Abstract
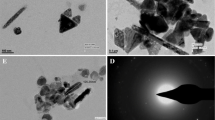
Thermal reduction has been applied to the preparation of copper nanoparticles (Cu-NPs) using three kinds of nonionic surfactants (Triton X-100, Tween-80, and dodecylamine). The Cu-NPs were formed by decomposition of copper(II) oxalate in presence of triphenylphosphine. The effect of the surfactants on the formation of the Cu-NPs was studied via X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive analysis of X-rays, transmission electron microscopy, thermogravimetric differential thermal analyses, and Fourier transform infra-red spectroscopy. It is shown that the Cu-NPs have an fcc crystal structure. Depending on the surfactant used, Cu-NPs with diameters between 8 and 20 nm can be prepared. The smallest Cu-NPs (8 nm) were formed in the presence of micelles of dodecylamine (yield 49%), while the largest particles (20 nm) were obtained with Triton X-100 (yield 99%). The use of Triton X-100 results in the highest yield and most uniform Cu-NPs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ozin GA (1992) Nanochemistry: synthesis in diminishing dimensions. Adv Mater 4:612–649
Daniel MC, Astruc D (2004) Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-sizerelated properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev 104:293–346
Hayat MA (1989) Colloidal gold: principles, methods and applications, vol I. Academic, New York
Abdulla-Al-Mamun M, Kusumoto Y, Muruganandham M (2009) Simple new synthesis of copper nanoparticles in water/acetonitrile mixed solvent and their characterization. Mater Lett 63:2007–2009
Arul Dhas N, Paul Raj C, Gedanken A (1998) Synthesis, characterization, and properties of metallic copper nanoparticles. Chem Mater 10:1446–1452
Vitulli G, Bernini M, Bertozzi S, Pitzalis E, Salvadori P, Coluccia S et al (2002) Nanoscale copper particles derived from solvated Cu atoms in the activation of molecular oxygen. Chem Mater 14:1183–1186
Huang HH, Yan FQ, Kek YM et al (1997) Synthesis, characterization, and nonlinear optical properties of copper nanoparticles. Langmuir 13:172–175
Liu Z, Bando YA (2003) Novel method for preparing copper nanorods and nanowires. Adv Mater 15:303–305
Campbell CT, Daube KA, White JM (1987) Cu/ZnO(0001) and Cu(111): model catalysts for methanol synthesis. Surf Sci 182:458–478
Shiau CY, Tsai JC (1997) Cu/Al2O3 catalyst prepared by electrolyses method. J Chin Chem Eng 28:55–59
Van der Meijden J (1981) PhD Thesis, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Du FL, Cui ZL, Zhang ZK, Chen SY (1997) Behavior of supported nano-copper catalyst in CO oxidation. J Nat Gas Chem 6:135–139
Dhas NA, Raj CP, Gedanken A (1998) Synthesis, characterization, and properties of metallic copper nanoparticles. Chem Mater 10:1446–1451
Kijenski J, Niedzielski PJ, Baiker A (1989) Synthesis of cyclic amines and their alkyl derivatives from amino-alcohols over supported copper catalysts. Appl Catal 53:107–112
Gredig SV, Koppel RA, Baiker A (1997) Synthesis of methylamines from carbon dioxide, hydrogen and ammonia over supported copper catalysts: influence of support. J Mol Catal A: Chem 127:133–138
Pereia R, Rufo M, Schuchardt U (1994) Copper (II) catalyzed oxidation of cyclohexane by tert-butyl hydroperoxide. J Braz Chem Soc 5:83–88
Shannon IJ, Rey F, Sankar G, Thomas JM, Maschmeyer T, Waller AM, Palomares AE, Corma A, Dent AJ, Greaves GN (1996) Hydrotalcite-derived mixed oxides containing copper: catalysts for the removal of nitric oxide. J Chem Soc Farad Trans 92:4331–4336
Ayaappan S, Gopalan RS, Subbanna GN, Rao CNR (1997) Nanoparticles of Ag, Au, Pd, and Cu produced by alcohol reduction of the salts. J Mater Res 12:398–404
Lisieski I, Pileni MP (1993) Synthesis of copper clusters using reverse micelles as microreactors. J Am Chem Soc 115:3887–3892
Lisieski I, Pileni MP (1995) Copper metallic particles synthesized “in situ” in reverse micelles: influence of various parameters on the size of particles. J Phys Chem 99:5077–5081
Lisieski I, Billoudet F, Pileni MP (1996) Control of the shape and the size of copper metallic particles. J Phys Chem 100:4160–4166
Vorobyova SA, Mushinsky VV, Lesnikovich AI (1997) Copper oxide produced by two-phase synthesis in “octane water” system. Dokl Acad Sci Belarus 41:62–67
Ding J, Tsuzuki T, McCormick PG, Street R (1996) Ultrafine Cu articles prepared by mechanical process. J Alloys Comp 234:L1–L8
Weins WN, Makinson JD, Angelis D, Axtell SC (1997) Low-frequency internal friction studies of nanocrystalline copper. Nanostruct Mater 9:509–514
Kellerson A, Knozinger E, Langel W, Giersig M (1995) Cu2O quantum-dot particles prepared from nanostructured copper. Adv Mater 7:652–659
Haas V, Birringer R (1992) The morphology and size of nano structured Cu, Pd, and W generated by sputtering. Nanostruct Mater 1:491–499
Champion Y, Bigot J (1996) Characterization of nanocrystalline copper powders preparing by melting in a cryogenic liquid. Mater Sci Eng A 217(218):58–64
Girardin D, Maurer M (1990) Ultrafine metallic powders prepared by high pressure plasma: synthesis and characterization. Mat Res Bull 25:119–125
Bouland D, Chouard JC, Briand A, Chartier F, Lacour JL, Mauchien P, Mermet JM (1992) Experimental study of aerosol production by laser ablation. J Aerosol Sci 23(1):225–229
Long NJ, Petford-Long AK (1986) In situ Electron-beaminduced reduction of CuO: a study of phase transformation in cupric oxide. Ultramicroscopy 20:151–157
Salavati-Niasari M, Davar F, Mir N (2008) Synthesis and characterization of metallic copper nanoparticles via thermal decomposition. Polyhedron 27:3514–3518
Salavati-Niasari M, Davar F (2009) Synthesis of copper and copper(I) oxide nanoparticles by thermal decomposition of a new precursor. Mater Lett 63:441–443
Salavati-Niasari M, Fereshteh Z, Davar F (2009) Synthesis of oleylamine capped copper nanocrystals via thermal reduction of a new precursor. Polyhedron 28:126–130
Zhong CJ, Luo J, Maye MM, Han L, Kariuki NN (2004) In: Zhou B, Hermans S, Somorjai GA (eds) Nanotechnology in catalysis, vol 1. Kluwer Academic/Plenum, New York, pp 222–248, Chapter 11
Zhong CJ, Kotov NA, Daniell W, Zamborini FP (2006) In: Warrendale PA (ed) Nanoparticles and Nanostructures in Sensors and Catalysis; MRS Proceedings; Vol. 900E
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the University of Isfahan for financially supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1344 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habibi, M.H., Kamrani, R. & Mokhtari, R. Fabrication and characterization of copper nanoparticles using thermal reduction: The effect of nonionic surfactants on size and yield of nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 171, 91–95 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0413-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0413-2