Abstract
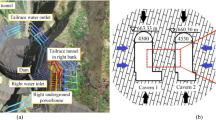
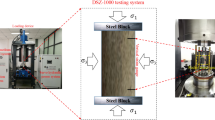
Understanding the time-dependent deformation and failure characteristics of columnar jointed rock masses (CJRM) exposed in the Baihetan hydropower station dam foundation is critical for the project’s long-term stability and safety. A series of short-term triaxial and cyclic loading creep tests for artificial CJRM specimens with various joint dip angles under a confining pressure of 5 MPa and pore pressure of 2 MPa were performed with a servo-controlled triaxial test. The influences of the joint dip angle on the short-term and creep mechanical behavior of the CJRM specimens were analyzed. The results show that the characteristic stresses, including the crack initiation stress (\(\sigma_{{{\text{ci}}}}\)), crack damage stress (\(\sigma_{{{\text{cd}}}}\)), peak strength (\(\sigma_{{\text{p}}}\)), residual strength (\(\sigma_{{\text{r}}}\)), long-term strength (\(\sigma_{\rm{L}}\)), and failure strength (\(\sigma_{{\text{f}}}\)), change with the joint dip angle in a U-shape pattern. The total axial strain comprises the instantaneous elastic strain, instantaneous plastic strain, visco-elastic strain, and visco-plastic strain, all of which depend on the joint dip angles and deviatoric stress levels. The visco-elastic strain converged to a particular value, and the visco-plastic strain increased with time. The steady-state creep strain rate increased exponentially with increasing stress ratio (\({\sigma \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\sigma {\sigma_{{\text{f}}} }}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {\sigma_{{\text{f}}} }}\)). Finally, three failure modes associated with joint dip angles were observed. Scanning electron microscope and energy dispersive spectroscopy tests were conducted on the failed CJRM specimens to examine the failure mechanism.
Highlights
• Short-term triaxial and cyclic loading creep tests on the artificial columnar jointed rock masses are performed.
• Short-term and creep anisotropic mechanical behavior of artificial columnar jointed rock masses are discussed.
• Failure modes and mechanism of the artificial columnar jointed rock masses are observed and revealed.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aydin A (2009) ISRM suggested method for determination of the schmidt hammer rebound hardness: revised version. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(3):627–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.01.020
Chen BR, Li QP, Feng XT, Xiao YX, Feng GL, Hu LX (2014) Microseismic monitoring of columnar jointed basalt fracture activity: a trial at the Baihetan hydropower station. China J Seismol 18(4):773–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-014-9445-0
Gatelier N, Pellet F, Loret B (2002) Mechanical damage of an anisotropic porous rock in cyclic triaxial tests. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 39(3):335–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(02)00029-1
Goehring L, Morris SW, Lin ZQ (2006) Experimental investigation of the scaling of columnar joints. Phys Rev e: Stat, Nonlin, Soft Matter Phys 74(3 Pt 2):036115. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.74.036115
Golewski GL (2019) A novel specific requirements for materials used in reinforced concrete composites subjected to dynamic loads. Compos Struct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.110939
Hatzor YH, Palchik V (1997) The influence of grain size and porosity on crack initiation stress and critical flaw length in dolomites. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 34(5):805–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1365-1609(96)00066-6
Hatzor YH, Feng XT, Li S, Gony YB, Jiang Q, Hu L (2015) Tunnel reinforcement in columnar jointed basalts: the role of rock mass anisotropy. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol 46:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2014.10.008
Ji H, Zhang JC, Xu WY, Wang RB, Wang HL, Yan L, Lin ZN (2017) Experimental investigation of the anisotropic mechanical properties of a columnar jointed rock mass: observations from laboratory-based physical modelling. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(7):1919–1931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1192-4
Jiang Q, Feng XT, Hatzor YH, Hao XJ, Li SJ (2014) Mechanical anisotropy of columnar jointed basalts: An example from the Baihetan hydropower station, China. Eng Geol 175:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.03.019
Jin CY, Yang CX, Fang D, Xu S (2014) Study on the failure mechanism of basalts with columnar joints in the unloading process on the basis of an experimental cavity. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48(3):1275–1288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-014-0625-6
Martin CD, Chandler NA (1994) The progressive fracture of Lac du Bonnet granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 31(6):643–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(94)90005-1
Muller G (1998) Experimental simulation of basalt columns. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 86:93–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-0273(98)00045-6
Schultz R (1995) Limits on strength and deformation properties of jointed basaltic rock masses. Rock Mech Rock Eng 28(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01024770
Shi AC, Wei YF, Zhang YH, Tang MF (2020) Study on the strength characteristics of columnar jointed basalt with a true triaxial apparatus at the Baihetan hydropower station. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(11):4947–4965. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02195-z
Tsai LS, Hsieh YM, Weng MC, Huang TH, Jeng FS (2008) Time-dependent deformation behaviors of weak sandstones. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 45:144–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2007.04.008
Wasantha PLP, Darlington WJ, Ranjith PG (2012) Characterization of mechanical behaviour of saturated sandstone using a newly developed triaxial apparatus. Exp Mech 53(5):871–882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-012-9690-5
Xiang ZP, Wang HL, Xu WY, Xie WC (2020) Experimental study on hydro-mechanical behaviour of anisotropic columnar jointed rock-like specimens. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(12):5781–5794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02245-6
Xiao YX, Feng XT, Chen BR, Feng GL, Yao ZB, Hu LX (2017) Excavation-induced microseismicity in the columnar jointed basalt of an underground hydropower station. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 97:99–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.04.012
Yang SQ, Hu B (2018) Creep and long-term permeability of a red sandstone subjected to cyclic loading after thermal treatments. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(10):2981–3004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1528-8
Zhang W, Chen JP, Cao ZX, Wang RY (2013) Size effect of RQD and generalized representative volume elements: a case study on an underground excavation in Baihetan dam, Southwest China. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol 35:89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2012.12.007
Zhang Y, Shao JF, Xu WY, Jia Y (2016) Time-dependent behavior of cataclastic rocks in a multi-loading triaxial creep test. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(9):3793–3803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-0948-6
Zhang T, Xu WY, Wang RB, Yan L, He MJ (2021) Deformation characteristics of cement mortar under triaxial cyclic loading: an experimental investigation. Int J Fatigue 150:106305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2021.106305
Zhao YL, Zhang LY, Wang WJ, Wan W, Li SQ, Ma WH, Wang YX (2017) Creep behavior of Intact and cracked Limestone under multi-Level loading and unloading cycles. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(6):1409–1424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1187-1
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFC0407004), the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51939004, 11772118, 11772116), and the 111 Project are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Xu, W., Wang, H. et al. Experimental Investigations on Short-Term and Creep Anisotropic Mechanical Behavior of Artificial Columnar Jointed Rock Masses. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55, 5393–5413 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-02880-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-02880-1