Abstract
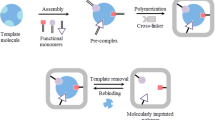
We have prepared a hydrophilic molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) for the hydrophobic compound bisphenol A (BPA) in aqueous solution using 3-acrylamido-N,N,N-trimethylpropan-1-aminium chloride (AMTC) as the functional monomer. Under redox-polymerization conditions, BPA forms an ion-pair with AMTC, which was confirmed by 1H-NMR titration. The imprinting effect in aqueous solution was evaluated by comparison of this material with the corresponding non-imprinted polymer (NIP) and with a control polymer (CP) bearing no AMTC. The MIP showed the highest activity among the three polymers, and the imprinting factors as calculated from the amount of BPA bound to the MIP divided by the amounts bound to NIP and CP, respectively, are 1.8 and 6.0. The MIP was selective for BPA in aqueous solution, while structurally related compounds are not recognized. Such a selectivity for a hydrophobic compound is rarely observed in aqueous medium because non-specific binding of BPA inevitably leads to hydrophobic interaction.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hengstler JG, Foth H, Gebel T, Kramer PJ, Lilienblum W, Schweinfurth H, Völkel W, Wollin KM, Gundert-Remy U (2011) Critical evaluation of key evidence on the human health hazard s of exposure to bisphenol A. Crit Rev Toxicol 41:263
Schecter A, Malik N, Haffner D, Smith S, Harris TR, Paepke O, Birnbaum L (2010) Bisphenol A (BPA) in U.S. Food. Environ Sci Technol 44:9425
Kandaraki E, Chatzigeorgiou A, Livadas S, Palioura E, Economou F, Koutsilieris M, Palimeri S, Panidis D, Diamanti-Kandarakis E (2011) Endocrine disruptors and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): elevated serum levels of Bisphenol A in women with PCOS. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(3):E480–E484. doi:10.1210/jc.2010-1658
López-Darias J, Pino V, Ayala JH, Afonso AM (2011) In-situ ionic liquid-dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method to determine endocrine disrupting phenols in seawaters and industrial effluents. Microchimica Acta 174:213
Ferrer E, Santoni E, Vittori S, Font G, Mañes J, Sagratini G (2011) Simultaneous determination of bisphenol A, octylphenol, and nonylphenol by pressurised liquid extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in powdered milk and infant formulas. Food Chem 126:360
Fontana AR, Muñoz de Toro MN, Altamirano JC (2011) One-step derivatization and preconcentration microextraction technique for determination of Bisphenol A in beverage samples by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 59:3559
Ballesteros-Gómez A, Rubio S, Pérez-Bendito D (2009) Analytical methods for the determination of bisphenol A in food. J Chromatogr A 1216:449
Kavlock RJ (1999) Overview of endocrine disruptor research activity in the United States. Chemosphere 39(8):1227
Marchesini GR, Meulenberg E, Haasnoot W, Irth H (2005) Biosensor immunoassays for the detection of bisphenol A. Anal Chim Acta 528:37–45
Sellergren B (2000) Molecularly imprinted polymers: man-made mimics of antibodies and their aplications in analytical chemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Komiyama M, Takeuchi T, Mukawa T, Asanuma H (2004) Molecular imprinting. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
Takeuchi T, Hishiya T (2008) Molecular imprinting of proteins emerging as a tool for protein recognition. Org Biomol Chem 6:2459
Araki K, Goto M, Furusaki S (2002) Enantioselective polymer prepared by surface imprinting technique using a bifunctional molecule. Anal Chim Acta 469:173
Ikegami T, Mukawa T, Nariai H, Takeuchi T (2004) Bisphenol A-recognition polymers prepared by covalent molecular imprinting. Anal Chim Acta 504:131
Sanbe H, Haginaka J (2003) Uniformly sized molecularly imprinted polymers for bisphenol A and beta-estradiol: retention and molecular recognition properties in hydro-organic mobile phases. J Pharm Biomed Anal 30:1835
Sasaki S, Ooya T, Takeuchi T (2010) Highly selective bisphenol A-imprinted polymers prepared by atom transfer radical polymerization. Polym Chem 1:1684
Ren Y, Ma W, Ma J, Wen Q, Wang J, Zhao F (2012) Synthesis and properties of bisphenol A molecular imprinted particle for selective recognition of BPA from water. J Colloid Interface Sci 367:355
Hirose K (2001) A practical guide for the determination of binding constants. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 39:193
Ito K, Nagase K, Morohashi N, Ohba Y (2005) Interaction between quaternary ammonium ions and dipeptides: positive anion allosteric effect. Chem Pharm Bull 53:90
Staples CA, Dome PB, Klecka GM, Oblock ST, Harris LR (1998) A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of bisphenol A. Chemosphere 36(10):2149–2173
Umpleby RJ, Baxter SC, Chen Y, Shah RN, Shimizu KD (2001) Characterization of molecularly imprinted polymers with the Langmuir-Freundlich Isotherm. Anal Chem 73(19):4584–4591
Acknowledgments
N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]acrylamide methyl chloride quaternary salt and N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-acrylamide were kindly provided by Kohjin Co. Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 84 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, N., Ooya, T. & Toshifumi, T. Hydrophilic molecularly imprinted polymers for bisphenol A prepared in aqueous solution. Microchim Acta 180, 1387–1392 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-0996-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-0996-5