Abstract
Purposes
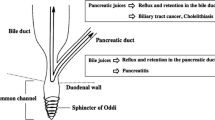
Congenital biliary dilatation (CBD), defined as pancreaticobiliary maljunction (PBM) with biliary dilatation, is a high risk factor for biliary tract cancer (BTC). KRAS and p53 mutations reportedly affect this process, but the mechanisms are unclear, as is the likelihood of BTC later in life in children with CBD. We investigated potential carcinogenetic pathways in children with CBD compared with adults.
Methods
The subjects of this study were nine children with CBD and 13 adults with PBM (10 dilated, 3 non-dilated) without BTC who underwent extrahepatic bile duct resections, as well as four control patients who underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy for non-biliary cancer. We evaluated expressions of Ki-67, KRAS, p53, histone deacetylase (HDAC) and activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) in the biliary tract epithelium immunohistochemically.
Results
The Ki-67 labeling index (LI) and expressions of KRAS, p53, HDAC, and AID in the gallbladder epithelium were significantly higher or tended to be higher in both the children with CBD and the adults with PBM than in the controls.
Conclusions
BTC may develop later in children with CBD and in adults with PBM, via HDAC and AID expression and through epigenetic and genetic regulation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AID:
-
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase
- BTC:
-
Biliary tract cancer
- CBD:
-
Congenital biliary dilatation
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase
- HDACs:
-
Histone deacetylases
- LI:
-
Labeling index
- PBM:
-
Pancreaticobiliary maljunction
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
Tashiro S, Imaizumi T, Ohkawa H, Okada A, Katoh T, Kawaharada Y, et al. Pancreaticobiliary maljunction: retrospective and nationwide survey in Japan. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2003;10(5):345–51.
Tsuchida A, Itoi T, Aoki T, Koyanagi Y. Carcinogenetic process in gallbladder mucosa with pancreaticobiliary maljunction. Oncol Rep. 2003;10(6):1693–9.
Funabiki T, Matsubara T, Miyakawa S, Ishihara S. Pancreaticobiliary maljunction and carcinogenesis to biliary and pancreatic malignancy. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2009;394(1):159–69.
Tanno S, Obara T, Fujii T, Mizukami Y, Shudo R, Nishino N, et al. Proliferative potential and k-ras mutation in epithelial hyperplasia of the gallbladder in patients with anomalous pancreaticobiliary ductal union. Cancer. 1998;83(2):267–75.
Nagai M, Watanabe M, Iwase T, Yamao K, Isaji S. Clinical and genetic analysis of noncancerous and cancerous biliary epithelium in patients with pancreaticobiliary maljunction. World J Surg. 2002;26(1):91–8.
Matsubara T, Sakurai Y, Zhi L-Z, Miura H, Ochiai M, Funabiki T. K-ras and p-53 gene mutations in noncancerous biliary lesions of patients with pancreatico biliary maljunction. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2002;9(3):312–21.
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Egawa N, Nakajima H, Tsuruta K, et al. Pathologic changes in the non-carcinomatous epithelium of the gallbladder in patients with a relatively long common channel. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;60(1):56–60.
Haberland M, Montgomery RL, Olson EN. The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and physiology: implications for disease and therapy. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10(1):32–42.
Minucci S, Pelicci PG. Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(1):38–51.
Glozak MA, Seto E. Histone deacetylases and cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26(37):5420–32.
Patra SK, Patra A, Dahiya R. Histone deacetylase and DNA methyltransferase in human prostate cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;287(3):705–13.
Zhu P, Martin E, Mengwasser J, Schlag P, Janssen KP, Göttlicher M. Induction of HDAC2 expression upon loss of APC in colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2004;5(5):455–63.
Lin RJ, Nagy L, Inoue S, Shao W, Miller WH Jr, Evans RM. Role of the histone deacetylase complex in acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 1998;391(6669):811–4.
Miyatani T, Kurita N, Mikami C, Kashihara H, Higashijima J, Yoshikawa K, et al. Malignant potential of Barrett’s esophagus: special reference to HDAC-1 and MTA-1 expression. Hepatogastroenterology. 2011;58(106):472–6.
