Abstract
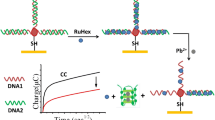
A DNA biosensor was constructed by immobilizing a 20-mer oligonucleotide probe and hybridizing it with its complementary oligomer on the surface of a glassy carbon electrode modified with gold nanoparticles. The properties of the biosensor and its capability of recognizing its complementary sequence were studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The oxidative stress caused by cadmium ions can be monitored by differential pulse voltammetry using the cobalt(III)tris(1,10-phenanthroline) complex and methylene blue as electrochemical indicators. The biosensor is capable of indicating damage caused by Cd(II) ions in pH 6.0 solution. The results showed that the biosensor can be used for rapid screening for DNA damage.

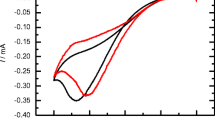
DPV of DNA biosensors before (a, c) and after hybridization (b, d) at 1.0 ×10–7 mol·L-1target DNA concentration, (a) probe DNA/Au/GCE and (b) dsDNA/Au/GCE (c) probe DNA/GCE, (d) dsDNA/GCE





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manca D, Richard AC, Trottier B, Chevalier G (1991) Studies on lipid peroxidation in rats tissues following administration of cadmium chloride. Toxicology 67:303
Bertin G, Averbeck D (2006) Cadmium: cellular effects, modifications of biomolecules, modulation of DNA repair and genotoxic consequences (a review). Biochimie 88:1549
Galazyn-Sidorczuk M, Brzȯska MM, Jurczuk M, Moniuszko-Jakoniuk J (2009) Oxidative damage to proteins and DNA in rats exposed to cadmium and/or ethanol. Chem Biol Interact 180:31
Lin AJ, Zhang XH, Chen MM, Cao Q (2007) Oxidative stress and DNA damages induced by cadmium accumulation. J Environ Sci 19:596
Valko CJ M, Rhodes J, Moncol IM, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160:1
Dalle-Donne I, Rossi R, Giustarini D, Milzani A, Colombo R (2003) Protein carbonyl groups as biomarkers of oxidative stress. Clin Chim Acta 329:23
Cooke MS, Olinski R, Evans MD (2006) Does measurement of oxidative damage to DNA have clinical significance. Clin Chim Acta 365:30
Dotan Y, Lichtenberg D, Pinchuk I (2004) Lipid peroxidation cannot be used as universal criterion of oxidative stress. Prog Lipid Res 43:200
Weinfel M, Liuzzi M, Paterson MC (1990) Response of phage T4 polynucleotide kinase toward dinucleotides containing apurinic sites: design of a 32 P-postlabeling assay for apurinic sites in DNA. Biochemistry 29:1737
Wild CP (1990) Antibodies to DNA alkylation adducts as analytical tools in chemical carcinogenesis. Mutat Res 233:219
Park JW, Ames BN (1988) 7-Methylguanine adducts in DNA are normally present at high levels and increase on aging: analysis by HPLC with electrochemical detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci 85:7467
Angelis KJ, McGuffie M, Menke M, Schubert I (2000) Adaptation to alkylation damage in DNA measured by the comet assay. Environ Mol Mutagen 36:146
Pacey GE, Puckett SD, Cheng L, Khatib-Shahidi S, Cox JA (2005) Detection of DNA damaging agents using layer-by-layer assembly. Anal Chim Acta 533:135
Liang M, Guo LH (2007) Photoelectrochemical DNA sensor for the rapid detection of DNA damage induced by styrene oxide and the fenton reaction. Environ Sci Technol 41:658
Wang J (2002) Electrochemical nucleic acid biosensors. Anal Chim Acta 469:63
Paleček E (2002) Past, present and future of nucleic acids electrochemistry. Talanta 56:809
Qiu YY, Fan H, Liu X, Ai SY, Tang TT, Han RX (2010) Electrochemical detection of DNA damage induced by in situ generated bisphenol A radicals through electro-oxidation. Microchim Acta 171:363
Qian P, Ai SY, Yin HS, Li JH (2010) Evaluation of DNA damage and antioxidant capacity of sericin by a DNA electrochemical biosensor based on dendrimer-encapsulated Au-Pd/chitosan composite. Microchim Acta 168:347
Ting BP, Zhang J, Gao Z, Ying JY (2009) A DNA biosensor based on the detection of doxorubicin-conjugated Ag nanoparticle labels using solid-state voltammetry. Biosens bioelectron 25:282
Gao HW, Zhong JH, Qin P, Lin C, Sun W (2009) Microplate electrochemical DNA detection for phosphinothricin acetyltransferase gene sequence with cadmium sulfide nanoparticles. Microchem J 93:78
Labuda J, Ovádeková R, Galandová J (2009) DNA-based biosensor for the detection of strong damage to DNA by the quinazoline derivative as a potential anticancer agent. Microchim Acta 164:371
Kerman K, Meric B, Dzkan D, Kara P, Erdem A, Ozsoz M (2001) Electrochemical DNA biosensor for the determination of benzo[a]pyrene–DNA adducts. Anal Chim Acta 450:45
Lopez E, Arce C, Oset-Gasque MJ (2006) Cadmium induces reactive oxygen species generation and lipid peroxidation in cortical neurons in culture. Free Radic Biol Med 40:940
Pathak N, Khandelwal S (2006) Oxidative stress and apoptotic changes in murine splenocytes exposed to cadmium. Toxicology 220:26
Huff J, Lunn RM, Waalkes MP, Tomatis L, Infante PF (2007) Cadmium-induced cancers in animals and in humans. Int J Occup Environ Health 13:202
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160:1
Yoshioka N, Nakashima H, Hosoda K, Eitaki Y, Shimada N, Omae K (2008) Urinary excretion of an oxidative stress marker, 8-hydroxyguanine (8-OH-Gua), among nickel-cadmium battery workers. J Occup Health 50:229
Yang WR, Ozsoz M, Hibbert DB, Gooding JJ (2002) Evidence for the direct interaction between methylene blue and guanine bases using DNA-modified carbon paste electrodes. Electroanalysis 14:1299
Wang XL, Jiao K (2010) Sensitively electrochemical detection of the DNA damage in situ by electro-Fenton reaction based on Fe@Fe2O3 core-shell nanonecklace and multi-walled carbon nanotube composite. Anal Chim Acta 664:34
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20775002) for financial support. The work was supported by the Program for Innovative Research Team in Anhui Normal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Nyquist diagrams recorded at the probe DNA/Au/GCE (a) and after hybridization reaction with different concentrations of sequence- specific DNA of PAT gene: (b) 1.0 × 10−12 mol.L−1, (c) 1.0 × 10−11 mol.L−1, (d) 1.0 × 10−10 mol.L−1, (e) 1.0 × 10−9 mol.L−1, (f) 1.0 × 10−8 mol.L−1, (g) 1.0 × 10−7 mol.L−1 and (h) 1.0 × 10−6 mol.L−1. (DOC 554 kb)
Fig. S2
Nyquist diagrams recorded of dsDNA/nano- Au/GCE in 5.0 mmol.L−1 pH 6.0 Tris–HCl buffer solution after damaged by 0.02 mmol.L−1 Cd2+ for different time: 0 min, 10 min, 20 min, 30 min,50 min (a→e). (DOC 475 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Dai, P. & Yang, Z. Sensitive DNA-hybridization biosensors based on gold nanoparticles for testing DNA damage by Cd(II) ions. Microchim Acta 173, 347–352 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0558-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0558-7