Abstract.
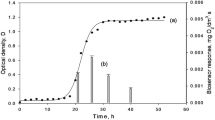
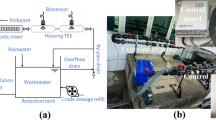
A microbial sensor for rapid determination of the concentration of biodegradable pollutants in wastewater has been developed using the salt-tolerant yeast Arxula adeninivorans LS3 immobilized by gel entrapment with poly (carbamoyl) sulfonate hydrogel (PCS gel) on a Clark-type oxygen electrode. This sensor needs 5 min for every measurement instead of 5 days for BOD5. The sensor has a linear response of up to 550 mg L−1 BOD with a correlation of coefficient R2 = 0.9785. The detection limit was calculated to be 2.1 mg L−1 BOD equivalents, and the determination limit was 6.0 mg L−1 BOD equivalents. The high tolerance to salt of the Arxula adeninivorans LS3 strain prevents the inactivation of cells caused by the seawater from affecting the measurements. In a 24-hour comparative study using real wastewater samples from an international college situated in Hong Kong, the microbial sensor showed a very good correlation (R2 = 0.9134) with the standard BOD5 method and truly reflected the ‘life cycle’ of the college people. The microbial sensor allows almost ideal real-time monitoring in water pollution and degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Renneberg, T., Kwan, R., Chan, C. et al. A Salt-Tolerant Yeast-Based Microbial Sensor for 24 Hour Community Wastewater Monitoring in Coastal Regions. Microchim. Acta 148, 235–240 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-004-0266-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-004-0266-7