Abstract
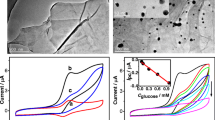
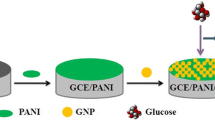
The one-step synthesis is reported of a nanofilm composed of iron oxide and gold nanoparticles in a chitosan matrix that can act as a novel matrix for the immobilization of glucose oxidase (GOx) to fabricate a glucose biosensor. The use for the composite film strongly increased the effective electrode surface for loading of GOx. The size and shape of the iron oxide nanoparticles were examined by transmission electron micrograph. Direct electron transfer and electrocatalysis by GOx was investigated via cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry. Under optimized conditions, the biosensor has a response time of 6 s and a linear response in the range between 3 μM and 0.57 mM of glucose, with a detection limit of 1.2 μM at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3. This novel and disposable mediatorless glucose biosensor may form the basis for a future mass-produced glucose biosensor.

In this paper, based on the direct electrochemistry of redox enzyme, we try to integrate the excellent properties of iron oxide-gold nanoparticle-chitosan composite film with the advantages of one-step electrodeposition to fabricate a sensitive and stable glucose biosensor.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang XJ, Ju HX, Wang J (2008) Electrochemical sensors, biosensors and their biomedical applications. Elsevier, New York
Heller A (1990) The role of oxygen in photooxidation of organic molecules on semiconductor particles. Acc Chem Res 23:128
Willner I, Katz E (2000) Integration of layered redox-proteins and conductive supports for bioelectronic applications. Angew Chem Int Ed 39:1180
Lojou É, Bianco P (2000) Membrane electrodes can modulate the electrochemical response of redox proteins-direct electrochemistry of cytochrome c. J Electroanal Chem 485:71
Gu H, Yu A, Chen H (2001) Direct electron transfer and characterization of hemoglobin immobilized on a gold colloid-cysteamine-modified gold electrode. J Electroanal Chem 516:119
Wang Q, Lu G, Yang B (2004) Myoglobin/sol-gel film modified electrode: direct electrochemistry and electrochemical catalysis. Langmuir 20:1342
Yang J, Zhang RY, Xu Y, He PG, Fang YZ (2008) Direct electrochemistry study of GOx on Pt nanoparticle-modified aligned carbon nanotubes electrode by the assistance of CS-CdS and its biosensoring for glucose. Electrochem Commun 10:1889
Liu Q, Lu XB, Li J, Yao X, Li JH (2007) Direct electrochemistry of GOx and electrochemical biosensing of glucose on quantum dots/carbon nanotubes electrodes. Biosens Bioelectron 22:3203
Salimi A, Roushani M (2005) Nonenzymatic glucose detection free of ascorbic acid interference using nickel powder and nafion sol-gel dispersed renewable carbon ceramic electrode. Electrochem Commun 7:879
Wang Y, Wei WZ, Liu XY, Zeng XD (2009) GNPs/CNTs/CS-based glucose biosensor prepared by a layer-by-layer technique. Mater Sci Eng C 29:50
Lin JH, He CY, Zhao Y, Zhang SS (2009) One-step synthesis of silver nanoparticles/CNTs/CS film and its application in glucose biosensor. Sens Actuators B 137:768
Xue MH, Xu Q, Zhou M, Zhu JJ (2006) In situ immobilization of GOx in CS-nanoparticle hybrid film on Prussian Blue modified for high sensitivity glucose detection. Electrochem Commun 8:1468
Luo XL, Xu JJ, Du Y, Chen HY (2004) A glucose biosensor based on CS-GOx-GNPs biocomposite formed by one-step electrodeposition. Anal Biochem 334:284
Wang KQ, Yang H, Zhu L, Liao JH, Lu TH, Xing W, Xing SY, Lv Q (2009) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of GOx immobilized on glassy carbon electrode modified by Nafion and ordered mesoporous silica-SBA-15. J Mol Catal B Enzym 58:194
Kim DK, Mikhaylova M, Zhang Y, Muhammed M (2003) Protective coating of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem Mater 15:1617
Zhang YJ, Shen YF, Han DX, Wang ZJ, Song JX, Li F, Niu L (2007) CNTs and GOx bionanocomposite bridged by ionic liquid-like unit: Preparation and electrochemical properties. Biosens Bioelectron 23:438
Kaushik A, Khan R, Solanki RP, Pandey P, Alam J, Ahmad S, Malhotra BD (2008) Fe3O4 nanoparticles-CS composite based glucose biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 24:676
Wang Y, Wei WZ, Zeng JX, Liu XY, Zeng XD (2008) Fabrication of a Cu/CS/CNTs-modified glassy carbon electrode for electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Microchim Acta 160:253
Qiu JD, Xie HY, Liang RP (2008) Preparation of porous CS/CNTs film modified electrode for biosensor application. Microchim Acta 162:57
Zeng JX, Wei WZ, Liu XY, Wang Y, Luo GM (2008) A simple method to fabricate a Prussian Blue nanoparticles/CNTs/poly(1,2-diaminobenzene) based glucose biosensor. Microchim Acta 160:261
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the NNSF of China (20675064), the Ministry of Education of China (Project 708073), the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing City (CSTC-2009BA1003) and High Technology Project Foundation of Southwest University (XSGX02), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 392 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Yuan, R. & Chai, Y. Simple construction of an enzymatic glucose biosensor based on a nanocomposite film prepared in one step from iron oxide, gold nanoparticles, and chitosan. Microchim Acta 173, 369–374 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0544-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0544-0