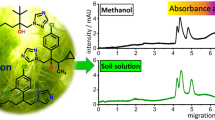
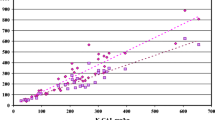
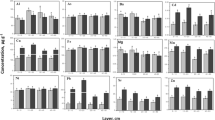
Abstract
Capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) along with ICP-OES was used for the determination of several chelating agents in clay and black soil, and in plants (Lolium perenne) grown in these matrices. Elemental levels in all the samples (Al, As, Ca, Cd, Cu, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Pb, S and Zn) were investigated by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES). Compared to previous methods, much shorter total analysis times were accomplished by the validation of an internal standard method for CZE analysis. The solubility of elements increased noticeably in the soils treated by the chelating agents before cultivation, and this phenomenon was strictly metal complex stability constant dependent. The most persistent chelating agents were triethylenetetraaminehexaacetic acid (TTHA) and 1,3-diaminopropanetetraacetic acid (PDTA). Both agents were bound to the growth medium and taken up by ryegrass, while only small proportions of them were degraded during cultivation. Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA), ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and nitrilotriamineacetic acid (NTA), mainly bound to the clay matrix during the 19 days cultivation, but after 40 days cultivation in black soil they were degraded to smaller acids. The results clearly show uptake of chelating agents by plants and are a clear indication of the degradation of chelating agents.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Egli T (2001) Biodegradation of metal-complexing aminopolycarboxylic acids. J Biosci Bioeng 92:89–97
Tandy S, Bossart K, Mueller R, Ritschel J, Hauser L, Schulin R, Nowack B (2004) Extraction of heavy metals from soils using biodegradable chelating agents. Environ Sci Technol 38:937–944
Udovic M, Leštan D (2007) The effect of earthworms on the fractionation and bioavailability of heavy metals before and after soil remediation. Environ Pollut 148:663–668
Tandy S, Ammann A, Schulin R, Nowack B (2006) Biodegradation and speciation of residual SS-ethylenediaminedisuccinic acid (EDDS) in soil solution left after soil washing. Environ Pollut 142:191–199
Kos B, Leštan D (2004) Chelator induced phytoextraction and in situ soil washing of Cu. Environ Pollut 132:333–339
Meers E, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2008) Degradability of ethylenediaminedisuccinic acid (EDDS) in metal contaminated soils: implications for its use soil remediation. Chemosphere 70:358–363
Andrade MD, Prasher SO, Hendershot WH (2007) Optimizing the molarity of a EDTA washing solution for saturated-soil remediation of trace metal contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 147:781–790
Fuentes A, Lloréns M, Sáez J, Soler A, Aguilar MI, Ortuño JF, Meseguer VF (2004) Simple and sequential extractions of heavy metals from different sewage sludges. Chemosphere 54:1039–1047
Ylivainio K, Jaakkola A, Aksela R (2004) Effects of Fe compounds on nutrient uptake by plants grown in sand media with different pH. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 167:602–608
Thayalakumaran T, Robinson BH, Vogeler I, Scotter DR, Clothier BE, Percival HJ (2003) Plant uptake and leaching of copper during EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of repacked and undisturbed soil. Plant and Soil 254:415–423
Kambhampati MS, Begonia GB, Begonia MFT, Bufford Y (2003) Phytoremediation of a lead-contaminated soil using morning glory: effects of a synthetic chelate. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 71:379–386
Tandy S, Schulin R, Nowack B (2006) The influence of EDDS on the uptake of heavy metals in hydroponically grown sunflowers. Chemosphere 62:1454–1463
Komárek M, Tlustoš P, Száková J, Chrastný V, Ettler V (2007) The use of maize and poplar in chelant-enhanced phytoextraction of lead from contaminated agricultural soils. Chemosphere 67:640–651
Nowack B, Schulin R, Robinson BH (2006) Critical assessment of chelant-enhanced metal phytoextraction. Environ Sci Technol 40:5225–5232
Collins RN, Onisko BC, McLaughlin MJ, Merrington G (2001) Determination of metal-EDTA complexes in soil solution and plant xylem by ion chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Technol 35:2589–2593
Collins RN, Merrington G, McLaughlin MJ, Knudsen C (2002) Uptake of intact zinc-ethylenediaminetetraaceticacid from soils is dependent on plant species and complex concentration. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1940–1945
Epstein AL, Gussman CD, Blaylock MJ, Yermiyahu U, Huang JW, Kapulnik Y, Orser CS (1999) EDTA and Pb-EDTA accumulation in Brassica juncea grown in Pb-amended soil. Plant and Soil 208:87–94
