Abstract
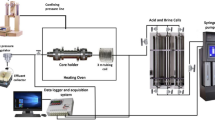
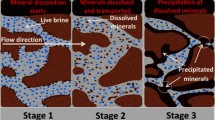
The key to groundwater restoration is to repair the mining-induced water-conducting fractures (WCF) in the overlying strata. In view of the difficulties faced by the traditional grouting sealing in solving this problem, the adsorption-consolidation sealing characteristics of chemical precipitation were used to conduct the permeability reduction experiments of CaCO3 on brown sandstone specimens with single fracture at room temperature. The aqueous solution of Na2CO3 was used as the simulated groundwater and that of CaCl2 was used as the repair reagent to simulate the water seepage conditions of fractured rock mass. Finally, the characteristics of permeability reduction in four rock specimens with different fracture development patterns were obtained under different ion concentrations. The experimental results show that CaCO3 could achieve significant repair effect in all the four rock specimens; no permeability rebound occurs even when the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet ends reaches up to 5 MPa and the permeability reduction amplitude is two orders of magnitude; in either experiment scheme, the permeability reduction rate displays a “slow → fast → slow” change process, which reflects the repair or blockage process of CaCO3 crystals. To be specific, this process consists of three stages: the adsorption and rooting, the growth and consolidation; the densification and scale formation. The more tortuous the seepage path on the fracture surface becomes and the greater the roughness/unevenness is and the smaller the fracture aperture is, the higher efficiency and better effect the permeability reduction will achieve; similarly, the slower the percentage of permeability reduction per unit time declines, the higher efficiency and better effect the permeability reduction will achieve. Once the key ion concentration in the precipitation reaction exceeds a critical value, the permeability reduction efficiency will not change significantly. the significant permeability reduction effect caused by CaCO3 precipitation usually appears in a certain pressure range, and its critical pressure value increases with the decrease of fracture aperture, but is basically not affected by ion concentration. The results can provide a reference for the restoration of aquifer ecological function by chemical precipitation for repairing mining-induced fractures in overburden.
Highlights
-
The key to groundwater restoration is to repair the water-conducting fractures.
-
CaCO3 precipitation can effectively repair and reduce permeability of fractures.
-
Four fractured specimens were used to test the repair effect of CaCO3 on fractures.
-
The rougher the fracture surface and the smaller the fracture aperture, the better the repair effect.
-
There exists a critical value of ion concentration in the precipitation reaction for the repair effect.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Al Nasser WN, Shaikh A, Morriss C, Hounslow MJ, Salman AD (2008) Determining kinetics of calcium carbonate precipitation by inline technique. Chem Eng Sci 63(5):1381–1389
Amadei B, Savage WZ (2001) An analytical solution for transient flow of Bingham viscoplastic materials in rock fractures. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 38(2):285–296
Bayesteh H, Sabermahani M (2020) Field study on performance of jet grouting in low water content clay. Eng Geol 237:105314
Ben Amor M, Zgolli D, Tlili MM, Manzola AS (2004) Influence of water hardness, substrate nature and temperature on heterogeneous calcium carbonate nucleation. Desalination 166(1–3):79–84
Bonacci O, Gottstein S, Roje-Bonacci T (2009) Negative impacts of grouting on the underground karst environment. Ecohydrology 2(4):492–502
Booth CJ (2006) Groundwater as an environmental constraint of longwall coal mining. Environ Geol 49(6):796–803
Chen T, Neville A, Yuan MD (2006) Influence of Mg2+ on CaCO3 formation-bulk precipitation and surface deposition. Chem Eng Sci 61(16):5318–5327
Colfen H, Qi LM (2001) A systematic examination of the morphogenesis of calcium carbonate in the presence of a double-hydrophilic block copolymer. Chem Eur J 7(1):106–116
