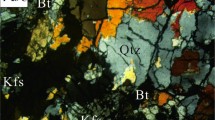
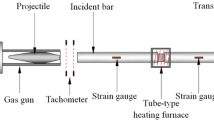
Abstract
The elevated temperature, high geostress environment, and strong dynamic loading are important factors that induce disasters in deep rock engineering work. The progressive damage and failure behaviors of granite under the coupling of elevated temperature, biaxial stress constraint, and high strain rate were studied by true triaxial split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) tests. The results show that the P-wave velocity attenuation rate kp increases exponentially with temperature, and kp is closely related to the thermal damage of granite grain structures. Under the biaxial stress constraint, the dynamic strength and elastic modulus of granite both increase at first, then decrease with the increase of temperature and a thermal enhancement effect is observed at 150 °C. The threshold temperature for the transition of dynamic failure from brittleness to plasticity is 500 °C. The dynamic strength generated by axial compression and lateral expansion increases exponentially with the strain rate. The lateral stress σ2 enhances the dynamic strength of granite. Under true triaxial stress condition (σ1 > σ2 > σ3 ≠ 0), the enhancement of the dynamic strength is further improved, and the lateral expansion of samples develops along the direction of the minimum principal stress. Under the same stress constraint, the number of impacts that can be borne by granite samples is linearly negatively correlated with heat treatment temperature. The samples are compacted apparently in the early stage of cyclic loading, and the maximum strain experiences three stages: a decrease, slow increase, and sharp increase. When the heat treatment temperature is 700 °C and above, the slow increase stage no longer occurs.
Highlights
-
1.
The progressive damage behaviors of thermally treated granite shows nonlinear growth under biaxial stress constraint and repeated impacts coupling.
-
2.
The dynamic strength of granite under biaxial stress constraint has both the strengthening effect of strain rate and the hardening and weakening effects of temperature.
-
3.
The lateral stress increases the dynamic strength of granite, and the lateral expansion develops along the direction of the minimum principal stress.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on request.
Abbreviations
- T :
-
Temperatures
- k p :
-
Attenuation rate of P-wave velocity
- ν 1, ν 2 :
-
P-Wave velocities of granite before and after high-temperature treatment
- S 1, S 2, S 3 :
-
Three loading directions of cubic samples
- A 0, E b, C b :
-
Cross-sectional area, Young’s modulus, and P-wave velocity of square bars
- A i-S, L I–S :
-
Cross-sectional area and length of samples, in which i represents X or Y
- ε Y +, ε Y− :
-
Stress wave signal output along the Y-axis square bars
- ε In, ε Re, ε tr :
-
Incident signal, reflected signals, transmission signals
- σ i, σ I -dyn( t ) :
-
Initial static pre-stress and dynamic stress
- D :
-
Cumulative damage factor
- ε n :
-
Maximum strain under the nth impact
- ε max :
-
Maximum strain to complete failure under impacts
- ε 0 :
-
Maximum strain in the damage stage
- SHPB:
-
Split Hopkinson pressure bar
References
Akdag S, Karakus M, Nguyen GD, Taheri A, Zhang QB, Zhao J (2023) Dynamic response and fracture characteristics of thermally-treated granite under dynamic loading. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 170:105482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2023.105482
Benge M, Katende A, Rutqvist J, Radonjic M, Bunger A (2023) Creep properties of shale and predicted impact on proppant embedment for the Caney Shale. Oklahoma Rock Mech Rock Eng 56:5903–5921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03362-8
Dong YQ, Zhu ZM, Zhou L, Ying P, Wang M (2018) Study of mode I crack dynamic propagation behaviour and rock dynamic fracture toughness by using SCT specimens. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 41:12823. https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.12823
Fan LF, Yang KC, Wang M, Wang LJ, Wu ZJ (2021) Experimental study on wave propagation through granite after high-temperature treatment. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 148:104946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104946
Farahmand K, Diederichs MS (2021) Calibration of coupled hydro-mechanical properties of grain-based model for simulating fracture process and associated pore pressure evolution in excavation damage zone around deep tunnels. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 13:60–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2020.06.006
Gong HL, Luo Y, Meng F, Du HJ (2023a) Failure behavior and strength deterioration model of high-performance concrete under coupled elevated temperature, biaxial constraint and impact loading. J Build Eng 75:107002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2023.107002
Gong HL, Luo Y, Zhou JR, Zhao CC, Li XP (2023b) Fracture behaviors and damage evolution anisotropy of granite under coupling of multiaxial confinement and dynamic loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 56:2515–2534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-03208-9
Griffiths L, Heap MJ, Baud P, Schmittbuhl J (2017) Quantification of microcrack characteristics and implications for stiffness and strength of granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 100:138–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.10.013
