Abstract
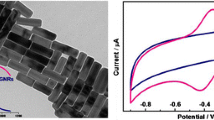
A novel amperometric biosensor for nitrite was developed by immobilization of hemoglobin (Hb) and a room temperature ionic liquid, 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium tetrafluoroborate (EMIT), on a multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) modified electrode. Compared with Hb/MWNTs modified electrode, the Hb/RTILs/MWNTs modified electrode showed better electrochemical response, indicating that EMIT can promote direct electron transfer of Hb. A pair of well-defined, quasi-reversible redox peaks of Hb with a formal potential of −0.315 V was observed. The immobilized Hb exhibited remarkable electrocatalytic activity for the reduction of nitrite. The linear response range was from 4.0 × 10−6 to 3.2 × 10−4 M with a detection limit of 8.1 × 10−7 M at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3. The resulting biosensor has been successfully applied to the determination of nitrite in water samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koch VR, Nanjundiah C, Carlin RT (1994) US Patent 5,827,602
Bonhote P, Dias AP, Armand M, Papageorgiou N, Kalyanasundaram K, Gratzel M (1996) Hydrophobic highly conductive ambient-temperature molten salts. Inorg Chem 35:1168
Katayama Y, Dan S, Miura T, Kishi T (2001) Electrochemical behavior of silver in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate molten salt. J Eletrochem Soc 148:C102
He P, Liu HT, Li ZY, Liu Y, Xu XD, Li JH (2004) Electrochemical deposition of silver in room temperature ionic liquids and its surface-enhanced Raman scattering effect. Langmuir 20:10260
Mukhopadhyay I, Aravinda CLR, Borissov D, Freyland W (2005) Electrodeposition of Ti from TiCl4 in the ionic liquid l-methyl-3-butyl-imidazolium bis (trifluoro methyl sulfone) imide at room temperature: study on phase formation by in situ electrochemical scanning tunneling microscopy. Electrochim Acta 50:1275
Yuyama K, Masuda G, Yoshida H, Sato T (2006) Ionic liquids containing the tetrafluoroborate anion have the best performance and stability for electric double layer capacitor applications. J Power Sources 162:1401
McEwen AB, Ngo HL, LeCompte K, Goldman JL (1999) Electrochemical properties of imidazolium salt electrolytes for electrochemical capacitor applications. J Electrochem Soc 146:1687
Lu W, Fadeev G, Qi B, Smela E, Mattes BR, Ding J, Spinks GM, Forsyth M (2002) Use of ionic liquids for p-conjugated polymer electrochemical devices. Science 297:983
Zhou D, Spinks GM, Wallace GG, Tiyapiboonchaiya C, MacFarlane DR, FoSun M (2003) Solid state actuators based on polypyrrole and polymer-in-ionic liquid electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 48:2355
Ricks-Laskoski HL, Snow AW (2006) Synthesis and electric field actuation of an ionic liquid polymer. J Am Chem Soc 128:12402
Garcia B, Lavallee S, Perron G (2004) Room temperature molten salts as lithium battery electrolyte. Electrochim Acta 49:4583
Goldman JL, McEween AB (1999) EMIIm and EMIBeti on aluminum anodic stability dependence on lithium salt and propylene carbonate. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 2:501
Compton DL, Laszlo JA (2003) Loss of cytochrome c Fe (III)/Fe (II) redox couple in ionic liquids. J Electroanal Chem 533:187
Ding SF, Xu MQ, Zhao GC, Wei XW (2007) Direct electrochemical response of myoglobin using a room temperature ionic liquid, 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3-methyl-imidazolium tetrafluoroborate, as supporting electrolyte. Electrochem Commun 9:216
Lu XB, Zhang Q, Zhang L, Li JH (2006) Direct electron transfer of horseradish peroxidase and its biosensor based on chitosan and room temperature ionic liquid. Electrochem Commun 8:874
López MŚ-P, Mecerreyes D, López-Cabarcos E, López-Ruiz B (2006) Amperometric glucose biosensor based on polymerized ionic liquid microparticles. Biosen Bioelectron 21:2320
Mirvish SS (1995) Role of N-nitroso compounds (NOC) and N-nitrosation in etiology of gastric, esophageal, nasopharyngeal and bladder cancer and contribution to cancer of known exposures to NOC. Cancer Lett 93:17
Momaghan JM, Cook K, Cara D (1997) Determination of nitrite and nitrate in human serum. J Chromatogr A 770:143
He DY, Zhang ZJ, Huang Y, Hu YF (2007) Chemiluminescence microflow injection analysis system on a chip for the determination of nitrite in food. Food Chem 101:667
Yang WW, Bai Y, Li YC, Sun CQ (2005) Amperometric nitrite sensor based on hemoglobin/colloidal gold nanoparticles immobilized on a glassy carbon electrode by a titania sol-gel film. Anal Bioanal Chem 382:44
Dai ZH, Xu XX, Ju HX (2004) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of myoglobin immobilized on a hexagonal mesoporous silica matrix. Anal Biochem 332:23
Hou PX, Bai S, Yang QH, Liu C, Cheng HM (2002) Multi-step purification of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 40:81
Liu Y, Zou XQ, Dong SJ (2006) Electrochemical characteristics of facile prepared carbon nanotubes-ionic liquid gel modified microelectrode and application in bioelectrochemistry. Electrochem Commun 8:1429
Fukushima T, Kosaka A, Ishimura Y, Yamamoto T, Takigawa T, Ishii N, Aida T (2003) Molecular ordering of organic molten salts triggered by single-walled carbon nanotubes. Science 300:2072
Zhao Q, Zhan D, Ma H, Zhang M, Zhao Y, Jing P, Zhu Z, Wan X, Shao Y, Zhuang Q (2005) Direct proteins electrochemistry based on ionic liquid mediated carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrode. Front Biosci 10:326
Murray RW, Bard AJ (1984) Electroanalytical chemistry. Marcel Dekker, New York, p 191
Murray RW, Bard AJ (1984) Electroanalytical chemistry. Marcel Dekker, New York, p 53
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (1980) Electrochemical method. Marcel Dekker, New York, p 121
Han X, Huang W, Jia J, Dong S, Wang E (2002) Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin in egg/phosphatidylcholine films and its catalysis to H2O2. Biosen Bioelectron 17:741
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Professor T. Ohsaka of Tokyo Institute of Technology for providing RTIL, EMIT. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation and Program for Innovative Research Team in Anhui Normal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, W., Jin, HH. & Zhao, GC. A reagentless nitrite biosensor based on direct electron transfer of hemoglobin on a room temperature ionic liquid/carbon nanotube-modified electrode. Microchim Acta 164, 167–171 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-008-0053-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-008-0053-y