Bell PF, McLaughlin MJ, Cozens C, Stevens DP, Owens G, South H (2003) Plant uptake of 14C-EDTA, 14C-citrate, and 14C-histidine from chelator-buffered and conventional hydroponic solutions. Plant and Soil 253:311–319
Sýkora V, Pitter P, Bitternova I, Lederer T (2001) Biodegradability of ethyleneamine-based complexing agents. Water Res 35:2010–2016
Bucheli-Witschel M, Egli T (2001) Environmental fate and microbial degradation of aminopolycarboxylic acids. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:69–106
Pitter P, Sýkora V (2001) Biodegradability of ethylenediamine-based complexing agents and related compounds. Chemosphere 44:823–826
Kaluza U, Klingelhöfer P, Taeger K (1998) Microbial degradation of EDTA in an industrial wastewater treatment plant. Water Res 32:2843–2845
Thomas RAP, Lawlor K, Bailey M, Macaskie LE (1998) Biodegradation of metal-EDTA complexes by an enriched microbial population. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1319–1322
Belly RT, Lauff JJ, Goodhue CT (1975) Degradation of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid by microbial populations from an aerated lagoon. Appl Microbiol 29:787–794
Sillanpää M (1997) Analysis and environmental fate of EDTA and DTPA. Dissertation, Helsinki University of Technology, Finland
Laamanen P-L, Mali A, Matilainen R (2005) Simultaneous determination of DTPA, EDTA, and NTA by capillary electrophoresis after complexation with copper. Anal Bioanal Chem 381:1264–1271
Laamanen P-L, Busi S, Lahtinen M, Matilainen R (2005) A new ionic liquid dimethyldinonylammonium bromide as a flow modifier for the simultaneous determination of eight carboxylates by capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 1095:164–171
Laamanen P-L, Blanco E, Cela R, Matilainen R (2006) Improving sensitivity in simultaneous determination of copper carboxylates by nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 1110:261–267
Laamanen P-L, Busi S, Lahtinen M, Matilainen R (2006) Separation of chelating agents as copper complexes by capillary zone electrophoresis using quaternary ammonium bromides as additives in N-methylformamide. Anal Chim Acta 580:91–98
Laamanen P-L, Matilainen R (2007) Determination of alternative and conventional chelating agents as copper(II) complexes by capillary zone electrophoresis—the first use of didecyldimethylammonium bromide as a flow reversal reagent. Anal Chim Acta 584:136–144
Owens G, Ferguson VK, McLaughlin MJ, Singleton I, Reid RJ, Smith FA (2000) Determination of NTA and EDTA and speciation of their metal complexes in aqueous solution by capillary electrophoresis. Environ Sci Technol 34:885–891
Wiley JP (1995) Determination of polycarboxylic acids by capillary electrophoresis with copper complexation. J Chromatogr A 692:267–274
Sheppard RL, Henion J (1997) Determination of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid as the nickel chelate in environmental water by solid-phase extraction and capillary electrophoresis/tandem mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 18:287–291
Sheppard RL, Henion J (1997) Quantitative capillary electrophoresis/ion spray tandem mass spectrometry determination of EDTA in human plasma and urine. Anal Chem 69:2901–2907
Meers E, Hopgood M, Lesage E, Vervaeke P, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2004) Enhanced phytoextraction: in search of EDTA alternatives. Int J Phytoremediation 6:95–109
Manouchehri N, Besancon S, Bermond A (2006) Major and trace metal extraction from soil by EDTA: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Anal Chim Acta 559:105–112
Nowack B, Kari FG, Hilger SU, Sigg L (1996) Determination of dissolved and adsorbed EDTA species in water and sediments by HPLC. Anal Chem 68:561–566
Pitter P, Sýkora V (2001) Biodegradability of ethylenediamine-based complexing agents and related compounds. Chemosphere 44:823–826
Martell AE, Smith RM (1974) Critical stability constants amino acids, vol 1. Plenum, New York
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to Master of Science students Anna Korpelainen and Milla Mänty for helping with the measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 425 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hakkarainen, PL., Matilainen, R. Analyzing several chelating agents and their effect on elemental composition of Lolium perenne and two growth media by capillary zone electrophoresis and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Microchim Acta 167, 231–240 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-009-0245-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-009-0245-0