Abstract
We report on a biosensing system for ultrasensitive detection of Dynabeads protein A (DPA) that employs the magnetoimpedance (GMI) effect. The system is capable of detecting DPA via magnetic signals in the form of a magnetoimpedance change. The GMI ratio shows distinctive changes because of the induced fringe field produced by the superparamagnetic Dynabeads. The GMI ratio undergoes an overall downturn at high frequencies, but the drop becomes smaller with increasing DPA concentration. This phenomenon has not been observed so far. At a concentration of 0.1 μg mL−1, the GMI ratio drops by 8.53 % at a frequency of 1.4 MHz. In other word: almost 90 Dynabeads can be detected. We believe that this novel scheme has a large potential in high-sensitivity and miniaturized immunoassays.

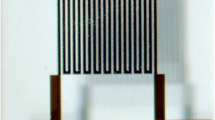
The GMI biosensing system is established for ultrasensitive detection of Dynabeads protein A. The rectangle nano-Au film is used for immobilization of the Dynabeads protein A. The longitudinal external field (He) is generated by a DC field source (0–125 Oe). The GMI biosensor is driven by AC with an amplitude of 10 mA (0.1–5 MHz).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guo SS, Deng YL, Zhao LB, Chan HLW, Zhao XZ (2008) Effect of patterned micro-magnets on superparamagnetic beads in microchannels. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:105008
Tang Z, Graefe K, March C, Karnes HT (2004) Magnetic separation immunoassay for digoxin in plasma with flow injection fluorescence detection. Microchim Acta 144:1–7
Li YP (2012) Chemiluminescent determination of the activity of caspase-3 using a specific peptide substrate and magnetic beads. Microchim Acta 177:443–447
Wang XF, Zhao Q (2012) A fluorescent sandwich assay for thrombin using aptamer modified magnetic beads and quantum dots. Microchim Acta 178:349–355
Pividor MI, Alegret S (2010) Micro and nanoparticles in biosensing systems for food safety and environmental monitoring. An example of converging technologies. Microchim Acta 170:227–242
Fan AP, Lau CW, Lu JZ (2005) Magnetic bead-based chemiluminescent metal immunoassay with a colloidal gold label. Anal Chem 77:3238–3242
Chen L, Bao CC, Yang H, Lei C, Zhou Y, Cui DX (2011) A prototype of giant magnetoimpedance-based biosensing system for targeted detection of gastric cancer cell. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3246–3253
Yang H, Chen L, Lei C, Zhang J, Li D, Zhou ZM, Bao CC, Hu HY, Chen X, Cui F, Zhang SX, Zhou Y, Cui DX (2010) Giant magnetoimpedance-based microchannel system for quick and parallel genotyping of human papilloma virus type 16/18. Appl Phys Lett 97:043702
Neurauter AA, Bonyhadi M, Lien E, Nokleby L, Ruud E, Camacho S, Aarvak T (2007) Cell isolation and expansion using dynabeads ((R)). Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 106:41–73
Graille M, Stura EA, Corper AL, Sutton BJ, Taussig MJ, Charbonnier JB, Silverman GJ (2000) Crystal structure of a Staphylococcus aureus protein A domain complexed with the Fab fragment of a human IgM antibody: structural basis for recognition of B-cell receptors and superantigen activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97:5399–5404
Yang GC, Gallo GR (1990) Protein A-gold immunoelectron microscopic study of amyloid fibrils, granular deposits, and fibrillar luminal aggregates in renal amyloidosis. Am J Pathol 137:1223
Ghitescu L, Bendayan M (1990) Immunolabelling efficiency of protein A-gold complexes. J Histochem Cytochem 38:1523–1530
Idusogie EE, Presta LG, Gazzano-Santoro H, Totpal K, Wong PY, Ultsch M, Meng YG, Mulkerrin MG (2000) Mapping of the C1q binding site on rituxan, a chimeric antibody with a human IgG1 Fc. J Immunol 164:4178–4184
Wilson R (2008) The use of gold nanoparticles in diagnostics and detection. Chem Soc Rev 37:2028–2045
