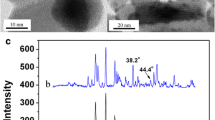
Abstract
We demonstrate that base mismatches of caspase-3 DNA sequences can be detected by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) following signal amplification by polymerase from Thermus aquaticus (Taq). The concentration of magnesium ions and the respective dNTPs for polymerase binding to the oligonucleotides on the sensing surface were optimized. Taq polymerase binds to double-stranded DNA that is self-assembled on the gold surface of the biosensor to induce an SPR signal. Experiments are presented on the effect of Mg(II) and dNTP concentrations on the activity of the polymerase on the sensing surface. The detection limits are 50 pM, 0.1 nM, 0.7 nM, 7 nM, and 20 nM for correctly matched, single-base mismatched, two-base mismatched, three-base mismatched and four-base mismatched DNA of caspase-3, respectively. This is attributed to the optimized experimental conditions, with samples containing 2 μM of Mg(II) and 0.3 mM of dNTP.

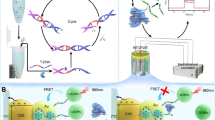
The process of detecting mismatched caspase-3 DNA oligonucleotides with SPR biosensor







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kothakota S, Azuma T (1997) Caspase-3–generated fragment of gelsolin: effector of morphological change in apoptosis. Science 278:294–298
Cragg GM, Grothaus PG, Newman DJ (2009) Impact of natural products on developing new anti-cancer agents. Chem Rev 109:3012–3043
Zhou FF, Da X, Wu SN et al (2010) Intravital imaging of tumor apoptosis with FRET probes during tumor therapy. Mol Imaging Biol 12:63–70
Benyahia S, Benayache S, Benayache F et al (2004) Isolation from eucalyptus occidentalis and identification of a new kaempferol derivative that induces apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia cells. J Nat Prod 67:527–531
Liu WK, Cheung FW, Che CT (2008) Stellettin A induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in HL-60 human leukemia and LNCaP prostate cancer cell lines. J Nat Prod 69:934–937
Chen CY, Chen CH, Lo YC et al (2008) Anticancer activity of isoobtusilactone A from Cinnamomum kotoense: involvement of apoptosis, cell-cycle dysregulation, mitochondria regulation, and reactive oxygen species. J Nat Prod 71:933–940
Lakhani SA, Kuid AM, Porter GA et al (2006) Caspases 3 and 7: key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science 311:847–851
Yakovlev AG, Ota K, Wang GP et al (2001) Differential expression of apoptotic protease-activating factor-1 and caspase-3 genes and susceptibility to apoptosis during brain development and after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci 21:7439–7446
Talanian RV, Brady KD, Cryns VL (2000) Caspases as targets for anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic drug discovery. J Med Chem 43:3351–3371
Kim K, Lee M, Park H et al (2006) Cell-permeable and biocompatible polymeric nanoparticles for apoptosis imaging. J Am Chem Soc 128:3490–3491
Lecaruyer P, Mannelli I, Courtois V et al (2006) Surface plasmon resonance imaging as a multidimensional surface characterization instrument –Application to biochip genotyping. Anal Chim Acta 573(574):333–340
Tsoi PY, Yang MS (2004) Surface plasmon resonance study of the molecular recognition between polymerase and DNA containing various mismatches and conformational changes of DNA-protein complexes. Biosens Bioelectron 19:1209–1218
Sakao Y, Nakamura F, Ueno N et al (2005) Hybridization of oligonucleotide by using DNA self-assembled monolayer. Colloid Surface B 40:149–152
Homola J, Wolfbeis OS (2006) Surface plasmon resonance based sensors. In: Homola J, Piliarik M (eds) Surface plasmon resonance sensors. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 45–68
Hasenbank MS, Fu E, Yager P (2006) Lateral spread of an amplification signal using an enzymatic system on a conductive surface. Langmuir 22:7451–7453
Lee HJ, Wark AW, Goodrich TT et al (2005) Surface enzyme kinetics for biopolymer microarrays: a combination of langmuir and michaelis-menten concepts. Langmuir 21:4050–4057
Gorodkiewicz E, Ostrowska H, Sankiewicz A (2011) SPR imaging biosensor for the 20S proteasome: sensor development and application to measurement of proteasomes in human blood plasma. Microchim Acta 175:177–184
Fujii E, Koike T, Nakamura K et al (2002) Application of an absorption-based surface plasmon resonance principle to the development of SPR ammonium ion and enzyme sensors. Anal Chem 74:6106–6110
He YH, Nie F (2011) Chemiluminescence assay for angiogenin using a signal amplification technology based on the cleavage of nicking endonucleases. Microchim Acta 174:375–382
Nakatani K, Sando S, Saito I (2001) Scanning of guanine–guanine mismatches in DNA by synthetic ligands using surface plasmon resonance. Nat Biotech 19:51–55
Hagihara S, Kumasawa H, Goto Y et al (2004) Detection of guanine- adenine mismatches by surface plasmon resonance sensor carrying naphthyridine- azaquinolone hybrid on the surface. Nucleic Acids Res 32:278–286
Huang MM, Arnheim N, Goodman MF (1992) Extension of base mispairs by taq DNA polymerase: implications for single nucleotide discrimination in PCR. Nucl Acids Res 20:4567–4573
Lee W, Lee DB, Oh BK et al (2004) Nanoscale fabrication of protein A on self-assembled monolayer and its application to surface plasmon resonance immunosensor. Enzyme Microb Tech 35:678–682
Singh A, Snyder S, Lee L et al (2010) Effect of oligonucleotide length on the assembly of DNA materials: molecular dynamics simulations of layer-by-layer DNA films. Langmuir 26:17339–17347
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31070772), Doctoral Program of Higher Education(200901011110136), Science and Technology Programs of Zhejiang Province (2011 C37029) and Science and Technology Programs of Suzhou (ZXG0920).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1475 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Mu, Y., Zhou, C. et al. Detection of mismatched caspase-3 DNA oligonucleotides with an SPR biosensor following amplification by Taq polymerase. Microchim Acta 177, 435–441 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0799-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0799-0