Abstract
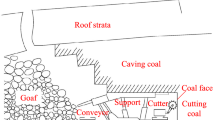
To investigate the temporal and spatial evolution process of overlying karst mountain instability caused by mining, the case of “8.28” mega landslide in Pusa, Nayong County, Guizhou Province, China, is taken as the example. Based on the results of the field investigation after the disaster, the complete process of rock strata fracture and slope instability under the descending and ascending mining conditions of gently inclined coal seam is reproduced by similitude model experiments. According to the key motion features of overburden deformation and fracture evolution law, the failure process of slope collapse controlled by deep and large karst fissures under mining action is summarized. And the change law of overburden pressure and displacement in the mining process is analyzed as well as the failure mode of slope collapse is proposed. The results show that the slope experiences four failure stages in the process of coal seam descending mining: coal seam roof caving, overburden cantilever tension fracture, overburden integral dumping subsidence and slope instability collapse, and the slope undergoes deformation toward the free surface and downward. During the ascending mining process, the slope experiences four failure stages: periodic caving of coal seam roof, upward transmission of separated fractures, overburden integral bending subsidence and slope instability collapse, and the slope undergoes deformation toward the inside of the slope and downward. The rock mass ahead of the advancing direction of working face has the phenomenon of tension–compression stress transformation. Along the mining direction, the overburden sequentially experiences the change process of pressure increase, decrease, or increase again, and stabilization. Deep and large karst fissures at the slope top are the structural basis for the occurrence of collapse. Coal mining activities have a certain promoting effect on mountain cracking and rock fragmentation. The failure mode of slope can be summarized as tension–shear–slip–toppling collapse failure. Improved understanding of the deformation movement characteristics and damage mode of slope can aid in early identification and timely warning of geo-hazards in karst area.
Highlights
-
This paper focuses on the deformation movement features and failure modes of mountains controlled by deep and large karst fissures under mining action.
-
The full process of rock strata fracture and slope instability under descending and ascending mining conditions is reproduced in a simulated model.
-
Extensive karst fissures at the slope top are the main structural basis for the occurrence of collapse.
-
Coal mining activities have a certain promoting effect on mountain cracking and rock fragmentation.
-
The failure mode of slopes can be summarized as tension-shear-slip-toppling collapse failure.



source area: a the dissolution cavities; b the dissolution pipelines; c the dissolution fissures; d the rock mass on the steep cliff wall is cut into blocks by well-developed joints

source area. In (a) and (b), A–E mark the zones of major sliding; I–III are different areas affected by instabilities

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekaert DPS, Handwerger AL, Agram P, Kirschbaum DB (2020) InSAR-based detection method for mapping and monitoring slow-moving landslides in remote regions with steep and mountainous terrain: an application to Nepal. Remote Sens Environ 249(1):111983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.111983
Benko B, Stead D (1998) The Frank slide: a reexamination of the failure mechanism. Can Geotech J 35(2):299–311. https://doi.org/10.1139/t98-005
Bentley SP, Siddle HJ (1996) Landslide research in the South Wales coalfield. Eng Geol 43(1):65–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(95)00084-4
Capparelli G, Damiano E, Greco R, Olivares L, Spolverino G (2019) Physical modeling investigation of rainfall infiltration in steep layered volcanoclastic slopes. J Hydrol 580:124199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124199
Chen SJ, Li YY, Guo WJ, Lu C, Wang HY, Yin DW (2015) Similar materials of colliery filling for physical simulation experiment. Mater Res Innov 19(S5):S5-304-S5-307. https://doi.org/10.1179/1432891714Z.0000000001098
Chen L, Fan SW, Zhao C, Zhang L, Cheng ZH (2019) Calculation method of overburden damage height based on fracture mechanics analysis of soft and hard rock layers. Geofluids 2019:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3790264
Chen L, Zhao C, Li B, He K, Ren C, Liu X, Liu D (2021) Deformation monitoring and failure mode research of mining-induced Jianshanying landslide in karst mountain area, China with ALOS/PALSAR-2 images. Landslides 18:2739–2750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01678-6
Cui FP, Li B, Xiong C, Yang ZP, Peng JQ, Li JS, Li HW (2022) Dynamic triggering mechanism of the Pusa mining-induced landslide in Nayong County, Guizhou Province, China. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 13(1):123–147. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2021.2017020
Cunningham DM (1988) A rockfall avalanche in a sandstone landscape, Nattai North, NSW. Australian Geogr 19(2):221–229. https://doi.org/10.1080/00049188808702961
