Abstract
Purpose
The association between perioperative and post-adjuvant carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) levels and recurrence and prognosis remains unclear. We aimed to evaluate whether perioperative CEA levels are an integral component of the assessment of recurrence and prognosis of patients with stage III colon cancer (CC).
Methods
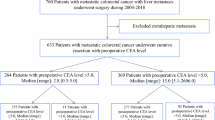
This retrospective study was conducted at the Cancer Institute Hospital of the Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research from 2005 to 2013. We enrolled patients with stage III CC who underwent complete resection of a primary tumor and received adjuvant chemotherapy. We analyzed the association between perioperative and post-adjuvant CEA levels and recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS).
Results
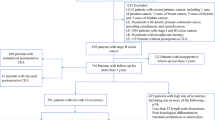
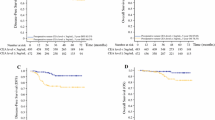
A total of 564 consecutive patients were included in the analysis. The RFS and OS of patients with high postoperative CEA levels were significantly worse than those of patients with normal postoperative CEA levels. In the multivariate analysis, high postoperative CEA levels were associated with shorter RFS and OS. The number of risk factors, postoperative CEA levels, and T/N-stage all had a cumulative effect on RFS and OS.
Conclusions
High postoperative CEA levels and the number of risk factors are associated with recurrence and worse prognosis for patients with stage III CC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. Cancer today. 2020. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home. Accessed 24 May 2023.
Grothey A, Sobrero AF, Shields AF, Yoshino T, Paul J, Taieb J, et al. Duration of adjuvant chemotherapy for Stage III colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1177–88.
Yoshino T, Argilés G, Oki E, Martinelli E, Taniguchi H, Arnold D, et al. Pan-Asian adapted ESMO clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis treatment and follow-up of patients with localised colon cancer. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:1496–510.
Cohen R, Taieb J, Fiskum J, Yothers G, Goldberg R, Yoshino T, et al. Microsatellite instability in patients with Stage III colon cancer receiving fluoropyrimidine with or without oxaliplatin: an accent pooled analysis of 12 adjuvant trials. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:642–51.
Meyerhardt JA, Mangu PB, Flynn PJ, Korde L, Loprinzi CL, Minsky BD, et al. Follow-up care, surveillance protocol, and secondary prevention measures for survivors of colorectal cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline endorsement. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:4465–70.
Argilés G, Tabernero J, Labianca R, Hochhauser D, Salazar R, Iveson T, et al. Localised colon cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:1291–305.
Gold P, Freedman SO. Demonstration of tumor-specific antigens in human colonic carcinomata by immunological tolerance and absorption techniques. J Exp Med. 1965;121:439–46.
Gold P, Freedman SO. Specific carcinoembryonic antigens of the human digestive system. J Exp Med. 1965;122:467–81.
Kuroki M, Arakawa F, Yamamoto H, Shimura H, Ikehara Y, Matsuoka Y. Active production and membrane anchoring of carcinoembryonic antigen observed in normal colon mucosa. Cancer Lett. 1988;43:151–7.
Saito G, Sadahiro S, Kamata H, Miyakita H, Okada K, Tanaka A, et al. Monitoring of serum carcinoembryonic antigen levels after curative resection of colon cancer: cutoff values determined according to preoperative levels enhance the diagnostic accuracy for recurrence. Oncology. 2017;92:276–82.
Huh JW, Oh BR, Kim HR, Kim YJ. Preoperative carcinoembryonic antigen level as an independent prognostic factor in potentially curative colon cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2010;101:396–400.
Takagawa R, Fujii S, Ohta M, Nagano Y, Kunisaki C, Yamagishi S, et al. Preoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen level as a predictive factor of recurrence after curative resection of colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:3433–9.
Auclin E, André T, Taieb J, Banzi M, Van Laethem JL, Tabernero J, et al. Association of post-operative CEA with survival and oxaliplatin benefit in patients with stage II colon cancer: a post hoc analysis of the Mosaic trial. Br J Cancer. 2019;121:312–7.
Konishi T, Shimada Y, Hsu M, Tufts L, Jimenez-Rodriguez R, Cercek A, et al. Association of preoperative and postoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen and colon cancer outcome. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:309–15.
Lin JK, Lin CC, Yang SH, Wang HS, Jiang JK, Lan YT, et al. Early postoperative CEA level is a better prognostic indicator than is preoperative CEA level in predicting prognosis of patients with curable colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2011;26:1135–41.
Jeffery M, Hickey BE, Hider PN. Follow-up strategies for patients treated for non-metastatic colorectal cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;9:CD002200.
Treasure T, Monson K, Fiorentino F, Russell C. The CEA second-look trial: a randomised controlled trial of carcinoembryonic antigen prompted reoperation for recurrent colorectal cancer. BMJ Open. 2014;4:e004385.
Weiser MR. AJCC 8th edition: colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25:1454–5.
Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013;48:452–8.
