containing neutral blue emitting cyclometalated iridium (III) emitters for oxygen sensing. Chem Mater 24(12):2330–2338. doi:10.1021/cm300575z
Wolfbeis OS (2005) Materials for fluorescence-based optical chemical sensors. J Mater Chem 15(27–28):2657–2669
Borchert N, Hempel A, Walsh H, Kerry JP, Papkovsky DB (2012) High throughput quality and safety assessment of packaged green produce using two optical oxygen sensor based systems. Food Control 28(1):87–93
Mistlberger G, Koren K, Borisov SM, Klimant I (2010) Magnetically remote-controlled optical sensor spheres for monitoring oxygen or pH. Anal Chem 82(5):2124–2128. doi:10.1021/Ac902393u
Marín-SuárezdelToro M, Fernández-Sánchez JF, Baranoff E, Nazeeruddin MK, Graetzel M, Fernández-Gutierrez A (2010) Novel luminescent Ir(III) dyes for developing highly sensitive oxygen sensing films. Talanta 82(2):620–626
Ergeneman O, Chatzipirpiridis G, Pokki J, Marin-Suarez M, Sotiriou GA, Medina-Rodríguez S, Fernández-Sanchez JF, Fernandez-Gutierrez A, Pane S, Nelson BJ (2012) In vitro oxygen sensing using intraocular microrobots. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59(11):3104–3109. doi:10.1109/tbme.2012.2216264
Esipova TV, Karagodov A, Miller J, Wilson DF, Busch TM, Vinogradov SA (2011) Two new “protected” oxyphors for biological oximetry: properties and application in tumor imaging. Anal Chem 83(22):8756–8765. doi:10.1021/ac2022234
Xu H, Aylott JW, Kopelman R, Miller TJ, Philbert MA (2001) A real-time ratiometric method for the determination of molecular oxygen inside living cells using sol-gel-based spherical optical nanosensors with applications to rat C6 glioma. Anal Chem 73(17):4124–4133. doi:10.1021/ac0102718
Borisov SM, Mayr T, Klimant I (2008) Poly (styrene-block-vinylpyrrolidone) beads as a versatile material for simple fabrication of optical nanosensors. Anal Chem 80(3):573–582. doi:10.1021/ac071374e
Borisov SM, Klimant I (2008) Optical nanosensors-smart tools in bioanalytics. Analyst 133(10):1302–1307
Koo Lee Y-E, Kopelman R (2012) Chapter twenty-one—nanoparticle PEBBLE sensors in live cells. In: Methods in enzymology, vol Volume 504. Academic Press, pp 419–470. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-391857-4.00021-5
Medina-Castillo AL, Mistlberger G, Fernández-Sánchez JF, Segura-Carretero A, Klimant I, Fernández-Gutiérrez A (2009) Novel strategy to design magnetic, molecular imprinted polymers with well-controlled structure for the application in optical sensors. Macromolecules 43(1):55–61. doi:10.1021/ma902095s
Mistlberger G, Koren K, Scheucher E, Aigner D, Borisov SM, Zankel A, Pölt P, Klimant I (2010) Multifunctional magnetic optical sensor particles with tunable sizes for monitoring metabolic parameters and as a basis for nanotherapeutics. Adv Funct Mater 20(11):1842–1851. doi:10.1002/adfm.201000321
Valero-Navarro Á, Gómez-Romero M, Fernández-Sánchez JF, Cormack PAG, Segura-Carretero A, Fernández-Gutiérrez A (2011) Synthesis of caffeic acid molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres and high-performance liquid chromatography evaluation of their sorption properties. J Chromatogr A 1218(41):7289–7296
Steiner M-S, Duerkop A, Wolfbeis OS (2011) Optical methods for sensing glucose. Chem Soc Rev 40(9):4805–4839
Dmitriev R, Papkovsky D (2012) Optical probes and techniques for O2 measurement in live cells and tissue. Cell Mol Life Sci 69(12):2025–2039. doi:10.1007/s00018-011-0914-0
Zhang P, Chen J, Huang F, Zeng Z, Hu J, Yi P, Zeng F, Wu S (2013) One-pot fabrication of polymer nanoparticle-based chemosensors for Cu2+ detection in aqueous media. Polym Chem 4(7):2325–2332
