Abstract
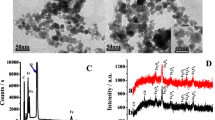
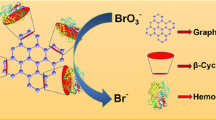
We have constructed a new electrochemical biosensor by immobilization of hemoglobin (Hb) and ZnWO4 nanorods in a thin film of chitosan (CTS) on the surface of carbon ionic liquid electrode. UV–vis and FT-IR spectra reveal that Hb remains in its native conformation in the film. The modified electrode was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry. A pair of well-defined redox peaks appears which indicates direct electron transfer from the electrode. The presence of CTS also warrants biocompatibility. The electron transfer coefficient and the apparent heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant were calculated to be 0.35 and 0.757 s−1, respectively. The modified electrode displays good electrocatalytic activity for the reduction of trichloroacetic acid with the detection limit of 0.613 mmol L−1 (3σ). The results extend the protein electrochemistry based on the use of ZnWO4 nanorods.

A ZnWO4 nanorods and hemoglobin nanocomposite material modified carbon ionic liquid electrode was used as the platform for the construction of an electrochemical hemoglobin biosensor.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rusling JF (1998) Enzyme bioelectrochemistry in cast biomembrane-like films. Acc Chem Res 31:363–369
Armstrong FA, Wilson GS (2000) Recent developments in faradaic bioelectrochemistry. Electrochim Acta 45:2623–2645
Xu J, Liu CH, Wu ZF (2011) Direct electrochemistry and enhanced electrocatalytic activity of hemoglobin entrapped in graphene and ZnO nanosphere composite film. Microchim Acta 172:425–430
Salimi A, Noorbakhsh A, Ghadermarz M (2005) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalytic activity of catalase incorporated onto multiwall carbon nanotubes-modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal Biochem 344:16–24
Lu XB, Hu JQ, Yao X, Wang ZP, Li JH (2006) Composite system based on chitosan and room-temperature ionic liquid: direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin. Biomacromolecules 7:975–980
Xu J, Liu CH, Teng YL (2010) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hydrogen peroxide using hemoglobin immobilized in hollow zirconium dioxide spheres and sodium alginate films. Microchim Acta 169:181–186
Liu HT, Liu Y, Li JH (2010) Ionic liquids in surface electrochemistry. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:1685–1697
Wasserscheid P, Welton T (2003) Ionic liquids in synthesis. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Liu J, Jiang G, Chi Y, Cai Y, Zhou Q, Hu J (2003) Use of ionic liquids for liquid-phase microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Anal Chem 75:5870–5876
Muhammad JAS, Angel AJT (2011) Application of ionic liquids in electrochemical sensing systems. Biosens Bioelectron 26:1775–1787
Opallo M, Lesniewski A (2011) A review on electrodes modified with ionic liquids. J Electroanal Chem 656:2–16
Yu P, Lin Y, Xiang L, Su L, Zhang J, Mao L (2005) Molecular films of water-miscible ionic liquids formed on glassy carbon electrodes: characterization and electrochemical applications. Langmuir 21:9000–9006
Wei W, Jin HH, Zhao GC (2009) A reagentless nitrite biosensor based on direct electron transfer of hemoglobin on a room temperature ionic liquid/carbon nanotube-modified electrode. Microchim Acta 164:167–171
Maleki N, Safavi A, Tajabadi F (2006) High-performance carbon composite electrode based on an ionic liquid as a binder. Anal Chem 78:3820–3826
Sun W, Gao RF, Jiao K (2007) Electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin in nafion/nano-CaCO3 film on a new ionic liquid BPPF6 modified carbon paste electrode. J Phys Chem B 111:4560–4567
Zhu ZH, Li X, Zeng Y, Sun W, Zhu WM, Huang XT (2011) Application of cobalt oxide nanoflower for direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin with ionic liquid as enhancer. J Phys Chem C 115(12547):12553
