Abstract
The first multisyringe-based low-pressure ion chromatographic method is presented. It is based on the use of short surfactant coated octadecyl-silica monolithic columns. As a first application, we have determined oxalate in beer and human urine via post-column chemiluminescence detection. Oxalate is separated from the sample matrix in the monolithic column by precise programmable fluid handling, and then detected by reaction with on-line generated tris(2,2′-bipyridyl)ruthenium(III). Column coating, un-coating, ion chromatography and chemiluminescence detection are quickly performed by using a simple low-pressure multi-burette. The factors influencing the separation of oxalate and its subsequent detection, including the column coating with surfactants and its stability have been studied. The chromatographic behavior of the oxalate in presence of potentially interfering species also was assessed. The method has limits of detection and quantification of 0.025 and 0.035 mg L−1, respectively, a relative standard deviation of 3.1% (for 10 consecutive measurements without column re-coating) and a throughput of 48 h−1. The results obtained with real samples were validated by using an enzymatic spectrophotometric test. The method is critically compared to recent methods for the determination of oxalate.

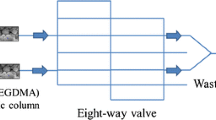
Automated MSFIA system incorporating a C18 monolithic column (MC) coated with CTAB for the separation of oxolate and its post-column chemiluminescence detection




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trojanowicz M (2008) Advances in flow analysis. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Kolev SD, McKelvie ID (2008) Advances in flow injection analysis and related techniques. Elsevier BV, Amsterdam
Armenta S, Garrigues S, de la Guardia M (2008) Green analytical chemistry. Trends Anal Chem 27:497
Maya F, Estela JM, Cerdà V (2009) Multisyringe flow injection technique for development of green spectroscopic analytical methodologies. Spectrosc Lett 42:312
Serra AM, Estela JM, Cerdà V (2009) An MSFIA system for mercury speciation base on an anion-exchange membrane. Talanta 78:790
Gonzalvez A, Armenta S, Cervera ML, de la Guardia M (2010) Non-chromatographic speciation. Trends Anal Chem 29:260
Manera M, Miró M, Estela JM, Cerdà V (2007) Multi-syringe flow injection solid-phase extraction system for on-line simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of nitro-substituted phenol isomers. Anal Chim Acta 582:41
Gomez V, Font J, Callao MP (2007) Sequential injection analysis with second-order treatment for the determination of dyes in the exhaustion process of tanning effluents. Talanta 71:1393
Maya F, Estela JM, Cerdà V (2008) Completely automated system for determining halogenated organic compounds by multisyringe flow injection analysis. Anal Chem 80:5799
Maya F, Estela JM, Cerdà V (2010) Flow analysis techniques as effective tools for the improved environmental analysis of organic compounds expressed as total índices. Talanta 81:1
Peters EC, Petro M, Svec F, Frechet JMJ (1997) Molded rigid polymer monoliths as separation media for capillary electrochromatography. Anal Chem 69:3646
Tanaka N, Kobayashi H, Ishizuka N, Minakuchi H, Nakanishi K, Hosoya K, Ikegami T (2002) Monolithic sílica columns for high-efficiency chromatographic separations. J Chromatogr A 965:35
Satinsky D, Solich P, Chocholous P, Karlicek R (2003) Monolithic columns—a new concept of separation in the sequential injection technique. Anal Chim Acta 499:205
Satinsky D, Huclova J, Solich P, Karlicek R (2003) Reversed-phase porous silica rods, an alternative approach to high-performance liquid chromatographic separation using the sequential injection chromatography technique. J Chromatogr A 1015:239
Fernández M, González-San Miguel HM, Estela JM, Cerdà V (2009) Contribution of multi-commuted flow analysis combined with monolithic columns to low-pressure, high performance chromatography. Trends Anal Chem 28:336
Kika FS (2009) Low pressure separations using automated flow and sequential injectin analysis coupled to monolithic columns. J Chromatogr Sci 47:648
Cerdà V, Estela JM, Forteza R, Cladera A, Becerra E, Altamira P, Sitjar P (1999) Flow techniques in water analysis. Talanta 50:695
Segundo MA, Magalhaes LM (2006) Multisyringe flow injection analysis: state-of-the-art and perspectives. Anal Sci 22:3
González-San Miguel HM, Alpízar-Lorenzo JM, Cerdà-Martín V (2007) Development of a new high performance low pressure chromatographic system using a Multisyringe burette coupled to a chromatographic monolithic column. Talanta 72:296
