Abstract
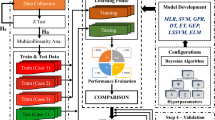
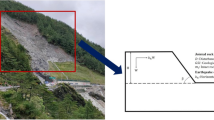
Shear strength criterion for rock discontinuities is a greatly important issue to most geoengineering analyses and designs. This paper aims to develop criteria and make a comparative study using statistical, lazy, and ensemble learning methods for fast predicting the shear strength of rock discontinuities. To do so, simple linear regression (SLR), multiple linear regression (MLR), least median squared regression (LMSR), isotonic regression (IR), pace regression (PR), k-nearest neighbors (kNN), and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) learning models are developed using compiled experimental data from direct shear tests based on commonly used variables in criteria. Statistical indices (RMSE, \({R}^{2}\), and MAE) and comparative analyses indicate that the adopted XGBoost model has a good generalization performance than other models. However, MLR- and PR-based-derived linear equations with \({R}^{2}\) = 0.98 and 0.96 for training and testing datasets are also promising new practical criteria. Interpretability and explainability of the proposed XGBoost model are demonstrated using feature important rank, partial dependence plots (PDPs), feature interaction, and local interpretable model-agnostic explanations (LIME) techniques. The Taylor diagram is also included to substantiate the capability of the developed data-driven surrogate models. Moreover, the proposed models provide satisfactory performance and comparable results to existing prediction models. Findings of this study will assist the geoengineers in estimating shear strength of rock discontinuities.
Highlights
-
Criteria developed to predict shear strength of rock discontinuities using statistical, lazy, and ensemble learning methods.
-
XGBoost showed best generalization performance, while MLR and PR-based equations were also promising practical criteria with high \({R}^{2}\) values.
-
XGBoost model's interpretability and explainability shown using various techniques.
-
Proposed models provide satisfactory performance and comparable results to existing prediction models.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data are provided within the manuscript.
References
Aha DW, Kibler D, Albert MK (1991) Instance-based learning algorithms. Mach Learn 6(1):37–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00153759
Babanouri N, Fattahi H (2018) Constitutive modeling of rock fractures by improved support vector regression. Environ Earth Sci 77(6):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7421-7
Babanouri N, Fattahi H (2020) An ANFIS–TLBO criterion for shear failure of rock joints. Soft Comput 24(7):4759–4773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04230-w
Barton N (1973) Review of a new shear-strength criterion for rock joints. Eng Geol 7(4):287–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(73)90013-6
Barton N, Choubey V (1977) The shear strength of rock joints in theory and practice. Rock Mech 10(1):1–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01261801
Chen T, Guestrin C (2016) Xgboost: a scalable tree boosting system. In: Proceedings of the 22nd acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 785–794
Cunningham P, Delany SJ (2021) k-nearest neighbour classifiers-A tutorial. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 54(6):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1145/3459665
De Leeuw J, Hornik K, Mair P (2010) Isotone optimization in R: pool-adjacent-violators algorithm (PAVA) and active set methods. J Stat Softw 32:1–24
Fathipour Azar H, Torabi SR (2014) Estimating fracture toughness of rock (KIC) using artificial neural networks (ANNS) and linear multivariable regression (LMR) models. In: 5th Iranian Rock Mechanics Conference
Fathipour-Azar H (2021a) Machine learning assisted distinct element models calibration: ANFIS, SVM, GPR, and MARS approaches. Acta Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-021-01303-9
Fathipour-Azar H (2021b) Data-driven estimation of joint roughness coefficient (JRC). J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 13(6):1428–1437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.09.003
Fathipour-Azar H (2022a) New interpretable shear strength criterion for rock joints. Acta Geotech 17:1327–1341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-021-01442-z
Fathipour-Azar H (2022b) Polyaxial rock failure criteria: Insights from explainable and interpretable data driven models. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55:2071–2089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02758-8
Fathipour-Azar H (2022c) Hybrid machine learning-based triaxial jointed rock mass strength. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10253-8
Fathipour-Azar H (2022d) Stacking ensemble machine learning-based shear strength model for rock discontinuity. Geotech Geol Eng 40:3091–3106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02081-1
Fathipour-Azar H (2022e) Data-oriented prediction of rocks’ Mohr-Coulomb parameters. Arch Appl Mech 92(8):2483–2494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-022-02190-6
Fathipour-Azar H (2022f) Multi-level machine learning-driven tunnel squeezing prediction: review and new insights. Arch Comput Methods Eng 29:5493–5509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-022-09774-z
Fathipour-Azar H (2023) Mean cutting force prediction of conical picks using ensemble learning paradigm. Rock Mech Rock Eng 56:221–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-03095-0
Fathipour-Azar H, Saksala T, Jalali SME (2017) Artificial neural networks models for rate of penetration prediction in rock drilling. J Struct Mech 50(3):252–255. https://doi.org/10.23998/rm.64969
Fathipour-Azar H, Wang J, Jalali SME, Torabi SR (2020) Numerical modeling of geomaterial fracture using a cohesive crack model in grain-based DEM. Comput Part Mech 7:645–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-019-00295-4
Friedman JH (2001) Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. Ann Stat. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1013203451
Friedman JH, Popescu BE (2008) Predictive learning via rule ensembles. Ann Appl Stat 2(3):916–954. https://doi.org/10.1214/07-AOAS148
Goldstein A, Kapelner A, Bleich J, Pitkin E (2015) Peeking inside the black box: visualizing statistical learning with plots of individual conditional expectation. J Comput Graph Statist 24(1):44–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/10618600.2014.907095
Grasselli G (2001) Shear strength of rock joints based on quantified surface description. Dissertation, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology.