Li XQ, Wang Y, Sun XY, Zhan TR, Sun W (2010) Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin entrapped in dextran film on carbon ionic liquid electrode. J Chem Sci 122:271–278
Yoon SH, Kim DW, Cho SY, Hong KS (2006) Investigation of the relations between structure and microwave dielectric properties of divalent metal tungstate compounds. J Eur Ceram Soc 26:2051–2054
Daturi M, Busca G, Borel MM, Leclaire A, Piaggio P (1997) Vibrational and XRD study of the system CdWO4-CdMoO4. J Phys Chem B 101:4358–4369
Lin J, Lin J, Zhu YF (2007) Controlled synthesis of the ZnWO4 nanostructure and effects on the photocatalytic performance. Inorg Chem 46:8372–8378
Li D, Shi R, Pan CS, Zhu YF, Zhao HJ (2011) Influence of ZnWO4 nanorod aspect ratio on the photocatalytic activity. CrystEngComm 13:4695–4700
Liu B, Yu SH, Li LJ, Zhang F, Zhang Q, Yoshimura M, Shen PK (2004) Nanorod-direct oriented attachment growth and promoted crystallization processes evidenced in case of ZnWO4. J Phys Chem B 108:2788–2792
Song XC, Yang E, Ma R, Chen HF, Ye ZL, Luo M (2009) Hydrothermal preparation and photoluminescence of bundle-like structure of ZnWO4 nanorods. Appl Phys A 94:185–188
Bi J, Wu L, Li Z, Ding Z, Wang X, Fu XJ (2009) A facile microwave solvothermal process to synthesize ZnWO4 nanoparticles. Alloy Comp 480:684–688
Zhao W, Xong X, Chen G, Sun SJ (2009) One-step template-free synthesis of ZnWO4 hollow clusters. Mater Sci 44:3082–3087
Zhao X, Liu HJ, Qu JH (2010) Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of organic contaminant at hybrid BDD-ZnWO4 electrode. Catal Comm 12:76–79
Shim HW, Cho IS, Hong KS, Lim AH, Kim DW (2011) Wolframite-type ZnWO4 nanorods as new anodes for Li-ion batteries. J Phys Chem C 115:16228–16233
Lin MS, Leu HJ (2005) A Fe3O4-based chemical sensor for cathodic determination of hydrogen peroxide. Electroanalysis 17:2068–2073
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (1980) Electrochemical methods. Wiley, New York
Laviron E (1979) General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J Electroanal Chem 101:19–28
Gu HY, Yu AM, Chen HY (2001) Direct electron transfer and characterization of hemoglobin immobilized on a Au colloid-cysteamine-modified gold electrode. J Electroanal Chem 516:119–126
Sun W, Wang D, Zhai Z, Gao R, Jiao K (2009) Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin immobilized in the sodium alginate and SiO2 nanoparticles bionanocomposite film on a carbon ionic liquid electrode. J Iran Chem Soc 6:412–419
Li Q, Luo G, Feng J (2001) Direct electron transfer for heme proteins assembled on nanocrystalline TiO2 film. Electroanalysis 13:359–363
Ma X, Liu XJ, Xiao H, Li GX (2005) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin in poly-3-hydroxybutyrate membrane. Biosens Bioelectron 20:1836–1842
Kamin RA, Willson GS (1980) Rotating ring-disk enzyme electrode for biocatalysis kinetic studies and characterization of the immobilized enzyme layer. Anal Chem 52:1198–1205
Wang SF, Chen T, Zhang ZL, Shen XC, Lu ZX, Pang DW, Wong KY (2005) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of heme proteins entrapped in agarose hydrogel films in room-temperature ionic liquids. Langmuir 21:9260–9266
Sun W, Wang DD, Li GC, Zhai ZQ, Zhao RJ, Jiao K (2008) Direct electron transfer of hemoglobin in a CdS nanorods and Nafion composite film on carbon ionic liquid electrode. Electrochim Acta 53:8217–8221
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the financial support of the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (2009GZC0031) and the S&T plan projects of Jiangxi Provincial Education Department (GJJ10590).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 101 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruan, C., Sun, Z., Liu, J. et al. Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin on an ionic liquid carbon electrode modified with zinc tungstate nanorods. Microchim Acta 177, 457–463 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0796-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0796-3