Ito K, Hibi K, Ando H, Hidemura K, Yamazaki T, Akiyama S, et al. Usefulness of analytical CEA doubling time and half-life time for overlooked synchronous metastases in colorectal carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2002;32:54–8.
Choi JS, Min JS. Significance of postoperative serum level of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and actual half-life of CEA in colorectal cancer patients. Yonsei Med J. 1997;38:1–7.
Yang KM, Park IJ, Kim CW, Roh SA, Cho DH, Kim JC. The prognostic significance and treatment modality for elevated pre- and postoperative serum CEA in colorectal cancer patients. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2016;91:165–71.
Nicholson BD, Shinkins B, Pathiraja I, Roberts NW, James TJ, Mallett S, et al. Blood CEA levels for detecting recurrent colorectal cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;12:CD011134.
Hara M, Kanemitsu Y, Hirai T, Komori K, Kato T. Negative serum carcinoembryonic antigen has insufficient accuracy for excluding recurrence from patients with Dukes C colorectal cancer: analysis with likelihood ratio and posttest probability in a follow-up study. Dis Colon Rectum. 2008;51:1675–80.
Zeng Z, Cohen AM, Urmacher C. Usefulness of carcinoembryonic antigen monitoring despite normal preoperative values in node-positive colon cancer patients. Dis Colon Rectum. 1993;36:1063–8.
Bhattacharjya S, Aggarwal R, Davidson BR. Intensive follow-up after liver resection for colorectal liver metastases: Results of combined serial tumour marker estimations and computed tomography of the chest and abdomen—a prospective study. Br J Cancer. 2006;95:21–6.
Margalit O, Mamtani R, Yang YX, Reiss KA, Golan T, Halpern N, et al. Assessing the prognostic value of carcinoembryonic antigen levels in stage I and II colon cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2018;94:1–5.
Nicholson BD, Shinkins B, Mant D. Blood measurement of carcinoembryonic antigen level for detecting recurrence of colorectal cancer. JAMA. 2016;316:1310–1.
Schøler LV, Reinert T, Ørntoft MW, Kassentoft CG, Árnadóttir SS, Vang S, et al. Clinical implications of monitoring circulating tumor DNA in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:5437–45.
Fan G, Zhang K, Yang X, Ding J, Wang Z, Li J. Prognostic value of circulating tumor DNA in patients with colon cancer: systematic review. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0171991.
Lecomte T, Berger A, Zinzindohoué F, Micard S, Landi B, Blons H, et al. Detection of free-circulating tumor-associated DNA in plasma of colorectal cancer patients and its association with prognosis. Int J Cancer. 2002;100:542–8.
Tie J, Wang Y, Tomasetti C, Li L, Springer S, Kinde I, et al. Circulating tumor DNA analysis detects minimal residual disease and predicts recurrence in patients with stage II colon cancer. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8:346ra92.
Osumi H, Shinozaki E, Yamaguchi K, Zembutsu H. Clinical utility of circulating tumor DNA for colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2019;110:1148–55.
Vidal J, Muinelo L, Dalmases A, Jones F, Edelstein D, Iglesias M, et al. Plasma ctDNA RAS mutation analysis for the diagnosis and treatment monitoring of metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2017;28:1325–32.
Bettegowda C, Sausen M, Leary RJ, Kinde I, Wang Y, Agrawal N, et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:224ra24.
Reinert T, Henriksen TV, Christensen E, Sharma S, Salari R, Sethi H, et al. Analysis of plasma cell-free DNA by ultradeep sequencing in patients with stages I to III colorectal cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:1124–31.
Tarazona N, Gimeno-Valiente F, Gambardella V, Zuñiga S, Rentero-Garrido P, Huerta M, et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing of circulating-tumor DNA for tracking minimal residual disease in localized colon cancer. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:1804–12.
Osumi H, Shinozaki E, Ooki A, Shimozaki K, Kamiimabeppu D, Nakayama I, et al. Correlation between circulating tumor DNA and carcinoembryonic antigen levels in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Med. 2021;10:8820–82.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the patients who participated in this study, their families, and all investigators. We also thank Ms. Hitomi Hannan, Ms. Yukie Naito, and Ms. Yuki Horiike for data management.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Kensei Yamagushi received honoraria from Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Eli Lilly, Japan K.K., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., and Bristol-Myers Squibb Co. Kensei Yamagushi received funding from Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Eiji Shinozaki received honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. and Yakult Honsha Co. Shohei Udagawa, Hiroki Osumi, Ryotaro Kozuki, Akira Ooki, Takeru Wakatsuki, Nozomi Kurihara, Toshiki Mukai, Tomohiro Yamaguchi, Takashi Akiyoshi, and Yosuke Fukunaga have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Udagawa, S., Osumi, H., Kozuki, R. et al. Clinical utility of the carcinoembryonic antigen level in patients with stage III colon cancer after surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy. Surg Today (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-023-02779-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-023-02779-6