Hasanipanah M, Meng D, Keshtegar B, Trung NT, Thai DK (2020) Nonlinear models based on enhanced Kriging interpolation for prediction of rock joint shear strength. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05252-4
Huang J, Zhang J, Gao Y (2021) Intelligently predict the rock joint shear strength using the support vector regression and firefly algorithm. Lithosphere. https://doi.org/10.2113/2021/2467126
Jaeger JC (1971) Friction of rocks and stability of rock slopes. Geotechnique 21(2):97–134. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1971.21.2.97
Johansson F, Stille H (2014) A conceptual model for the peak shear strength of fresh and unweathered rock joints. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 69:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.03.005
Kulatilake PHSW, Shou G, Huang TH, Morgan RM (1995) New peak shear strength criteria for anisotropic rock joints. Int Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 32(7):673–697. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(95)00022-9
Ladanyi B, Archambault G (1969) Simulation of shear behavior of a jointed rock mass. In: Proceedings of the 11th US symposium on rock mechanics (USRMS), Berkeley, CA, pp 105–125.
Lanaro F, Stephansson O (2003) A unified model for characterisation and mechanical behaviour of rock fractures. Pure Appl Geophys 160(5):989–998. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00012577
Li Y, Tang CA, Li D, Wu C (2020) A new shear strength criterion of three-dimensional rock joints. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(3):1477–1483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01976-5
Maksimović M (1996) The shear strength components of a rough rock joint. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 33(8):769–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(95)00005-4
Patton FD (1966) Multiple modes of shear failure in rock. In: Proceedings of the 1st ISRM Congress, Lisbon, pp 509–513.
Peng K, Amar MN, Ouaer H, Motahari MR, Hasanipanah M (2020) Automated design of a new integrated intelligent computing paradigm for constructing a constitutive model applicable to predicting rock fractures. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01173-x
Ribeiro MT, Singh S, Guestrin C (2016) “Why should i trust you?” Explaining the predictions of any classifier. Proc ACM SIGKDD Int Conf Knowl Discov Data Min 5:5. https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939778
Rousseeuw PJ (1984) Least median of squares regression. J Am Stat Assoc 79(388):871–880
Salanti G (2003) The isotonic regression framework: estimating and testing under order restrictions. Doctoral dissertation, Ludwig-Maximilians University of Munich, Munich, Germany
Seidel JP, Haberfield CM (1995) The application of energy principles to the determination of the sliding resistance of rock joints. Rock Mech Rock Eng 28(4):211–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01020227
Singh HK, Basu A (2018) Evaluation of existing criteria in estimating shear strength of natural rock discontinuities. Eng Geol 232:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.11.023
Tang ZC, Jiao YY, Wong LNY, Wang XC (2016) Choosing appropriate parameters for developing empirical shear strength criterion of rock joint: review and new insights. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(11):4479–4490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1014-0
Tatone BS (2009) Quantitative characterization of natural rock discontinuity roughness in-situ and in the laboratory. Master’s thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Toronto, Canada
Taylor KE (2001) Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J Geophys Res 106(D7):7183–7192. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JD900719
Tian Y, Liu Q, Liu D, Kang Y, Deng P, He F (2018) Updates to Grasselli’s peak shear strength model. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(7):2115–2133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1469-2
Wang Y, Witten IH (2002) Modeling for optimal probability prediction. In: Proceedings of the Nineteenth International Conference in Machine Learning, 2002, Sydney, Australia, pp 650–657
Wang H, Lin H (2018) Non-linear shear strength criterion for a rock joint with consideration of friction variation. Geotech Geol Eng 36(6):3731–3741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0567-y
Wang Y (2000) A new approach to fitting linear models in high dimensional spaces. Doctoral dissertation, University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand.
Witten IH, Frank E (2005) Data mining: practical machine learning tools and techniques. Morgan Kaufmann Pub, San Francisco
Xia CC, Tang ZC, Xiao WM, Song YL (2014) New peak shear strength criterion of rock joints based on quantified surface description. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47(2):387–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0395-6
Xia C, Huang M, Qian X, Hong C, Luo Z, Du S (2019) Novel intelligent approach for peak shear strength assessment of rock joints on the basis of the relevance vector machine. Math Probl Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3182736
Yang J, Rong G, Cheng L, Hou D, Wang X (2015) Experimental study of peak shear strength of rock joints. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 34(5):884–894
Yang J, Rong G, Hou D, Peng J, Zhou C (2016) Experimental study on peak shear strength criterion for rock joints. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(3):821–835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0791-1
Zhang WG, Li HR, Wu CZ, Li YQ, Liu ZQ, Liu HL (2020a) Soft computing approach for prediction of surface settlement induced by earth pressure balance shield tunneling. Undergr Space. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.undsp.2019.12.003
Zhang W, Zhang R, Wu C, Goh ATC, Lacasse S, Liu Z, Liu H (2020b) State-of-the-art review of soft computing applications in underground excavations. Geosci Front 11(4):1095–1106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2019.12.003
Zhang W, Zhang R, Wu C, Goh AT, Wang L (2020c) Assessment of basal heave stability for braced excavations in anisotropic clay using extreme gradient boosting and random forest regression. Underground Space. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.undsp.2020.03.001
Zhao J (1997) Joint surface matching and shear strength part B: JRC-JMC shear strength criterion. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 34(2):179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0148-9062(96)00063-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fathipour-Azar, H. Shear Strength Criterion for Rock Discontinuities: A Comparative Study of Regression Approaches. Rock Mech Rock Eng 56, 4715–4725 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03302-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03302-6