Abstract
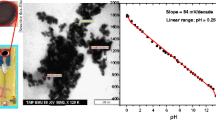
EIS (electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor) sensors based on the functionalization of uncoated gold nanoparticles supported on a Si/SiO2 structure are presented. Oxygen plasma etching at moderate power (<200 W) provides a convenient and efficient way to remove organic capping agents from the gold nanoparticles without significant damage. Higher power intensities destroy the linkage between the SiO2 and the gold nanoparticles, and some of the gold nanoparticles are removed from the surface. The flat-band potential shift, i.e. the pH dependence of the gold-coated EIS sensors is similar (33 mV/pH) to the uncoated EIS pH-sensor. Lead, penicillin and glucose sensors were prepared by immobilization of β-cyclodextrin, penicillinase and glucose oxidase by various immobilization techniques.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brust M, Walker M, Bethell D, Schiffrin DJ, Whyman R (1994) Synthesis of thiol-derivatised gold nanoparticles in a 2-phase liquid–liquid system. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 7:801–802
Guoa S, Wang E (2007) Synthesis and electrochemical applications of gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 598:181–192
Kharitonov AB, Shipway AN, Katz E, Willner I (1999) Gold-nanoparticle/bis-bipyridinium cyclophane-functionalized ion-sensitive field-effect transistors: novel assemblies for the sensing of neurotransmitters. Anal Chem 18:255–260
Katz E, Willner I (2003) Probing biomolecular interactions at conductive and semiconductive surfaces by impedance spectroscopy: routes to impedimetric immunosensors, DNA-sensors, and enzyme biosensors. Electroanalysis 15:913–947
Kielbassa S, Habich A, Schnaidt J, Bansmann J, Weigl F, Boyen HG, Ziemann P, Behm RJ (2006) On the morphology and stability of Au nanoparticles on TiO2(110) prepared from micelle-stabilized precursors. Langmuir 22:7873–7880
Raiber K, Terfort A, Benndorf C, Krings N, Strehblow HH (2005) Removal of self-assembled monolayers of alkanethiolates on gold by plasma cleaning. Surf Sci 595:56–63
Hesse E, Creighton JA (1999) Investigation by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of the effect of oxygen and hydrogen plasmas on adsorbate-covered gold and silver island films. Langmuir 15:3545–3550
Gun J, Schöning MJ, Abouzar MH, Poghossian A, Katz E (2008) Field-effect nanoparticle-based glucose sensor on a chip: amplification effect of co-immobilized redox species. Electroanalysis (in press)
Brust M, Bethell D, Schiffrin DJ, Kiely CJ (1995) Novel gold-dithiol nano-networks with nonmetallic electronic-properties. Adv Mater 7:795–803
Fishelson N, Shkrob I, Lev O, Gun J, Modestov AD (2001) Studies on charge transport in self-assembled gold dithiol films: conductivity, photoconductivity and Photoelectrochemical measurements. Langmuir 17:403–412
Schmitt J, Machtle P, Eck D, Mohwald H (1999) Preparation and optical properties of colloidal gold monolayers. Langmuir 15:3256–3266
Russell CP, Salek JS, Sikorski CT, Kumaravel G, Lin FT (1990) Cooperative binding by aggregated mono-6-(alky1amino)-β-cyclodextrins. J Am Chem Soc 112:3860–3868
Thermo Scientific (2007) Tech Tip #2: attach a protein onto a gold surface. Available at http://www.Piercenet.com
Tang DY, Xia BY, Zhang YQ (2008) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin in a multilayer {nanogold/PDDA}(n) inorganic-organic hybrid film. Microchim Acta 160:367–374
Wuelfing WP, Green SJ, Pietron JJ, Cliffel DE, Murray RW (2000) Electronic Conductivity of solid-state, mixed-valent, monolayer-protected Au clusters. J Am Chem Soc 122:11465–11472
Poghossian A, Abouzar MH, Sakkari M, Kassab T, Han Y, Ingebrandt S, Offenhäusser A, Schöning MJ (2006) Field-effect sensors for monitoring the layer by-layer adsorption of charged macromolecules. Sens Actuators B Chem 118:163–170
Cane C, Gracia I, Merlos A (1997) Microtechnologies for pH ISFET chemical sensors. Microelectron J 28:389–405
Schöning MJ, Poghossian A (2006) BioFEDs (Field-effect devices): state-of-the-art and new directions. Electroanalysis 18:1893–1900
Schöning MJ, Tsarouchas D, Schaub A, Beckers L, Zander W, Schubert J, Kordos P, Lüth H (1996) A highly long-term stable silicon-based pH sensor using pulsed laser deposition technique. Sens Actuators B Chem 35:228–233
Poghossian A, Schöning MJ (2007) In: Grimes CA, Dickey EC, Pishko MV (eds) Encyclopedia of sensors, chapter 24, vol 9. American Scientific, Stevenson Ranch, USA, pp 463–534
Poghossian A, Schöning MJ (2008) In: Marks RS, Cullen DC, Karube I, Lowe CR, Weetall HH (eds) Handbook of biosensors and biochips, chapter 24. Wiley, Weinheim, Germany, pp 1–17