Do TN, Wu JH (2019) Simulating a mining-triggered rock avalanche using DDA: a case study in Nattai North, Australia. Eng Geol 264:105386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105386
Do TN, Wu JH (2020a) Simulation of the inclined jointed rock mass behaviors in a mountain tunnel excavation using DDA. Comput Geotech 117:103249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.103249
Do TN, Wu JH (2020b) Verifying discontinuous deformation analysis simulations of the jointed rock mass behavior of shallow twin mountain tunnels. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 130(2):104322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104322
Du WG, Chai J, Zhang DD, Lei WL (2021) Application of optical fiber sensing technology in similar model test of shallow-buried and thick coal seam mining. Measurement 191(3):109559. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEASUREMENT.2021.109559
Eberhardt E, Thuro K, Luginbuehl K (2005) Slope instability mechanisms in dipping interbedded conglomerates and weathered marls-the 1999 Rufi landslide, Switzerland. Eng Geol 77(1–2):35–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2004.08.004
Egorov PV, Kalinin SI, Agudalin BP (2001) Technological and geomechanical parameters of room-and-pillar system of mining a thick flat seam. J Min Sci 37(5):472–474. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015166906969
Erginal AE, Türkeş M, Ertek TA, Baba A, Bayrakdar C (2008) Geomorphological investigation of the excavation-induced Dündar Landslide, Bursa-Turkey. Geogr Ann Ser B 90(2):109–123. https://doi.org/10.2307/40204885
Fan XM, Xu Q, Scaringi G, Zheng G, Huang RQ, Dai LX, Ju YZ (2019) The “long” runout rock avalanche in Pusa, China, on August 28, 2017: a preliminary report. Landslides 16:139–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1084-z
Feng Z, Li B, Cai QP, Cao JW (2016) Initiation Mechanism of the Jiweishan Landslide in Chongqing, Southwestern China. Environ Eng Geosci 22(4):341–351. https://doi.org/10.2113/gseegeosci.22.4.341
Fernández PR, Granda GR, Krzemień A, Cortés SG, Valverde GF (2020) Subsidence versus natural landslides when dealing with property damage liabilities in underground coal mines. Int J Rock Mech Min 126:104175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104175
Ghadafi MA, Toha MT, Setiabudidaya D (2017) Effect of ground vibration to slope stability, case study landslide on the mouth of railway tunnel Gunung Gajah Village Lahat District. Sriwijaya J Environ 2(3):67–71. https://doi.org/10.22135/sje.2017.2.3.67-71
He K, Gao Y, Wang WP, Zhu SN (2018) Physical model experimental study on deformation and failure of overlying rock slope under the condition of steep coal seam mining. J Geomech 24(3):399–406 (in Chinese)
Hu XL, He CC, Zhou C, Xu C, Zhang H, Wang Q, Wu SS (2019) Model test and numerical analysis on the deformation and stability of a landslide subjected to reservoir filling. Geofluids. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5924580
Kratcsch H (1986) Mining subsidence engineering. Environ Geol 8(3):133–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02509900
Lana MS (2014) Numerical modeling of failure mechanisms in phyllite mine slopes in Brazil. Int J Min Sci Technol 24(6):777–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2014.10.007
Li B, Feng Z, Wang GZ, Wan WP (2016) Processes and behaviors of block topple avalanches resulting from carbonate slope failures due to underground mining. Environ Earth Sci 75(8):694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5529-1
Li Y, Wang JP, Chen YD, Lei MX, Yang DP, Yang KP, Yuan YH (2020) Study on effect of interburden on movement of overburden in multiple coal seams. Coal Sci Technol 48(4):246–255 (in Chinese)
Liao Z, Feng T, Yu WJ, Wu GS, Li K, Gong FQ (2020) Experimental and theoretical investigation of overburden failure law of fully mechanized work face in steep coal seam. Adv Civil Eng 4:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8843172
Lin F, Wu LZ, Huang RQ, Zhang H (2018) Formation and characteristics of the Xiaoba landslide in Fuquan, Guizhou, China. Landslides 15(2):669–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0897-5
Liu TQ (1995) Influence of mining activities on mine rockmass and control engineering. J China Coal Soc 20(1):1–5 (in Chinese)
Liu CZ (2014) Genetic types of landslide and debris flow disasters in China. Geol Rev 60(4):858–868
Liu QC, Xiong CR, Ma JW (2015) Study of Guizhou Province Guanling Daz-Hai landslide instability process under the rainstorm. Appl Mech Mater 733:446–450. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.733.446
Liu H, Deng KZ, Zhu XJ, Jiang CL (2019) Effects of mining speed on the developmental features of mining-induced ground fissures. Bull Eng Geol Env 78:6297–6309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01532-z
Liu WT, Pang LF, Xu BC, Sun X (2020) Study on overburden failure characteristics in deep thick loose seam and thick coal seam mining. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 11(1):632–653. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2020.1737584