Wang X-d, Stolwijk JA, Lang T, Sperber M, Meier RJ, Wegener J, Wolfbeis OS (2012) Ultra-small, highly stable, and sensitive dual nanosensors for imaging intracellular oxygen and pH in cytosol. J Am Chem Soc 134(41):17011–17014. doi:10.1021/ja308830e
Napp J, Behnke T, Fischer L, Würth C, Wottawa M, Katschinski DM, Alves F, Resch-Genger U, Schäferling M (2011) Targeted luminescent near-infrared polymer-nanoprobes for in vivo imaging of tumor hypoxia. Anal Chem 83(23):9039–9046. doi:10.1021/ac201870b
Fercher A, Borisov SM, Zhdanov AV, Klimant I, Papkovsky DB (2011) Intracellular O2 sensing probe based on cell-penetrating phosphorescent nanoparticles. ACS Nano 5(7):5499–5508. doi:10.1021/nn200807g
Kondrashina AV, Dmitriev RI, Borisov SM, Klimant I, O’Brien I, Nolan YM, Zhdanov AV, Papkovsky DB (2012) A phosphorescent nanoparticle-based probe for sensing and imaging of (Intra) cellular oxygen in multiple detection modalities. Adv Funct Mater 22(23):4931–4939. doi:10.1002/adfm.201201387
Acosta MA, Ymele-Leki P, Kostov YV, Leach JB (2009) Fluorescent microparticles for sensing cell microenvironment oxygen levels within 3D scaffolds. Biomaterials 30(17):3068–3074. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.02.021
Anker JN, Koo YE, Kopelman R (2007) Magnetically controlled sensor swarms. Sensors Actuators B Chem 121(1):83–92
Koren K, Mistlberger G, Aigner D, Borisov S, Zankel A, Pölt P, Klimant I (2010) Characterization of micrometer-sized magnetic optical sensor particles produced via spray-drying. Monatsh Chem Chem Mon 141(6):691–697. doi:10.1007/s00706-010-0262-z
Mistlberger G, Borisov SM, Klimant I (2009) Enhancing performance in optical sensing with magnetic nanoparticles. Sensors Actuators B Chem 139(1):174–180
Nasongkla N, Bey E, Ren J, Ai H, Khemtong C, Guthi JS, Chin S-F, Sherry AD, Boothman DA, Gao J (2006) Multifunctional polymeric micelles as cancer-targeted, MRI-ultrasensitive drug delivery systems. Nano Lett 6(11):2427–2430. doi:10.1021/nl061412u
Kopelman R, Lee Koo Y-E, Philbert M, Moffat BA, Ramachandra Reddy G, McConville P, Hall DE, Chenevert TL, Bhojani MS, Buck SM, Rehemtulla A, Ross BD (2005) Multifunctional nanoparticle platforms for in vivo MRI enhancement and photodynamic therapy of a rat brain cancer. J Magn Magn Mater 293(1):404–410
Kim J, Lee JE, Lee SH, Yu JH, Lee JH, Park TG, Hyeon T (2008) Designed fabrication of a multifunctional polymer nanomedical platform for simultaneous cancer- targeted imaging and magnetically guided drug delivery. Adv Mater 20(3):478–483. doi:10.1002/adma.200701726
Hurst SJ, Lee Y-E, Kopelman R (2011) Polymeric nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. In: Biomedical nanotechnology, vol 726. Methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, pp 151–178. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-052-2_11
He C, Yin L, Tang C, Yin C (2012) Size-dependent absorption mechanism of polymeric nanoparticles for oral delivery of protein drugs. Biomaterials 33(33):8569–8578
Kim S-H, Cho Y-S, Jeon S-J, Eun TH, Yi G-R, Yang S-M (2008) Microspheres with tunable refractive index by controlled assembly of nanoparticles. Adv Mater 20(17):3268–3273. doi:10.1002/adma.200702622
Marín-Suárez M, Medina-Castillo AL, Fernández-Sánchez JF, Fernández-Gutiérrez A (2012) Atom-Transfer Radical Polymerisation (ATRP) as a tool for the development of optical sensing phases. Israel J Chem 52(3–4):264–275. doi:10.1002/ijch.201100123