Panina LV, Mohri K (2000) Magneto-impedance in multilayer films. Sens Actuators A 81:71–77
Meydan T (1994) Application of amorphous materials to sensors. J Magn Magn Mater 133:525–532
Panina LV, Mohri K (1994) Magneto–impedance effect in amorphous wires. Appl Phys Lett 65:1189
Li XP, Zhao ZJ, Chua C, Seet HL, Lu L (2003) Enhancement of giant magnetoimpedance effect of electroplated NiFe/Cu composite wires by dc Joule annealing. J Appl Phys 94:7626
Sinnecker JP, Knobel M, Pirota KR, Garcia JM, Asenjo A, Vazquez M (2000) Frequency dependence of the magnetoimpedance in amorphous CoP electrodeposited layers. J Appl Phys 87:4825
Atalay FE, Kaya H, Atalay S (2006) Magnetoimpedance effect in electroplated NiFeRu/Cu wire. J Phys D Appl Phys 39:431
Morikawa T, Nishibe Y, Yamadera H, Nonomura Y, Takeuchi M, Sakata J (1996) Enhancement of giant magneto-impedance in layered film by insulator separation. IEEE Trans Magn 32:4965
Zhou Y, Yu JQ, Zhao XL, Cai BC (2001) Giant magnetoimpedance in layered FeSiB/Cu/FeSiB films. J Appl Phys 89:1816–1819
Makhnovskiy DP, Panina LV, Fry N, Mapps DJ (2004) Magneto-impedance in NiFe/Au/NiFe sandwich films with different types of anisotropy. J Magn Magn Mater 1866:272–276
Makhotkin VE, Shurukhin BP, Lopatin VA, Marchukov PY, Levin YK (1991) Magnetic field sensors based on amorphous ribbons. Sens Acta A 27:759–762
Phan MH, Peng HX, Wisnom MR, Yu SC, Nghi NH, Kim CG (2006) Effect of annealing temperature on permeability and giant magneto-impedance of Fe-based amorphous ribbon. Sens Acta A 129:62–65
Alves F, Rached LA, Moutoussamy J, Coillot C (2008) Trilayer GMI sensors based on fast stress-annealing of FeSiBCuNb ribbons. Sens Acta A 142:459–463
Kurlyandskaya GV, Sanchez ML, Hernando B, Prida VM, Gorria P, Tejedor M (2003) Giant-magnetoimpedance-based sensitive element as a model for biosensors. Appl Phys Lett 82:3053
Chiriac H, Tibu M, Moga A, Herea D (2005) Magnetic GMI sensor for detection of biomolecules. J Magn Magn Mater 293:671–676
Chiriac H, Herea D, Corodeanu S (2007) Microwire array for giant magneto-impedance detection of magnetic particles for biosensor prototype. J Magn Magn Mater 311:425–428
Kurlyandskaya G, Levit V (2005) Magnetic Dynabeads® detection by sensitive element based on giant magnetoimpedance. Biosens Bioelectron 20:1611–1616
Kumar A, Mohapatra S, Fal-Miyar V, Cerdeira A, Garcia J, Srikanth H, Gass J, Kurlyandskaya G (2007) Magnetoimpedance biosensor for Fe3O4 nanoparticle intracellular uptake evaluation. Appl Phys Lett 91:143902
Béguin FB, Nabily S, Gieraltowski J, Turzo A, Querellou S, Salaun PY (2009) Cytotoxicity and GMI bio-sensor detection of maghemite nanoparticles internalized into cells. J Magn Magn Mater 321:192–197
Ludwig F, Mäuselein S, Heim E, Schilling M (2005) Magnetorelaxometry of magnetic nanoparticles in magnetically unshielded environment utilizing a differential fluxgate arrangement. Rev Sci Instrum 76:106102
Ludwig F, Heim E, Mäuselein S, Eberbeck D, Schilling M (2005) Magnetorelaxometry of magnetic nanoparticles with fluxgate magnetometers for the analysis of biological targets. J Magn Magn Mater 293:690–695
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61074168 and No.61273065),The National Science and Technology Support Program (2012BAK08B05), Basic Research Program of Science & Technology Committee of Shanghai (No. 09JC1408600), The Analytical and Testing Center in Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and The National Key Laboratory Research Found (No. 9140C790403110C7905).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Zhou, Y., Lei, C. et al. Ultrasensitive detection of Dynabeads protein A using the giant magnetoimpedance effect. Microchim Acta 180, 1211–1216 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1016-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1016-5