Zhang H, Yang B, Pomerantz RJ, Zhang C, Arunachalam SC, Gao L. The cytidine deaminase CEM15 induces hypermutation in newly synthesized HIV-1 DNA. Nature. 2003;424(6944):94–8.
Honjo T, Kinoshita K, Muramatsu M. Molecular mechanism of class switch recombination: linkage with somatic hypermutation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:165–96.
Wedekind JE, Dance GS, Sowden MP, Smith HC. Messenger RNA editing in mammals: new members of the APOBEC family seeking roles in the family business. Trends Genet. 2003;19(4):207–16.
Cascalho M. Advantages and disadvantages of cytidine deamination. J Immunol. 2004;172(11):6513–8.
Kinoshita K, Nonaka T. The dark side of activation-induced cytidine deaminase: relationship with leukemia and beyond. Int J Hematol. 2006;83(3):201–7.
Matsumoto Y, Marusawa H, Kinoshita K, Endo Y, Kou T, Morisawa T, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection triggers aberrant expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase in gastric epithelium. Nat Med. 2007;13(4):470–6.
Li M, Liu W, Zhu YF, Chen YL, Zhang BZ, Wang R. Correlation of COX-2 and K-ras expression to clinical outcome in gastric cancer. Acta Oncol. 2006;45(8):1115–9.
Theocharis S, Klijanienko J, Giaginis C, Rodriguez J, Jouffroy T, Girod A, et al. Histone deacetylase-1 and -2 expression in mobile tongue squamous cell carcinoma: associations with clinicopathological parameters and patients survival. J Oral Pathol Med. 2011;40(9):706–14.
Nakanishi Y, Kondo S, Wakisaka N, Tsuji A, Endo K, Murono S, et al. Role of activation-induced cytidine deaminase in the development of oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(4):e62066.
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Sneige N, Buzdar AU, Valero V, Kau SW, Broglio K, et al. p53 expression as a prognostic marker in inflammatory breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(18 Pt 1):6215–21.
Kato T, Matsuda K, Kayaba H, Enomoto S, Hebiguchi T, Koyama K, et al. Pathology of anomalous junction of the pancreaticobiliary ductal system: mutagenicity of the contents of the biliary tract and nuclear atypia of the biliary epithelium. Keio J Med. 1989;38(2):167–76.
Kamisawa T, Kurata M, Honda G, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A. Biliopancreatic reflux-pathophysiology and clinical implications. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2009;16(1):19–24.
Shimada K, Yanagisawa J, Nakayama F. Increased lysophosphatidylcholine and pancreatic enzyme content in bile of patients with anomalous pancreaticobiliary ductal junction. Hepatology. 1991;13(3):438–44.
Tsuchida A, Itoi T. Carcinogenesis and chemoprevention of biliary tract cancer in pancreaticobiliary maljunction. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2010;2(3):130–5.
Kamisawa T, Kuruma S, Chiba K, Tabata T, Koizumi S, Kikuyama M. Biliary carcinogenesis in pancreaticobiliary maljunction. J Gastroenterol. 2017;52(2):158–63.
Morine Y, Shimada M, Takamatsu H, Araida T, Endo I, Kubota M, et al. Clinical features of pancreaticobiliary maljunction: update analysis of 2nd Japan-nationwide survey. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2013;20(5):472–80.
Hanada K, Itoh M, Fujii K, Tsuchida A, Ooishi H, Kajiyama G. K-ras and p53 mutations in stage I gallbladder carcinoma with an anomalous junction of the pancreaticobiliary duct. Cancer. 1996;77(3):452–8.
Singh MK, Chetri K, Pandey UB, Kapoor VK, Mittal B, Choudhuri G. Mutational spectrum of K-ras oncogene among Indian patients with gallbladder cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;19(8):916–21.
Tazuma S, Kajiyama G. Carcinogenesis of malignant lesions of the gall bladder: the impact of chronic inflammation and gallstones. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2001;386(3):224–9.
Tomono H, Nimura Y, Aono K, Nakashima I, Iwamoto T, Nakashima N. Point mutations of the c-Ki-ras gene in carcinoma and atypical epithelium associated with congenital biliary dilatation. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91(6):1211–4.
