Abstract
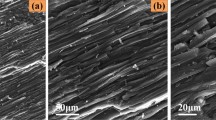
Liquid nitrogen (LN2) cooling can induce significant cracking damage in coalbed methane (CBM) reservoirs. To investigate the combined effects of LN2 cooling and bedding angles on the mechanical behaviors of bedded coal, coal specimens with different bedding angles (0°, 30°, 60° and 90°) were cooled. The variations in the surface features and P-wave velocity of the specimens were analyzed. The mechanical properties (tensile strength, peak strain and absorbed energy) were measured under Brazilian test conditions and compared. Furthermore, the crack propagation processes and the failure mechanisms were observed and compared. The results showed that LN2 cooling can induce considerable thermal damage inside the coal, resulting in the deterioration of the coal’s mechanical properties. This deterioration led to easier cracking and a higher fragmentation degree under splitting load. In addition, the reductions in tensile strength, peak strain and absorbed energy exhibited obvious anisotropic characteristics. The thermal cracks induced by LN2 cooling participated in the formation of macrocracks. After LN2 cooling, the failure mode remained unchanged from that before cooling at bedding angles of 0°, 30° and 90°. Notably, a transition from mixed-mode failure (primarily caused by tensile failure) to tensile failure occurred at the 60° bedding angle. This transition caused the specimen to fail at a relatively lower load, resulting in maximum reductions in tensile strength (34.8%), peak strain (27.6%) and absorbed energy (55.0%) at the 60° bedding angle. This paper provides new insights into the LN2 fracturing of bedded coal seams.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhondzadeh H, Keshavarz A, Al-Yaseri AZ, Ali M, Awan FUR, Wang X, Yang YF, Iglauer S, Lebedev M (2020) Pore-scale analysis of coal cleat network evolution through liquid nitrogen treatment: a micro-computed tomography investigation. Int J Coal Geol 219:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2019.103370
Alvarez-Ramirez RE, Echeverria JC (2005) Detrending fluctuation analysis based on moving average filtering. Phys A 354:199–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2005.02.020
Cai CZ, Li GS, Huang ZW, Shen ZH, Tian SC, Wei JW (2014a) Experimental study of the effect of liquid nitrogen cooling on rock pore structure. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 21:507–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2014.08.026
Cai CZ, Li GS, Huang ZW, Shen ZH, Tian SC (2014b) Rock pore structure damage due to freeze during liquid nitrogen fracturing. Arab J Sci Eng 39(12):9249–9257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1472-1
Cai CZ, Gao F, Li GS, Huang ZW, Tian SC, Shen ZH, Fu X (2015) Experiment of coal damage due to super-cooling with liquid nitrogen. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 22:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2014.11.016
Cai CZ, Gao F, Li GS, Huang ZW, Hou P (2016) Evaluation of coal damage and cracking characteristics due to liquid nitrogen cooling on the basis of the energy evolution law. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 29:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2015.12.041
Cao YH, Chen W, Yuan YN, Wang TX, Sun JF (2020) Experimental study of coalbed methane thermal recovery. Energy Sci Eng 8(5):1857–1867. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.637
Carpinteri A, Corrado M, Lacidogna G (2013) Heterogeneous materials in compression: correlations between absorbed, released and acoustic emission energies. Eng Fail Anal 33:236–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2013.05.016
Cheng JY, Wan ZJ, Zhang YD, Li WF, Peng SS, Zhang P (2015) Experimental study on anisotropic strength and deformation behavior of a coal measure shale under room dried and water saturated conditions. Shock Vib 2015:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/290293
Cho JW, Kim H, Jeon S, Min KB (2012) Deformation and strength anisotropy of Asan gneiss Boryeong shale, and Yeoncheon schist. Int J Rock Mech Min 50:158–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2011.12.004
Coetzee S, Neomagus HWJP, Bunt JR, Strydom CA, Schobert HH (2014) The transient swelling behaviour of large (− 20+16 mm) south African coal particles during low-temperature devolatilization. Fuel 136:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.07.021
Du ML, Gao F, Cai CZ, Su SJ, Wang ZK (2020) Study on the surface crack propagation mechanism of coal and sandstone subjected to cryogenic cooling with liquid nitrogen. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 81:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2020.103436
Duan MK, Jiang CB, Gan Q, Zhao HB, Yang Y, Li ZK (2020) Study of permeability anisotropy of bedded coal under true triaxial stress and its application. Trans Porous Med 131(3):1007–1035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-019-01375-y
