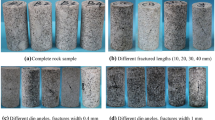
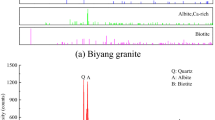
Abstract
Based on the research background of the damage of high-temperature jointed rock masses, this paper studies the mechanical properties of jointed granite under high-temperature conditions and analyzes the failure law of jointed rock masses with increasing temperature, decreasing temperature and types of joints. The results have important scientific and engineering value. The main research results are as follows: (1) high-temperature conditions change the mechanical properties of granite, especially when the temperature is higher than 400 °C, and the peak stress of granite decreases sharply; the change rate of the mechanical parameters of granite under the condition of water cooling is higher than that under the condition of natural cooling. (2) The uniaxial compressive strength of jointed granite increases with increasing angle α between the joint and the maximum principal plane, and the peak strength of intact granite is higher than that of jointed granite with either conjugate or echelon joints (referred to as conjugate or echelon jointed granite here). (3) The conjugate jointed granite exhibits three failure modes, in which the fractures are all tensile fractures; the echelon jointed granite exhibits three failure modes, most of which include tensile and shear fracturing.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- T :
-
Treatment temperature (°C)
- t :
-
Time of heating/cooling treatment (min)
- α :
-
Angle between joint and horizontal plane (°)
- 2a :
-
Length of joint (mm)
- 2b :
-
Length of rock bridge (mm)
- l :
-
Length of granite specimen (mm)
- d :
-
Width of granite specimen (mm)
- h :
-
Thickness of granite specimen (mm)
- σ p :
-
Peak stress (MPa)
- ε p :
-
Peak strain (%)
- E :
-
Elastic modulus (GPa)
- σ c -T/σ c-25 :
-
Ratio between the strength of jointed granite and that at 25 °C
- σ c -α/σ c-30 :
-
Ratio between the strength of jointed granite and that with α = 30°
References
Chen YL, Ni J, Shao W, Azzam R (2012) Experimental study on the influence of temperature on the mechanical properties of granite under uniaxial compression and fatigue loading. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 56:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.07.026
Christiansson R, Hudson JA (2003) ISRM suggested methods for rock stress estimation—part 4: quality control of rock stress estimation. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40(7–8):1021–1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2003.07.004
Duan ZF, Wang XY (2012) Study on optimal reinjection strategy of geothermal field: a case study from Tianjin, north China. Adv Mater Res 7:524–527. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.524-527.3165
Emirov SN, Ramazanova AE (2013) Experimental study of heat transfer on the borders of grains in ordered and disordered media. Bull Russ Acad Sci Phys 77(3):284–287. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1062873813030106
Fairhurst CE, Hudson JA (1999) Draft ISRM suggested method for the complete stress-strain curve for the intact rock in uniaxial compression. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 36:279–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0148-9062(99)00006-6
Hoek E (1983) Strength of jointed rock masses. Géotechnique 33(33):187–223
Huang YH, Yang SQ, Tian WL, Zhao J, Ma D, Zhang CS (2017) Physical and mechanical behavior of granite containing pre-existing holes after high temperature treatment. Arch Civ Mech Eng 17(4):912–925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2017.03.007
Lee H, Jeon S (2011) An experimental and numerical study of fracture coalescence in pre-cracked specimens under uniaxial compression. Int J Solids Struct 48(6):979–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2010.12.001
Liu S, Xu J (2014) Mechanical properties of Qinling biotite granite after high temperature treatment. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 71:188–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.07.008
Liu S, Xu J (2015) An experimental study on the physico-mechanical properties of two post-high-temperature rocks. Eng Geol 185(4):63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.11.013
Morgan SP, Johnson CA, Einstein HH (2013) Cracking processes in Barre granite: fracture process zones and crack coalescence. Int J Fract 180(2):177–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-013-9810-y
Nolter MA, Vice DH (2004) Looking back at the Centralia coal fire: a synopsis of its present status. Int J Coal Geol 59(1–2):99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2003.12.008
Shafiei A, Dusseault MB (2013) Geomechanics of thermal viscous oil production in sandstones. J Petrol Sci Eng 103:121–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2013.02.001
Shao SS, Ranjith PG, Wasantha PLP, Chen BK (2015) Experimental and numerical studies on the mechanical behaviour of Australian Strathbogie granite at high temperatures: an application to geothermal energy. Geothermics 54:96–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2014.11.005
Sirdesai NN, Mahanta B, Ranjith PG, Singh TN (2019) Effects of thermal treatment on physico-morphological properties of Indian fine-grained sandstone. Bull Eng Geol Env 78(2):883–897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1149-6
Smith AG, Pells PJN (2008) Impact of fire on tunnels in Hawkesbury sandstone. Tunnel Undergr Space Technol 23(1):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2006.11.003
Somerton WH, Boozer GD (1961) A method of measuring thermal diffusivities of rocks at elevated temperatures. AIChE J 7(1):87–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690070121
Steiger M, Charola AE, Sterflinger K (2011) Stone in architecture. Springer, Berlin
Sun Q, Zhang W, Xue L, Zhang Z, Su T (2015) Thermal damage pattern and thresholds of granite. Environ Earth Sci 74(3):2341–2349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4234-9
Sundberg J, Back PE, Christiansson R, Hökmark H, Ländell M, Wrafter J (2009) Modelling of thermal rock mass properties at the potential sites of a Swedish nuclear waste repository. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(6):1042–1054