Matsubara T, Funabiki T, Jinno O, Sakurai Y, Hasegawa S, Imazu H, et al. p53 gene mutations and overexpression of p53 product in cancerous and noncancerous biliary epithelium in patients with pancreaticobiliary maljunction. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1999;6(3):286–93.
Wistuba II, Gazdar AF. Gallbladder cancer: lessens from rare tumour. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(9):695–706.
Weichert W. HDAC expression and clinical prognosis in human malignancies. Cancer Lett. 2009;280(2):168–76.
Shukla S, Khan S, Kumar S, Sinha S, Farhan M, Bora HK, et al. Cucurbitacin B alters the expression of tumor-related genes by epigenetic modifications in NSCLC and inhibits NNK-induced lung tumorigenesis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2015;8(6):552–62.
Tong X, Yin L, Giardina C. Butylrate suppresses Cox-2 activation in colon cancer cells through HDAC inhibition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;317(2):463–71.
Biran A, Brownstein M, Haklai R, Kloog Y. Downregulation of survivin and aurora A by histone deacetylase and RAS inhibitors: a new drug combination for cancer therapy. Int J Cancer. 2011;128(3):691–701.
Toh Y, Nicolson GL. The role of the MTA family and their encoded proteins in humancancers: molecular functions and clinical implications. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2009;26(3):215–27.
Søreide K, Søreide JA. Bile duct cyst as precursor to biliary tract cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14(3):1200–11.
Chaudhuri J, Alt FW. Class-switch recombination: interplay of transcription, DNA deamination and DNA repair. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4(7):541–52.
Muramatsu M, Kinoshita K, Fagarasan S, Yamada S, Shinkai Y, Honjo T. Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell. 2000;102(5):553–63.
Endo Y, Marusawa H, Kou T, Nakase H, Fujii S, Fujimori T, et al. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase links between inflammation and the development of colitis-associated colorectal cancers. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(3):889–98.
Komori J, Marusawa H, Machimoto T, Endo Y, Kinoshita K, Kou T, et al. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase links bile duct inflammation to human cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 2008;47(3):888–96.
Morita S, Matsumoto Y, Okuyama S, Ono K, Kitamura Y, Tomori A, et al. Bile acid-induced expression of activationinduced cytidine deaminase during the development of Barrett’s oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32(11):1706–12.
Kou T, Marusawa H, Kinoshita K, Endo Y, Okazaki IM, Ueda Y, et al. Expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase in human hepatocytes during hepatocarcinogenesis. Int J Cancer. 2007;120(3):469–76.
Morisawa T, Marusawa H, Ueda Y, Iwai A, Okazaki IM, Honjo T, et al. Organ-specific profiles of genetic changes in cancers caused by activation-induced cytidine deaminase expression. Int J Cancer. 2008;123(12):2735–40.
Ono S, Tokiwa K, Iwai N. Cellular activity in the gallbladder of children with anomalous arrangement of the pancreaticobiliary duct. J pediatr surg. 1999;34(6):962–6.
Saikusa N, Naito S, Iinuma Y, Ohtani T, Yokoyama N, Nitta K. Invasive cholangiocarcinoma identified in congenital biliary dilatation in a 3-year-old boy. J Pediatr Surg. 2009;44(11):2202–5.
Nakamura H, Katayose Y, Rikiyama T, Onogawa T, Yamamoto K, Yoshida H, et al. Advanced bile duct carcinoma in a 15-year-old patient with pancreaticobiliary maljunction and congenital biliary cystic disease. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2008;15(5):554–9.
Tanaka S, Kubota M, Yagi M, Okuyama N, Ohtaki M, Yamazaki S, et al. An 11-year-old male patient demonstrating cholangiocarcinoma associated with congenital biliary dilatation. J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41(1):e15–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical statements
The protocol for this research project was approved by the Ethics Committee of our institution (No. 3010) and conforms to the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mori, H., Masahata, K., Umeda, S. et al. Risk of carcinogenesis in the biliary epithelium of children with congenital biliary dilatation through epigenetic and genetic regulation. Surg Today 52, 215–223 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-021-02325-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-021-02325-2