Feng RM, Chen SN, Bryant S (2020a) Investigation of anisotropic deformation and stress-dependent directional permeability of coalbed methane reservoirs. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(2):625–639. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01932-3
Feng G, Kang Y, Wang XC, Hu YQ, Li XL (2020b) Investigation on the failure characteristics and fracture classification of shale under Brazilian test conditions. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(7):3325–3340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02110-6
Gong FQ, Luo S, Yan JY (2018) Energy storage and dissipation evolution process and characteristics of marble in three tension-type failure tests. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(11):3613–3624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1564-4
Grundmann SR, Rodvelt GD, Dials GA, Allen RE (1998) Cryogenic nitrogen as a hydraulic fracturing fluid in the Devonian shale. In: SPE Eastern Regional Meeting. https://doi.org/10.2118/51067-MS
Huang QM, Liu SM, Wang G, Cheng WM (2021) Evaluating the changes of sorption and diffusion behaviors of Illinois coal with various water-based fracturing fluid treatments. Fuel 283:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118884
Kordatos EZ, Aggelis DG, Matikas TE (2012) Monitoring mechanical damage in structural materials using complimentary NDE techniques based on thermography and acoustic emission. Compos Part B Eng 43(6):2676–2686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.12.013
Li YW, Zhang J, Liu Y (2016) Effects of loading direction on failure load test results for Brazilian tests on coal rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(6):2173–2180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0841-8
Li R, Wang SW, Lyu SF, Lu W, Li GF, Wang JC (2020a) Geometry and filling features of hydraulic fractures in coalbed methane reservoirs based on subsurface observations. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(5):2485–2492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02046-x
Li CY, Wu CZ, Jang BA (2020b) Effect of bedding plane on the permeability evolution of typical sedimentary rocks under triaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(11):5283–5291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02204-1
Li YT, Zhao YX, Jiang YD, Zhang B, Song HH, Liu B (2020c) Characteristics of pore and fracture of coal with bursting proneness based on DIC and fractal theory. Energies 13(20):1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13205404
Lin YB, Qin Y, Ma DM, Zhao JL (2020) Experimental research on dynamic variation of permeability and porosity of low-rank inert-rich coal under stresses. ACS Omega 5(43):28124–28135. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c03774
Liu YS, He CS, Wang SM, Peng YX, Lei Y (2020a) Dynamic splitting tensile properties and failure mechanism of layered slate. Adv Civ Eng 2020:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1073608
Liu XL, Liu Z, Li XB, Gong FQ, Du K (2020b) Experimental study on the effect of strain rate on rock acoustic emission characteristics. Int J Rock Mech Min 133:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104420
Ma TS, Peng N, Zhu Z, Zhang QB, Yang CH, Zhao J (2018) Brazilian tensile strength of anisotropic rocks: review and new insights. Energies 11(304):1–25. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11020304
McDaniel BW, Grundmann SR, Kendrick WD (1997) Field applications of cryogenic nitrogen as a hydraulic fracturing fluid. In: Proceedings-SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition 561–572. https://doi.org/10.2118/38623-MS
Qin L, Zhai C, Liu SM, Xu JZ, Tan ZQ, Yu GQ (2016) Failure mechanism of coal after cryogenic freezing with cyclic liquid nitrogen and its influences on coalbed methane exploitation. Energ Fuel 30(10):8567–8578. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b01576
Ren LF, Deng J, Li QW, Ma L, Zou L, Bin LW, Shu CM (2019) Low-temperature exothermic oxidation characteristics and spontaneous combustion risk of pulverised coal. Fuel 252:238–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.04.108
Ritter M, Huttel S, Odening M, Seifert S (2020) Revisiting the relationship between land price and parcel size in agriculture. Land Use Pol 97:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104771
Rodriguez P, Celestino TB (2019) Application of acoustic emission monitoring and signal analysis to the qualitative and quantitative characterization of the fracturing process in rocks. Eng Fract Mech 210:54–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.06.027
Samann F, Schanze T (2019) An efficient ECG denoising method using discrete wavelet with Savitzky-Golay filter. Curr Dir Biomed Eng 5(1):385–388. https://doi.org/10.1515/cdbme-2019-0097
Shao ZL, Ye S, Tao SJ, Feng XW, Wang Y (2021) Experimental study of the effect of liquid nitrogen penetration on damage and fracture characteristics in dry and saturated coals. J Petrol Sci Eng 201:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108374
Su SJ, Gao F, Cai CZ, Du ML, Wang ZK (2020) Experimental study on coal permeability and cracking characteristics under LN2 freeze-thaw cycles. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 83:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2020.103526