Groccia C, Cai M, Punkkinen A (2016) Quantifying rock mass bulking at a deep underground nickel mine. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 81:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.06.014
Guan XM, Yang N, Zhang WJ, Li MG, Liu ZL, Wang XH, Zhang SL (2022) Vibration response and failure modes analysis of the temporary support structure under blasting excavation of tunnels. Eng Fail Anal 136:106188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106188
Han ZY, Li DY, Li XB (2022) Dynamic mechanical properties and wave propagation of composite rock-mortar specimens based on SHPB tests. Int J Min Sci Technol 32(4):793–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2022.05.008
Hu LH, Ma K, Liang X, Tang C, Wang ZW, Yan LB (2018) Experimental and numerical study on rockburst triggered by tangential weak cyclic dynamic disturbance under true triaxial conditions. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 81:602–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2018.08.014
Hu YF, Hu YQ, Zhao GK, Jin PH, Zhao ZR, Li C (2022) Experimental investigation of the relationships among p-wave velocity, tensile strength, and mode-I fracture toughness of granite after high-temperature treatment. Nat Resour Res 31:801–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-022-10020-3
Huang ZK, Zhang DM, Pitilakis K, Tsinidis G, Huang HW, Zhang DM, Argyroudis S (2022) Resilience assessment of tunnels: Framework and application for tunnels in alluvial deposits exposed to seismic hazard. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 162:107456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2022.107456
Huo XF, Shi XZ, Qiu XY, Zhou J, Gou YG, Yu Z, Zhang SA (2022) A study on raise blasting and blast-induced vibrations in highly stressed rock masses. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 123:104407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2022.104407
Kang FC, Li YC, Tang CA (2021) Grain size heterogeneity controls strengthening to weakening of granite over high-temperature treatment. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 145:104848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104848
Kant MA, Ammann J, Rossi E, Madonna C, Höser D, Rohr PRV (2017) Thermal properties of central Aare granite for temperatures up to 500 °C: irreversible changes due to thermal crack formation. Geophys Res Lett 44:772–776. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL070990
Katende A (2022) The impact of rock lithology and microstructural properties on proppant embedment and fracture conductivity: a case study of the Caney Shale, Southern Oklahoma. Oklahoma State University
Katende A, Boyou NV, Ismail I, Chung DZ, Sagala F, Sagala N, Sagala MS (2019) Improving the performance of oil based mud and water based mud in a high temperature hole using nanosilica nanoparticles. Colloid Surface a 577:645–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.05.088
Katende A, Rutqvist J, Rutqvist M, Seyedolali A, Bunger A, Puckette JO, Rhin A, Radonjic M (2021) Convergence of micro-geochemistry and micro-geomechanics towards understanding proppant shale rock interaction: a Caney shale case study in southern Oklahoma, USA. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 96:104296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2021.104296
Katende A, Rutqvist J, Massion C, Radonjic M (2023a) Experimental flow-through a single fracture with monolayer proppant at reservoir conditions: a case study on Caney Shale, Southwest Oklahoma. USA Energy 273:127181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.127181
Katende A, Allen C, Rutqvist J, Nakagawa S, Radonjic M (2023b) Experimental and numerical investigation of proppant embedment and conductivity reduction within a fracture in the Caney Shale, Southern Oklahoma. USA Fuel 341:127571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2023.127571
Kumari WGP, Ranjith PG, Perera MSA, Shao S, Chen BK, Lashin A, Arifi NA, Rathnaweera TD (2017) Mechanical behaviour of Australian Strathbogie granite under in-situ stress and temperature conditions: an application to geothermal energy extraction. Geothermics 65:44–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2016.07.002
Lasheen ESR, Rashwan M, Azer MK (2023) Effect of mineralogical variations on physico-mechanical and thermal properties of granitic rocks. Sci Rep 13:10320. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-36459-9
Li X, Li BJ, Li XB, Yin TB, Wang Y, Dang WG (2020) Thermal shock effects on the mechanical behavior of granite exposed to dynamic loading. Archiv Civ Mech Eng 20:66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-020-00070-w
Liu S, Xu JY (2015) Effect of strain rate on the dynamic compressive mechanical behaviors of rock material subjected to high temperatures. Mech Mater 82:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmat.2014.12.006
Liu K, Zhang QB, Wu G, Li JC, Zhao J (2019) Dynamic mechanical and fracture behaviour of sandstone under multiaxial loads using a triaxial Hopkinson bar. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:2175–2195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1691-y
Luo Y, Gong HL, Huang JH, Wang G, Li XP, Wan S (2022) Dynamic cumulative damage characteristics of deep-buried granite from Shuangjiangkou hydropower station under true triaxial constraint. Int J Impact Eng 165:104215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104215
Mardoukhi A (2017) Effects of microstructural features, thermal shocks and strain rate on the mechanical response of granitic rocks. Tampere University of Technology. https://trepo.tuni.fi/handle/10024/115121.