Schöning MJ, Brinkmann D, Rolka D, Demuth C, Poghossian A (2005) CIP (cleaning-in-place) suitable “non-glass” pH sensor based on a Ta2O5-gate EIS structure. Sens Actuators B Chem 111–112:423–429
Thust M, Schöning MJ, Schroth P, Malkoc Ü, Dicker CI, Steffen A, Kordos P, Lüth H (1999) Enzyme immobilisation on planar and porous silicon substrates for biosensor applications. J Mol Catal B Enzym 7:77–83
Liao CW, Chou JC, Sun TP, Hsiung SK, Hsieh JH (2007) Preliminary investigations on a glucose biosensor based on the potentiometric principle. Sens Actuators B Chem 21:720–726
Yao K, Zhu YH, Wang P, Yang XL, Cheng PZ, Lu H (2007) ENFET glucose biosensor produced with mesoporous silica microspheres. Mater Sci Eng C 27:736–740
Xiao Y, Patolsky F, Katz E, Hainfeld JF, Willner I (2003) “Plugging into enzymes”: nanowiring of redox enzymes by a gold nanoparticle. Science 299:1877–1881
Cavaliere-Jaricot S, Darbandi M, Kucur E, Nann T (2008) Silica coated quantum dots: a new tool for electrochemical and optical glucose detection. Mikrochim Acta 160:375–383
Bharathi S, Lev O (1998) Sol-gel-derived nanocrystalline gold-silicate composite biosensor. Anal Commun 35:29–31
Liu Y, Hu LM, Yang SQ (2008) Amplification of bioelectrocatalytic signalling based on silver nanoparticles and DNA-derived horseradish peroxidase biosensors. Mikrochim Acta 160:357
Zhao J, Yu JJ, Wang F, Hu SS (2006) Fabrication of gold nanoparticle-dihexadecyl hydrogen phosphate film on a glassy carbon electrode. Mikrochim Acta 156:277–282
Parke SA, Birch GG, MacDougall DB, Stevens DA (1997) Tastes, structure and solution properties of D-glucono-1,5-lactone. Chem Senses 22:53–65
Katz EY (1990) A chemically modified electrode capable of a spontaneous immobilization of amino-compounds due to its functionalization with succinimidyl groups. J Electroanal Chem 291:257–264
Bergmeyer HU, Gawehn K, Grassl M (1974) In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol 1, 2nd edn. Academic, NY, USA, pp 457–458
Papariello GJ, Mukherji AK, Shearer CM (1973) Penicillin selective enzyme electrode. Anal Chem 45:790–792
Caras S, Janata J (1980) Field-effect transistor sensitive to penicillin. Anal Chem 52:1935–1937
Poghossian A, Thust M, Schroth P, Steffen A, Lüth H, Schöning MJ (2001) Penicillin detectionby means of silicon-based field-effect structures. Sens Mater 13:207–223
Poghossian A, Yoshinobu T, Simonis A, Ecken H, Lüth H, Schöning MJ (2001) Penicillin detection by means of field-effect based sensors: EnFET, capacitive EIS sensor or LAPS? Sens Actuators B Chem 78:237–242
Poghossian A, Schöning MJ, Schroth P, Simonis A, Lüth H (2001) An ISFET-based penicillin sensor with high sensitivity, low detection limit and long lifetime. Sens Actuators B Chem 76:519–526
Poghossian A, Thust M, Schöning MJ, Müller-Veggian M, Kordos P, Lüth H (2000) Cross-sensitivity of a capacitive penicillin sensor combined with a diffusion barrier. Sens Actuators B Chem 68:260–265
Wang J (1988) Electroanalytical techniques in clinical chemistry and laboratory medicine. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany
Thust M, Schöning MJ, Vetter J, Kordos P, Lüth H (1996) A long-term stable penicillin-sensitive potentiometric biosensor with enzyme immobilized by heterobifunctional crosslinking. Anal Chim Acta 323:115–121
Szejtli J (1988) Cyclodextrine technology. Kluwer, Boston, USA
Li S, Purdy WC (1992) Cyclodextrins and their applications in analytical-chemistry. Chem Rev 92:1457–1470
Lahiani-Skiba M, Coquard A, Bounoure F, Verite P, Arnaud P, Skiba M (2007) Mebendazole complexes with various cyclodextrins: preparation and physicochemical characterization. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 57:197–201
Ben Ali M, Kalfat R, Sfihi H, Ben Ouada H, Chovelon JM, Jafferezic-Renault N (1998) Cyclodextrin-polymethylhydrosiloxane gel as sensitive membrane for heavy ion sensors. Mater Sci Eng C 6:53–58
Ben Ali M, Kalfat R, Sfihi H, Ben Ouada H, Chovelon JM, Jafferezic-Renault N (2000) Sensitive cyclodextrin-polysiloxane gel membrane on EIS structure and ISFET for heavy metal ion detection. Sens Actuators B Chem 62:233–237
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the technical assistance of H.-P. Bochem and A. Besmehn for the surface characterization with HRSEM and XPS and to A. Voskevich for the very useful discussions. J. Gun thanks the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gun, J., Rizkov, D., Lev, O. et al. Oxygen plasma-treated gold nanoparticle-based field-effect devices as transducer structures for bio-chemical sensing. Microchim Acta 164, 395–404 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-008-0073-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-008-0073-7