Tavallali A, Vervoort A (2010) Effect of layer orientation on the failure of layered sandstone under Brazilian test conditions. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47(2):313–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.01.001
Wang L, Yao BW, Cha MS, Alqahtani NB, Patterson TW, Kneafsey TJ, Miskimins JL, Yin XL, Wu YS (2016) Waterless fracturing technologies for unconventional reservoirs opportunities for liquid nitrogen. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 35:160–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2016.08.052
Wang Y, Tan WH, Liu DQ, Hou ZQ, Li CH (2019) On anisotropic fracture evolution and energy mechanism during marble failure under uniaxial deformation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(10):3567–3583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01829-1
Wegmueller SA, Leach NR, Townsend PA (2020) Loess radiometric correction for contiguous scenes (Loraccs): improving the consistency of radiometry in high-resolution satellite image mosaics. Int J Appl Earth Obs 97:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2020.102290
Wu XG, Huang ZW, Li R, Zhang SK, Wen HT, Huang PP, Dai XW, Zhang CC (2018) Investigation on the damage of high-temperature shale subjected to liquid nitrogen cooling. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 57:284–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2018.07.005
Wu XG, Huang ZW, Song HY, Zhang SK, Cheng Z, Li R, Wen HT, Huang PP, Dai XW (2019) Variations of physical and mechanical properties of heated granite after rapid cooling with liquid nitrogen. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(7):2123–2139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1727-3
Xiong WW, Yan L, Wang T, Gao YG (2020) Substitution effect of natural gas and the energy consumption structure transition in China. Sustainability 12(19):1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12197853
Yang SQ, Yin PF, Huang YH (2019) Experiment and discrete element modelling on strength, deformation and failure behaviour of shale under brazilian compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(11):4339–4359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01847-z
Yang H, Cheng YX, Li GH (2021) A denoising method for ship radiated noise based on Spearman variational mode decomposition, spatial-dependence recurrence sample entropy, improved wavelet threshold denoising, and Savitzky–Golay filter. Alex Eng J 60:3379–3400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.01.055
Yao QL, Chen T, Tang CJ, Sedighi M, Wang SW, Huang QX (2019) Influence of moisture on crack propagation in coal and its failure modes. Eng Geo 258:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105156
Yeh PT, Lee LZZ, Chang KT (2020) 3D Effects of permeability and strength anisotropy on the stability of weakly cemented rock slopes subjected to rainfall infiltration. Eng Geo 266:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105459
Zhai C, Qin L, Liu SM, Xu JZ, Tang ZQ, Wu SL (2016) Pore structure in coal: pore evolution after cryogenic freezing with cyclic liquid nitrogen injection and its implication on coalbed methane extraction. Energ Fuel 30(7):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b00920
Zhai SB, Su GS, Yin SD, Zhao B, Yan LB (2020) Rockburst characteristics of several hard brittle rocks: a true triaxial experimental study. J Rock Mech Geotech 12(2):276–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2019.07.013
Zhang SW, Shou KJ, Xian XF, Zhou JP, Liu GJ (2018) Fractal characteristics acoustic emission of anisotropic shale in Brazilian tests. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 71:298–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2017.08.031
Zhang ZY, Mao JC, Yang XJ, Zhao JZ, Smith GS (2019) Advances in waterless fracturing technologies for unconventional reservoirs. Energ Sour Part A 41(2):237–251. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2018.1514430
Zhou Z, Wang H, Cai X, Chen L, Cheng R (2019) Damage evolution and failure behavior of post-mainshock damaged rocks under aftershock effects. Energies 12(23):1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234429
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51934007 & 51604263); the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20160252); and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M650120).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MD and FG conceived and designed the study. MD and CC carried out the experiment. MD, SS and ZW analyzed results of experiment. MD wrote the paper. FG and CC reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, M., Gao, F., Cai, C. et al. Experimental Study on the Damage and Cracking Characteristics of Bedded Coal Subjected to Liquid Nitrogen Cooling. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54, 5731–5744 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02584-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02584-y