Mardoukhi A, Mardoukhi Y, Hokka M, Kuokkala VT (2021) Effects of test temperature and low temperature thermal cycling on the dynamic tensile strength of granitic rocks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54:443–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02253-6
Mario MG, Diego IB, Javier DF (2015) On the environmental suitability of high-and low-enthalpy geothermal systems. Geothermics 53:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2014.03.012
Memon KR, Ali M, Awan FUR, Mahesar AA, Abbasi GR, Mohanty US, Akhondzadeh H, Tunio AH, Iglauer S, Keshavarz A (2021) Influence of cryogenic liquid nitrogen cooling and thermal shocks on petro-physical and morphological characteristics of Eagle Ford shale. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 96:104313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2021.104313
Meng FZ, Song J, Wong LNY, Wang ZQ, Zhang CQ (2021) Characterization of roughness and shear behavior of thermally treated granite fractures. Eng Geol 293:106287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106287
Meng QB, Liu JF, Huang BX, Pu H, Wu JY, Zhang ZZ (2022) Effects of confining pressure and temperature on the energy evolution of rocks under triaxial cyclic loading and unloading conditions. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55:773–798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02690-x
Miao ST, Pan PZ, Zhao XG, Shao CY, Yu PY (2021) Experimental study on damage and fracture characteristics of Beishan granite subjected to high-temperature treatment with DIC and AE techniques. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54:721–743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02271-4
Millon O, Ruiz-Ripoll ML, Hoerth T (2016) Analysis of the behavior of sedimentary rocks under impact loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49:4257–4272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1010-4
Morad D, Hatzor YH, Sagy A (2019) Rate effects on shear deformation of rough limestone discontinuities. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:1613–1622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1693-9
Padmanabha V, Schäfer F, Rae ASP, Kenkmann T (2023) Dynamic split tensile strength of basalt, granite, marble and sandstone: strain rate dependency and fragmentation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 56:109–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-03075-4
Pan XK, Berto F, Zhou XP (2022) Investigation of creep damage mechanical behaviors of red sandstone considering temperature effect. Fatigue Fract Eng M 45(2):411–424. https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.13604
Patel S, Martin CD (2020) Effect of stress path on the failure envelope of intact crystalline rock at low confining stress. Minerals 10:1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/min1012111
Pérez-Rey I, Muñoz-Ibáñez A, González-Fernández MA, Muñiz-Menéndez M, Herbón-Penabad M, Estévez-Ventosa X, Delgado J, Alejano RL (2023) Size effects on the tensile strength and fracture toughness of granitic rock in different tests. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 15(9):2179–2192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.11.005
Plúa C, Vu MN, Seyedi DM, Armand G (2021) Effects of inherent spatial variability of rock properties on the thermo-hydro-mechanical responses of a high-level radioactive waste repository. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 145:104682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104682
Qin Y, Tian H, Xu NX, Chen Y (2020) Physical and mechanical properties of granite after high-temperature treatment. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:305–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01919-0
Rong G, Peng J, Cai M, Yao MD, Zhou CB, Sha S (2018) Experimental investigation of thermal cycling effect on physical and mechanical properties of bedrocks in geothermal fields. Appl Therm Eng 141:174–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.05.126
Shao ZL, Wang Y, Tang XH (2020) The influences of heating and uniaxial loading on granite subjected to liquid nitrogen cooling. Eng Geo 271:105614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105614
Shen YJ, Yuan JQ, Hou X, Hao JS, Bai ZP, Li T (2021) The strength changes and failure modes of high-temperature granite subjected to cooling shocks. Geomech Geophys Geo 7:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-020-00214-5
Shen Y, Zhu HH, Yan ZG, Zhou L, Zhang T, Men YQ, Lu Y (2023) Thermo-mechanical analysis of fire effects on the structural performance of shield tunnels. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 132:104885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2022.104885
Su HJ, Qin XF, Feng YJ, Yu LY, Sun ZZ (2022) Experimental investigation of mixed mode I-II fracture property of thermally treated granite under dynamic loading. Theor Appl Fract Mech 118:103267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2022.103267
Sun Y, Zhai C, Xu JZ, Yu X, Cong YZ, Zheng YF, Tang W, Li YJ (2022) Damage and failure of hot dry rock under cyclic liquid nitrogen cold shock treatment: a non-destructive ultrasonic test method. Nat Resour Res 31:261–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-021-10005-8