Miguel HMGS, Alpízar-Lorenzo JM, Cerdà V (2007) Simultaneous determination of β-lactamic antibiotics by a new high-performance low-pressure chromatographic system using a Multisyringe burette coupled to a monolithic column (MSC). Anal Bioanal Chem 387:663
Obando MA, Estela JM, Cerdà V (2008) Multisyringe chromatography (MSC) system for the on-line solid-phase extraction and determination of hydrochlorothiazide and losartan potassium in superficial water, groundwater and wastewater outlet samples. J Pharm Biomed Anal 48:212
Adcock JL, Francis PS, Agg KM, Marshall GD, Barnett NW (2007) A hybrid FIA/HPLC system incorporating monolithic column chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 600:136
Maya F, Estela JM, Cerdà V (2010) Interfacing on-line solid phase extraction with monolithic column Multisyringe chromatography and chemiluminescence detection: An effective tool for fast, sensitive and selective determination of thiazide diuretics. Talanta 80:1333
Victory D, Nesterenko P, Paull B (2004) Low-pressure gradient micro-ion chromatography with ultra-short monolithic anion exchange column. Analyst 129:700
Pelletier S, Lucy CA (2006) Achieving rapid low-pressure ion chromatography separations on short silica-based monolithic columns. J Chromatogr A 1118:12
Barron L, Nesterenko PN, Diamond D, O’Toole M, Tong-Lau K, Paull B (2006) Low pressure ion chromatography with a low cost paired emitter-detector diode based detector for the determination of alkaline earth metals in water samples. Anal Chim Acta 577:32
Paull B, Nesterenko PN (2005) New possibilities in ion chromatography using porous monolithic stationary-phase media. Trends Anal Chem 24:295
Gerardi RD, Barnett NW, Lewis SW (1999) Analytical applications of tris(2, 2´-bipyridyl)ruthenium(III) as a chemiluminescent reagents. Anal Chim Acta 378:1
Gorman BA, Francis PS, Barnett NW (2006) Tris(2, 2´-bipyridyl)ruthenium (II) chemiluminescence. Analyst 131:616
Cat. No. 10755 699 035. Roche Biopharm AG. www.r-biopharm.com
Zuo G, Jiang X, Liu H, Zhang J (2010) A novel urinary oxalate determination method via a catalase model compound with oxalate oxidase. Anal Methods 2:254
Skotty DR, Nieman TA (1995) Determination of oxalate in urine and plasma using reversed-phase ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography with tris(2, 2´-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II)-electrogenerated chemiluminescence detection. J Chromatogr B 665:27
Pérez-Ruiz T, Martínez-Lozano C, Tomás V, Martín J (2004) High-performance liquid chromatographic separation and quantification of citric, lactic, malic, oxalic and tartaric acids using a post-column photochemical reaction and chemiluminescence detection. J Chromatogr A 1026:57
Dionex. Application Note 36. http://www.dionex.com/en-us/webdocs/4126-AN36_V15.pdf
Masar M, Zuborova M, Kaniansky D, Stanislawski B (2003) Determination of oxalate in beer by zone electrophoresis on a chip with conductivity detection. J Sep Sci 26:647
Muñoz JA, Lopez-Mesas M, Valiente M (2010) Development and validation of a simple determination of urine metabolites (oxalate, citrate, uric and creatinine) by capillary zone electrophoresis. Talanta 81:392
Becerra E, Cladera A, Cerdà V (1999) Design of a very versatile software program for automating analytical methods. Lab Rob Autom 11:131
Glenn KM, Lucy CA (2008) Stability of surfactant coated columns for ion chromatography. Analyst 133:1581
Magalhaes LM, Segundo MA, Reis S, Lima JLFC, Estela JM, Cerdà V (2007) Automatic in vitro determination of hypochlorous acid scavenging capacity exploiting Multisyringe flow injection analysis and chemiluminescence. Anal Chem 79:3933
Maya F, Estela JM, Cerdà V (2007) Improving the chemiluminescence-based determination of sulphide in complex environmental samples by using a new, automated multi-syringe flow injection analysis system coupled to a gas diffusion unit. Anal Chim Acta 601:87
Acknowledgements
This work was supported from the “Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia, Gobierno de España” through the project CTQ2010-15541. F. Maya is very grateful to the “Conselleria d’Economia, Hisenda i Innovació, Govern de les Illes Balears”, for its support through a PhD grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maya, F., Estela, J.M. & Cerdà, V. Multisyringe ion chromatography with chemiluminescence detection for the determination of oxalate in beer and urine samples. Microchim Acta 173, 33–41 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0511-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0511-1