Lu GZ, Tang JQ, Song ZQ (2010) Difference between cyclic fracturing and cyclic weighting interval of transferring rock beams. Chinese J Geotech Eng 32(4):538–541 (in Chinese)
Ma GT, Hu XW, Yin YP, Luo G, Pan YX (2018) Failure mechanisms and development of catastrophic rockslides triggered by precipitation and open-pit mining in Emei, Sichuan, China. Landslides 15:1401–1414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-0981-5
Ma CQ, Yuan YF, Zha JL, Li HZ, Xu YY (2020) Determine method of effective experimental period of similar material model for improving the simulation results. Energy Sources A Recov Utilization Environ Effects. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1815909
Nie L, Li ZC, Zhang M, Xu LN (2015) Deformation characteristics and mechanism of the landslide in West Open-Pit Mine, Fushun China. Arab J Geosci 8(7):57–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1560-2
Ning JG, Wang J, Tan YL, Xu Q (2019) Mechanical mechanism of overlying strata breaking and development of fractured zone during close-distance coal seam group mining. Int J Min Sci Technol 30(2):207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2019.03.001
Ouyang G, Lan ZX (2009) Construction report design of collapse geological hazard treatment project of Pusa coal mine in Zhangjiawan town, Nayong County. Guizhou Dikuang Engineering Investigation Corporation, Guiyang (in Chinese)
Palchik V (2005) Localization of mining-induced horizontal fractures along rock layer interfaces in overburden: field measurements and prediction. J Environ Geol 48:68–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-005-1261-y
Palchik V (2015) Bulking factors and extents of caved zones in weathered overburden of shallow abandoned underground workings. J Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 79:227–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.07.005
Salmi EF, Nazem M, Karakus M (2017) Numerical analysis of a large landslide induced by coal mining subsidence. Eng Geol 217:141–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.12.021
Scaringi G, Fan XM, Xu Q, Liu C, Ouyang CJ, Domènech G, Yang F, Dai LX (2018) Some considerations on the use of numerical methods to simulate past landslides and possible new failures: the case of the recent Xinmo landslide (Sichuan, China). Landslides 15(7):1359–1375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-0953-9
Sebastian W, Peter T, James H (2014) New insights into the emplacement dynamics of volcanic island landslides. Oceanography 27(2):46–57. https://doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2014.39
Singh R, Singh TN (1999) Wide stall mining for optimal recovery of coal from a thick seam under surface features. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 36(2):155–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0148-9062(98)00177-6
Singhal BBS, Gupta RP (1999) Fractures and discontinuities. In: Singhal BBS, Gupta RP (eds) Applied hydrogeology of fractured rocks. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 13–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-9208-6_2
Sun Y, Yao B (1983) Research on failure mechanism of rockfall in Yanchi River phosphorite. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 1–7 (in Chinese)
Tangri A, Rawat S (2021) Soil nails for slope reinforcement: a lab-based model study. Mater Today Proc 1:728
Tao X, Tian H, Yang C (2015) Mining induced strata movement and roof behavior in underground coal mine. Geomech Geophys Geo-Energy Geo-Resour 1:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-015-0010-2
Tao ZG, Shu Y, Yang XJ, Peng YY, Chen QH, Zhang HJ (2020) Physical model test study on shear strength characteristics of slope sliding surface in Nanfen open-pit mine. Int J Min Sci Technol 3:421–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2020.05.006
Unrug K, Szwilski TB (1982) Methods of roof caveability prediction. State of the art of ground control in longwall mining and mining subsidence. AIME, New York, pp 13–29
Valentin G, Giona P, Erik E (2016) Numerical investigation of seismically induced rock mass fatigue as a mechanism contributing to the progressive failure of deep-seated landslides. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(6):2457–2478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0821-z
Wang C, Zhang NC, Han YF, Xiong ZQ, Qian DY (2015) Experiment research on overburden mining-induced fracture evolution and its fractal characteristics in ascending mining. Arab J Geosci 8(1):13–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1178-9
Wang HW, Xue S, Shi RM, Jiang YS, Gong WL, Mao LT (2019) Investigation of fault displacement evolution during extraction in longwall panel in an underground coal mine. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(10):1809–1826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-02015-z
Wang HW, Shi RM, Deng DX, Jiang YD, Wang G, Gong WL (2020) Characteristic of stress evolution on fault surface and coal bursts mechanism during the extraction of longwall face in Yima mining area, China. J Struct Geol 136(1):104071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2020.104071