Tian WL, Yang SQ, Wang JG, Dong JP (2021) Failure behavior of the thermal treated granite under triaxial cyclic loading–unloading compression. Geomech Geophys Geo 7:19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-021-00218-9
Wang ZL, Tian NC, Wang JG, Liu JC, Hong L (2018) Experimental study on damage mechanical characteristics of heat-treated granite under repeated impact. J Mater Civ Eng 30:0002465. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002465
Wang P, Yin TB, Li XB, Zhang SS, Bai L (2019) Dynamic properties of thermally treated granite subjected to cyclic impact loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:991–1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1606-y
Wang P, She CW, Chen JM, Xu ZJ, Chen YQ (2023) Study of slope effect on smoke back-layering length and ceiling temperature in tunnel fires under natural ventilation. Int J Therm Sci 185:108046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2022.108046
Wei J, Liao HL, Wang HJ, Chen JK, Li N, Liang HJ, Liu CF, Zhang DR, Teng ZX (2022) Experimental investigation on the dynamic tensile characteristics of conglomerate based on 3D SHPB system. J Pet Sci Eng 213:110350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2022.110350
Wong LNY, Zhang YH, Wu ZJ (2020) Rock strengthening or weakening upon heating in the mild temperature range? Eng Geol 272:105619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105619
Wong LNY, Cui X, Zhang YH, Wu ZJ, Gao TY (2022) Experimental investigation of thermal strengthening in Sichuan marble. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55:6683–6702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-02995-5
Xu RC, Zhang SZ, Li Z, Yan XM (2023) Experimental investigation of the strain rate effect on crack initiation and crack damage thresholds of hard rock under quasi-static compression. Acta Geotech 18:903–920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-022-01631-4
Yang SQ, Ranjith PG, Jing HW, Tian WL, Ju Y (2017) An experimental investigation on thermal damage and failure mechanical behavior of granite after exposure to different high temperature treatments. Geothermics 65:180–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2016.09.008
Yang FJ, Hu DW, Zhou H, Lu JJ (2020) Physico-mechanical behaviors of granite under coupled static and dynamic cyclic loadings. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:2157–2173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-02040-y
Yin WT, Zhao YS, Feng ZJ (2020) Experimental research on permeability of fractured-subsequently-filled granite under high temperature and triaxial stresses. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 39:2234–2243. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0491
Yin TB, Ma JX, Wu Y, Zhang DD, Yang Z (2022) Effect of high temperature on the brittleness index of granite: an experimental investigation. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81:476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02953-z
Yoon S, Kim MJ, Chang S, Lee GJ (2022) Evaluation on the buffer temperature by thermal conductivity of gap-filling material in a high-level radioactive waste repository. Nucl Eng Technol 54:4005–4012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2022.06.008
Zhao XG, Zhao Z, Guo Z, Cai M, Li X, Li PF, Chen L, Wang J (2018) Influence of thermal treatment on the thermal conductivity of beishan granite. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51:2055–2074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1479-0
Zhao JS, Chen BR, Jiang Q, Lu JF, Hao XJ, Pei SF, Wang F (2022) Microseismic monitoring of rock mass fracture response to blasting excavation of large underground caverns under high geostress. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55:733–750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02709-3
Zhou XP, Li GQ, Ma HC (2020) Real-time experiment investigations on the coupled thermomechanical and cracking behaviors in granite containing three pre-existing fissures. Eng Fract Mech 224:106797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2019.106797
Zuo JP, Xie HP, Zhou HW, Peng SP (2010) SEM in situ investigation on thermal cracking behaviour of Pingdingshan sandstone at elevated temperatures. Geophys J Int 181:593–603. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04532.x
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51979208), the Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province (Grant No. 521CXTD444), and the China Scholarship Council Project (to the first author, No.202206950050).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (51979208), Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province (521CXTD444), China Scholarship Council (202206950050).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, H., Luo, Y., Wang, G. et al. Investigations of the Progressive Damage and Failure Behaviors of Thermally Treated Granite Under the Coupling Action of Biaxial Stress Constraint and High Strain Rate. Rock Mech Rock Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-024-03945-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-024-03945-z