Tang X, Wang M, Dong C, Tong J, Wang Y (2017) Sensitivity analysis for shear strength of flat interface between shotcrete and granite in high temperature tunnel. Int Conf Renew Energy Environ Technol. https://doi.org/10.2991/icreet-16.2017.27
Ulusay R (2014) The ISRM suggested methods for rock characterization, testing and monitoring: 2007–2014. Springer International Publishing 15(1):47–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07713-0
Voigt S, Tetzlaff A, Zhang J, Künzer C, Zhukov B, Strunz G, Oeter D, Roth A, Dijk P, Mehl H (2004) Integrating satellite remote sensing techniques for detection and analysis of uncontrolled coal seam fires in North China. Int J Coal Geol 59(1–2):121–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2003.12.013
Wang LL, Bornert M, Yang DS, Héripré E, Chanchole S, Halphen B, Pouya A, Caldemaison D (2015) Microstructural insight into the nonlinear swelling of argillaceous rocks. Eng Geol 193:435–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.05.019
Wang S, Liu J, Sun Y, Liu S, Gao X, Sun C, Li H (2018) Study on the geothermal production and reinjection mode in Xiong County. J Groundw Sci Eng 5(3):178–186. https://doi.org/10.19637/j.cnki.2305-7068.2018.03.003
Whitehouse AE, Mulyana AAS (2004) Coal fires in Indonesia. Int J Coal Geol 59(1–2):91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2003.08.010
Winkler EM (1997) Stone in architecture, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-10070-7
Wong LNY, Einstein HH (2009) Systematic evaluation of cracking behavior in specimens containing single flaws under uniaxial compression. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(2):239–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.03.006
Xu X, Karakus M (2018) A coupled thermo-mechanical damage model for granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 103:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.01.030
Yang SQ (2013) Study of strength failure and crack coalescence behavior of sandstone containing three pre-existing fissures. Rock Soil Mech 34(1):31–39
Yang SQ, Jing HW (2011) Strength failure and crack coalescence behavior of brittle sandstone samples containing a single fissure under uniaxial compression. Int J Fract 168(2):227–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-010-9576-4
Yang SQ, Yang DS, Jing HW, Li YH, Wang SY (2012) An experimental study of the fracture coalescence behavior of brittle sandstone specimens containing three fissures. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45(4):563–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-011-0206-x
Yang SQ, Jing HW, Huang YH, Ranjith PG, Jiao YY (2014) Fracture mechanical behavior of red sandstone containing a single fissure and two parallel fissures after exposure to different high temperature treatments. J Struct Geol 69:245–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2014.10.014
Yang SQ, Ranjith PG, Jing HW, Tian WL, Ju Y (2017) An experimental investigation on thermal damage and failure mechanical behavior of granite after exposure to different high temperature treatments. Geothermics 65:180–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2016.09.008
Yin Q, Jing HW, Zhu TT (2016) Experimental study on mechanical properties and cracking behavior of pre-cracked sandstone specimens under uniaxial compression. Indian Geotech J 47(3):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-016-0210-x
Zhang XP, Wong LNY (2013) Loading rate effects on cracking behavior of flaw-contained specimens under uniaxial compression. Int J Fract 180(1):93–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-012-9803-2
Zhang XP, Wong LNY, Wang S (2015) Effects of the ratio of flaw size to specimen size on cracking behavior. Annu Meeting Inst Geol Geophys Chin Acad Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-014-0596-6
Zhang F, Zhao J, Hu D, Skoczylas F, Shao J (2018) Laboratory investigation on physical and mechanical properties of granite after heating and water-cooling treatment. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(3):677–694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603017-1350-8
Zhang W, Sun Q, Zhang Y (2019) Effects of pre-existing cracks and temperature on failure mode of granite from Eastern China. J Struct Geol 126:330–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2019.06.018
Zhao F, Sun Q, Yang D, Zhang W (2019a) Thermal effects on failure characteristics of granite with pre-existing fissures. Geotech Res 6(4):302–311. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgere.19.00019
Zhao F, Sun Q, Pan XH (2019b) Effects of pre-existing fissures on surface macro-crack characteristics of granite subjected to elevated temperatures. Acta Geodyn Geomater 16(4):441–450. https://doi.org/10.13168/AGG.2019.0037
Zhou XP, Zhang JZ, Wong LNY (2018) Experimental study on the growth, coalescence and wrapping behaviors of 3d cross-embedded flaws under uniaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51:1379–1400. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-1508(06)60035-1
Zhu TT, Jing HW, Su HJ (2016) Physical and mechanical properties of sandstone containing a single fissure after exposure to high temperatures. Int J Min Sci Technol 26(02):142–148 ((CNKI:SUN:ZHKD.0.2016-02-018))
Zhu ZN, Tian H, Jiang GS, Cheng W (2018) Effects of high temperature on the mechanical properties of Chinese marble. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(6):1937–1942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1426-0
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41672279, 41972288) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2019YFC1509702). We also thank the technicians who helped during the experiments and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, F., Shi, Z. & Sun, Q. Fracture Mechanics Behavior of Jointed Granite Exposed to High Temperatures. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54, 2183–2196 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02393-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02393-3