Abstract
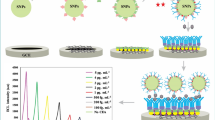
A new potentiometric immunoassay protocol for the determination of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) in human serum was designed by using a novel transparent immunoaffinity reactor. To construct such an affinity reactor, Fe3O4 nanorods with average diameter of 40 nm and length of 1.0 μm were initially synthesized through hydrolysis of FeCl3 and FeSO4 in the urea solution, and then the synthesized nanorods were used as the immobilized affinity support for the conjugation of anti-CEA antibodies (bionanorods). With an external magnet, the magnetic bionanorods were attached to the surface of a self-made carbon paste electrode. The performance and factors influencing the immunosensors were evaluated. Under optimal conditions, the binding of CEA in the samples onto the immobilized anti-CEA changed the potential response, a dynamic range from 1.5 to 80 ng·mL−1, and a detection limit of 0.9 ng·mL−1 CEA (at 3σ). The immunosensors show good precision, high sensitivity, acceptable stability and reproducibility. The CEA concentrations of the clinical serum specimens assayed by the immunosensor show consistent results in comparison with those obtained by commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kojima R, Mawatari K, Renberg B, Tsukahara T, Kitamori T (2009) Integration of immunoassay into extended nanospace. Microchim Acta 164:307
Wang L, Gan X (2009) Antibody-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for electrochemical immunoassay of α-1-fetoprotein in human serum. Microchim Acta 164:231
Billah M, Hays H, Millner P (2008) Development of a myoglobin impedimetric immunosensor based on mixed self-assembled monolayer onto gold. Microchim Acta 160:447
Campanella L, Martini E, Tomassetti M (2008) Determination of HIgG and anti-HIgG using a single potentiometric immunosensor and two different “competitive methods”: application to the analysis of globulin G in human serum. Sens Actu B 130:520
Piao M, Noh H, Rahman M, Won M, Shim Y (2008) Label-free detection of bisphenol A using a potentiometric immunosensor. Electroanalysis 20:30
Li J, Gao H (2008) A renewable potentiometric immunosensor based on Fe3O4 nanoparticles immobilized anti-IgG. Electroanalysis 20:881
de la Escosura-Muniz A, Ambrosi A, Merkoci A (2008) Electrochemical analysis with nanoparticle-based biosystems. TRAC-Trend Anal Chem 27:568
Bratov A, Ramon-Azcon J, Abramova N, Merlos A, Adrian J, Sanchez-Baeza F, Marco M, Dominguez C (2008) Three-dimensional interdigitated electrode array as a transducer for label-free biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 24:729
Grabowska I, Ksok E, Wyzkiewicz I, Chudy M (2009) Miniaturized module with biosensor for potentiometric determination of urea. Microchim Acta 164:299
Kamahori M, Ishige Y, Shimoda M (2007) A novel enzyme immunoassay based on potentiometric measurement of molecular adsorption events by an extended-gate field-effect transistor sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 22:3080
Chen X, Zhao T, Zou J (2009) A novel mimetic peroxidase catalyst by using magnetite-containing silica nanoparticles as carriers. Microchim Acta 164:93
Ai K, Zhang B, Lu L (2009) Europium-based fluorescence nanoparticle sensor for rapid and ultrasensitive detection of an anthrax biomarker. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:304
Xu Z, Yue Q, Zhuang Z, Xiao D (2008) Flow injection amperometric determination of acetaminophen at a gold nanoparticle modified carbon paste electrode. Microchim Acta 164:387
Martin E Jr, Kibbey W, Divecchia L, Anderson G, Catalano P, Minton J (1976) Carcinoembryonic antigen. Clinical and historical aspects. Cancer 37:62
Lian S, Wang E, Kang Z, Bai Y, Gao L, Jiang M, Hu C, Xu L (2004) Synthesis of magnetite nanorods and porous hematite nanorods. Solid State Commun 129:485
Feng C, Xu Y, Song L (2000) Study on highly sensitive potentiometric IgG immunosensor. Sens Actu B 66:190
Yuan R, Tang D, Chai Y, Zhong X, Liu Y, Dai J (2004) Ultrasensitive potentiometric immunosensor based on SA and OCA techniques for immobilizaiton of HBsAb with colloidal Au and polyvinyl butyral as matrixes. Langmuir 20:7240
Tang D, Ren J (2005) Direct and rapid detection diphtherotoxin via potentiometric immunosensor based on nanoparticles mixture and polyvinyl butyral as matrixes. Electroanalysis 17:2208
Zhang L, Yuan R, Huang X, Chai Y, Cao S (2004) Potentiomtric immunosensors based on antiserum of Japanese B encephalitis immobilized in nao-Au/polymerized o-phenylenediamine film. Eletrochem Commun 6:1222
Acknowledgements
The project was supported by Scientific Research Fund of Sichuan Provincial Education Department (Grant no. 08zb001). The authors also gratefully acknowledge the Tumor Hospital of Chengdu for providing the clinical serum samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 130 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, X., Wang, J., Li, N. et al. Label-free electrochemical immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen in human serum using magnetic nanorods as sensing probes. Microchim Acta 165, 437–442 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-009-0159-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-009-0159-x