Abstract
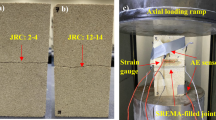
Soundless chemical demolition agents (SCDA), also known as expansive cement, represent a potentially viable method for fracturing rock without explosives. Traditionally, expansive cement is used for surface applications, such as block splitting in dimension stone quarries and demolition of concrete foundations. For deep underground applications, the major challenge with the use of expansive cement in an excavation face has been the presence of high biaxial stress field that would hinder the development of fractures in a mining face. This study aims to explore how expansive cement can be potentially used for rock fragmentation in deep underground environments. To do so, large-scale tests on 1 m × 1 m × 0.25 m concrete and granite panels with a novel drilling pattern are prepared, instrumented, and tested under biaxial confinement conditions. Test results show that the proposed drill pattern for expansive cement boreholes is capable of fracturing both panels under biaxial stresses. A 3D finite-difference modelling code FLAC3D 7.0 was developed and validated with observed panel breakage process and failure mechanisms. Both large-scale tests and numerical modelling show that expansive cement induces significant fracturing parallel to the loading plane. These findings should lay the groundwork and provide guidelines for the future application of expansive cement to underground hard rock excavations.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper.
References
Alvarez De La Garma, J. (2021). Numerical simulation of rock fracturing due to borehole expansive pressure under biaxial loading condition. Master of Science Thesis. McGill University. Montreal. Canada
Arjang B, Herget G (1997) In situ ground stresses in the Canadian hardrock mines: an update. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 34(3–4):15-e1
Chen T, Vennes I, Mitri HS (2022) Investigation into Rock Breakage with Expansive Cement Under Biaxial Confinement. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55(10):6263–6277
Cho H, Nam Y, Kim K, Lee J, Sohn D (2018) Numerical simulations of crack path control using soundless chemical demolition agents and estimation of required pressure for plain concrete demolition. Mater Struct 51(6):1–13
De Silva RV, Pathegama Gamage R, Anne Perera MS (2016) An alternative to conventional rock fragmentation methods using SCDA: a review. Energies 9(11):958
De Silva VRS, Ranjith PG, Perera MSA, Wu B, Rathnaweera TD (2017) Investigation of the mechanical, microstructural and mineralogical morphology of soundless cracking demolition agents during the hydration process. Mater Charact 130:9–24
De Silva VRS, Ranjith PG, Perera MSA, Wu B, Wanniarachchi WAM (2018) A low energy rock fragmentation technique for in-situ leaching. J Clean Prod 204:586–606
De Silva VRS, Ranjith PG, Perera MSA, Wu B (2019) The effect of saturation conditions on fracture performance of different soundless cracking demolition agents (SCDAs) in geological reservoir rock formations. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 62:157–170
Guo T, Zhang S, Ge H, Qu Z (2015) A novel" soundless cracking agent fracturing" for shale gas reservoir stimulation. Int J Environm Sci Develop 6(9):681
Habib KM, Shnorhokian S, Mitri HS (2022a) Evaluating the application of rock breakage without explosives in underground construction—a critical review of chemical demolition agents. Minerals 12(2):220
Habib K, Vennes I, Mitri HS (2022b) Laboratory investigation into the use of soundless chemical demolitions agents for the breakage of hard rock. Int J Coal Sci Technol. 9(1):701–10
Habib KM, Vennes I, Mitri HS (2023) Methodology for the estimation of expansive cement borehole pressure. Int J Min Sci Technol 33(1):73–81
Harada T, Idemitsu T, Watanabe A, Takayama SI (1989) The design method for the demolition of concrete with expansive demolition agents. In Fracture of Concrete and Rock, Springer, New York, NY
Hinze J, Brown J (1994) Properties of soundless chemical demolition agents. J Constr Eng Manag 120(4):816–827
Kim K, Cho H, Sohn D, Lee J (2021) The use of expansive chemical agents for concrete demolition: Example of practical design and application. Constr Build Mater 272:121849
Li Y, Li K, Feng X, Cai M (2018) Development and evaluation of artificial expandable pillars for hard rock mining. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 110:68–75
Li R, Yan Y, Jiang Z, Zheng W, Li G (2021) Impact of hole parameters and surrounding constraint on the expansive pressure distribution and development in soundless chemical demolition agents. Constr Build Mater 307:124992
Ma J, Du F, Zhang S (2020) Acoustic emission characteristics of normal and layered concrete blocks during dilating/static Fracture. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2020:14
Musunuri A, Mitri H (2009) Laboratory investigation into rock fracturing with expansive cement. Int J Min Mineral Eng 1(4):327–345
Natanzi AS, Laefer DF, Kakali G, Iman Zolanvari SM (2019) Temperature-induced chemical changes in soundless chemical demolition agents. J Mater Civ Eng 31(7):04019098
Natanzi, A. S., & Laefer, D. F. (2014). Using chemicals as demolition agents near historic structures. In 9th International Conference on Structural Analysis of Historical Constructions, Mexico City, Mexico, 14–17
Shang J, Hencher SR, West LJ, Handley K (2017) Forensic excavation of rock masses: a technique to investigate discontinuity persistence. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(11):2911–2928
Tang W, Zhai C, Xu J, Sun Y, Cong Y, Zheng Y (2021) The influence of borehole arrangement of soundless cracking demolition agents (SCDAs) on weakening the hard rock. Int J Min Sci Technol 31(2):197–207
Wang L, Duan K, Zhang Q, Li X, Jiang R (2022) Study of the dynamic fracturing process and stress shadowing effect in granite sample with two holes based on SCDA fracturing method. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55:1–17
Xu S, Hou P, Cai M, Li Y (2019) An experiment study on a novel self-swelling anchorage bolt. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:4855–4862
Xu S, Hou P, Li R, Cai M (2021a) An experimental study on the mechanical properties and expansion characteristics of a novel self-swelling cartridge for rock breakage. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54(2):819–832
Xu S, Yang Z, Cai M, Hou P (2021b) An experimental study on the anchoring characteristics of an innovative self-swelling Split-set. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 112:103919
Xu S, Hou P, Li R, Suorineni FT (2022) An improved outer pipe method for expansive pressure measurement of static cracking agents. Int J Min Sci Technol 32(1):27–39
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by a research grant from Natural Resources Canada, Clean Growth. Program, Grant No. CGP-17-1003 and industry partner Newmont Corporation. The authors are grateful for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T., Vennes, I. & Mitri, H.S. Biaxially Confined Rock Breakage with SCDA: Large-Scale Tests and Numerical Modelling. Rock Mech Rock Eng 56, 5525–5541 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03332-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03332-0