Wang X-d, Meier RJ, Wolfbeis OS (2012) A fluorophore-doped polymer nanomaterial for referenced imaging of pH and temperature with sub-micrometer resolution. Adv Funct Mater 22(20):4202–4207. doi:10.1002/adfm.201200813
Roberge S, Dubé MA (2006) The effect of particle size and composition on the performance of styrene/butyl acrylate miniemulsion-based PSAs. Polymer 47(3):799–807
Rao JP, Geckeler KE (2011) Polymer nanoparticles: preparation techniques and size-control parameters. Prog Polym Sci 36(7):887–913. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2011.01.001
Mistlberger G, Medina-Castillo A, Borisov S, Mayr T, Fernández-Gutiérrez A, Fernández-Sánchez J, Klimant I (2010) Mini-emulsion solvent evaporation: a simple and versatile way to magnetic nanosensors. Microchim Acta 172(3):299–308. doi:10.1007/s00604-010-0492-0
Borisov SM, Mayr T, Mistlberger G, Waich K, Koren K, Chojnacki P, Klimant I (2009) Precipitation as a simple and versatile method for preparation of optical nanochemosensors. Talanta 79(5):1322–1330
Chiewpattanakul P, Covis R, Vanderesse R, Thanomsub B, Marie E, Durand A (2010) Design of polymeric nanoparticles for the encapsulation of monoacylglycerol. Colloid Polym Sci 288(9):959–967. doi:10.1007/s00396-010-2216-8
Bally F, Garg DK, Serra CA, Hoarau Y, Anton N, Brochon C, Parida D, Vandamme T, Hadziioannou G (2013) Improved size-tunable preparation of polymeric nanoparticles by microfluidic nanoprecipitation. Polym (UK) 53(22):5045–5051
Medina-Castillo AL, Fernández-Sánchez JF, Segura-Carretero A, Fernández-Gutiérrez A (2010) Micrometer and submicrometer particles prepared by precipitation polymerization: thermodynamic model and experimental evidence of the relation between Flory’s parameter and particle size. Macromolecules 43(13):5804–5813. doi:10.1021/ma100841c
Bezerra MA, Santelli RE, Oliveira EP, Villar LS, Escaleira LA (2008) Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 76(5):965–977
Ramírez LP, Landfester K (2003) Magnetic polystyrene nanoparticles with a high magnetite content obtained by miniemulsion processes. Macromol Chem Phys 204(1):22–31. doi:10.1002/macp.200290052
Amao Y, Miyashita T, Okura I (2001) Platinum tetrakis(pentafluorophenyl)porphyrin immobilized in polytrifluoroethylmethacrylate film as a photostable optical oxygen detection material. J Fluor Chem 107(1):101–106
Mistlberger G, Chojnacki P, Klimant I (2008) Magnetic sensor particles: an optimized magnetic separator with an optical window. J Phys D Appl Phys 41(8):085003
Khuri AI, Mukhopadhyay S (2010) Response surface methodology. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Stat 2(2):128–149. doi:10.1002/wics.73
Hendriks MMWB, de Boer JH, Smilde AK, Doornbos DA (1992) Multicriteria decision making. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 16(3):175–191
Lakowicz JR (2006) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy, vol 1. 3rd edn. Springer
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Junta de Andalucía (Excellence Project P07-FQM-2625, P07-FQM-2738 and Marín-Suárez’s grant) and the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness CTQ2011-25316. The authors are also grateful to Santiago Medina-Rodriguez for his advice using MATLAB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 43 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marín-Suárez, M., Arias-Martos, M.C., Galeano-Díaz, T. et al. Modelling the size and polydispersity of magnetic hybrid nanoparticles for luminescent sensing of oxygen. Microchim Acta 180, 1201–1209 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1054-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1054-z