Wu JH, Ohnishi Y, Nishiyama S (2004) Investigation on block displacements due to a shallow tunnel excavation in an inclined brick-type jointed rock mass using discontinuous deformation analysis. J Chin Inst Eng 27(3):307–314. https://doi.org/10.1080/02533839.2004.9670878
Wu K, Cheng GL, Zhou DW (2015) Experimental research on dynamic movement in strata overlying coal mines using similar material modeling. Arab J Geosci 8(9):6521–6534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1685-3
Wu LZ, Zhou Y, Sun P, Shi JS, Liu GG, Bai LY (2017) Laboratory characterization of rainfall-induced loess slope failure. CATENA 150:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.11.002
Wu QS, Jiang LS, Wu QL, Xue YC, Gong B (2018) A study on the law of overlying strata migration and separation space evolution under hard and thick strata in underground coal mining by similar simulation. DYNA 94(1):175–181. https://doi.org/10.6036/8678
Xiao RH, Chen HQ, Leng YY, Wei YJ, Wang WP (2018) Preliminary analysis on the failure process and mechanism of the August 28 collapse in Nayong County, Guizhou Province. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 29(1):3–9 (in Chinese)
Xu Q, Liu H, Ran J, Li W, Sun X (2016) Field monitoring of groundwater responses to heavy rainfalls and the early warning of the Kualiangzi landslide in Sichuan Basin, southwestern China. Landslides 13(6):1555–1570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0717-3
Xu Q, Li WL, Dong XJ, Xiao XX, Fan XM, Pei XJ (2017) The Xinmocun landslide on June 24, 2017 in Maoxian, Sichuan: characteristics and failure mechanism. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 36(11):2612–2628 (in Chinese)
Xue JH, Wang HP, Zhou W, Ren B, Duan CR, Deng DS (2015) Experimental research on overlying strata movement and fracture evolution in pillarless stress-relief mining. Int J Coal Sci Technol 2(1):38–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-015-0067-0
Yang ZP, Jiang YW, Li B, Gao Y, Liu XR, Zhao YL (2020) Study on the mechanism of deep and large fracture propagation and transfixion in karst slope under the action of mining. J Geomech 26(4):459–470 (in Chinese)
Yin YP, Liu CZ, Chen HQ, Ren J, Zhu CB (2013) Investigation on catastrophic landslide of January 11, 2013 at Zhaojiagou, Zhenxiong county, Yunnan province. J Eng Geol 21(1):6–15 (in Chinese)
Yin ZM, Liu XR, Yang ZP, Jiang YW, Zhao YL, Li SQ (2020) Shear characteristics and failure mode of hard brittle marl with parallel discontinuous structural plane. Arab J Sci Eng 45:8219–8229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04674-5
Yin ZM, Liu XR, Yang ZP, Wang YL (2021) Shear behavior of marlstone containing parallel fissure under normal unloading. KSCE J Civ Eng 25:1283–1294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-0959-z
Yu F, Liu SQ, Xu YC, Zhao L (2020) Failure analysis of thin bedrock and clay roof in underground coal mining: case study in Longdong coal mine. Int J Geomech 20(10):04020187. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001839
Yuan AY, Zhang ZQ, Li Y (2016) Study on the influence rule of underlying working face to overlying rock and high level tunnel. In: Proceedings of the 2015 2nd international conference on machinery, materials engineering, chemical engineering and biotechnology. https://doi.org/10.2991/mmeceb-15.2016.169
Zhang S, Xu Q, Hu Z (2016) Effects of rainwater softening on red mudstone of deepseated landslide, Southwest China. Eng Geol 204:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.01.013
Zhang Y, Cao SG, Guo SA, Wan T, Wang JJ (2018a) Mechanisms of the development of water-conducting fracture zone in overlying strata during shortwall block backfill mining: a case study in Northwestern China. Environ Earth Sci 77(14):543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7726-6
Zhang YQ, Tang HM, Li CD, Lu GY, Cai Y, Zhang JR, Tan FL (2018b) Design and testing of a flexible inclinometer probe for model tests of landslide deep displacement measurement. Sensors 18(1):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010224
Zheng D, Frost JD, Huang RQ, Liu FZ (2015) Failure process and modes of rockfall induced by underground mining: a case study of Kaiyang phosphorite mine rockfalls. Eng Geol 197:145–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.08.011
Zhong ZL, Wang NY, Li B, Liu XR, Cui FP, Yang ZP (2020) Experimental study on the deformation mechanism of upper-hard and lower-soft gently dipping rock on high slopes under the mining effect. Carsolog Sin 39(4):509–517 (in Chinese)
Zhou D, Ye YC, Hu NY, Wang WQ, Wang XH (2021) Crack evolution of soft-hard composite layered rock-like specimens with two fissures under uniaxial compression. Front Struct Civ Eng 15:1372–1389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-021-0772-2
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1504802), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41972266).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Zhao, Q., Liu, X. et al. Experimental Study on the Movement and Failure Characteristics of Karst Mountain with Deep and Large Fissures Induced by Coal Seam Mining. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55, 4839–4867 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-02910-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-02910-y