Fan LM, Ma XD (2018) A review on investigation of water-preserved coal mining in western China. Int J Coal Sci Technol 5(4):411–416
Fleming IR, Rowe RK (2004) Laboratory studies of clogging of landfill leachate collection and drainage systems. Can Geotech J 41(1):134–153
Gothall R, Stille H (2010) Fracture–fracture interaction during grouting. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 25(3):199–204
Heinemann F, Gummich M, Radmacher M, Fritz M (2011) Modification of CaCO3 precipitation rates by water-soluble nacre proteins. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl 31(2):99–105
Ju JF, Li QS, Xu JL, Li JJ, Cao ZG (2020a) Experimental study on water permeability decrease character due to restoration function on chemical precipitation on holes or fractures in mining failure rock mass. Coal Sci Technol 48(2):89–96
Ju JF, Li QS, Xu JL, Wang XZ, Lou JF (2020b) Self-healing effect of water-conducting fractures due to water-rock interactions in undermined rock strata and its mechanisms. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79(1):287–297
Ju JF, Xu JL, Yang J (2021) Experimental study on the flow behavior of grout used in horizontal directional drilling borehole grouting to seal mining-induced overburden fractures. Geofluids 88:23902
Ketrane R, Saidani B, Gil O, Leleyter L, Baraud F (2009) Efficiency of five scale inhibitors on calcium carbonate precipitation from hard water: Effect of temperature and concentration. Desalination 249(3):1397–1404
Ma XM, Cui WG, Yang L, Yang YY, Chen HF, Wang K (2015) Efficient biosorption of lead(II) and cadmium(II) ions from aqueous solutions by functionalized cell with intracellular CaCO3 mineral scaffolds. Bioresour Technol 185:70–78
Mondal D, Roy PNS, Kumar M (2020) Monitoring the strata behavior in the destressed zone of a shallow Indian longwall panel with hard sandstone cover using mine-microseismicity and borehole televiewer data. Eng Geol 271:105593
Park D, Oh J (2018) Permeation grouting for remediation of dam cores. Eng Geol 233:63–75
Pavlakou EI, Sygouni V, Lioliou MG, Koutsoukos PG, Paraskeva CA (2016) Precipitation of sparingly soluble salts in packed sandbeds in the presence of miscible and immiscible organic substances. Cryst Res Technol 51(2):167–177
Poulsen BA, Adhikary D, Guo H (2018) Simulating mining-induced strata permeability changes. Eng Geol 237:208–216
Qu QD, Xu JL, Wu RL, Qin W, Hu GZ (2015) Three-zone characterisation of coupled strata and gas behaviour in multi-seam mining. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 78:91–98
Roels SM, El Chatib N, Nicolaides C, Zitha PLJ (2016) Capillary-driven transport of dissolved salt to the drying zone during CO2 injection in homogeneous and layered porous media. Transport Porous Med 111(2):411–424
Salimian HM, Baghbaban A, Hashemolhosseini H, Dehghanipoodeh M, Norouzi S (2017) Effect of grouting on shear behavior of rock joint. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 98:159–166
Solanki YS, Agarwal M, Gupta S, Shukla P, Maheshwari K, Midda MO (2019) Application of synthesized Fe/Al/Ca based adsorbent for defluoridation of drinking water and its significant parameters optimization using response surface methodology. J Environ Chem Eng 7(6):103465
Song XW, Cao YW, Bu XZ, Luo XP (2020) Porous vaterite and cubic calcite aggregated calcium carbonate obtained from steamed ammonia liquid waste for Cu2+ heavy metal ions removal by adsorption process. Appl Surf Sci 536(15):147958
van Beek CGEM (2018) Well-screen and well-head clogging by hydrous ferric oxides. Hydrogeol J 26(8):2919–2932
Zheng TW, Qian CX (2020) Influencing factors and formation mechanism of CaCO3 precipitation induced by microbial carbonic anhydrase. Process Biochem 91:271–281
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2020ZDPYMS19). The authors would acknowledge Professor Shaogang Lei and Dr. Yu Zhang for their help in data collection and processing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ju, J., Li, Q., Xu, J. et al. Experimental Investigations on the Effect of CaCO3 Precipitation on Permeability Reduction in Single Brown Sandstone Fracture. Rock Mech Rock Eng 56, 6647–6666 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03417-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03417-w