Abstract
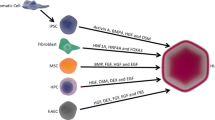
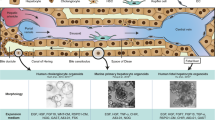
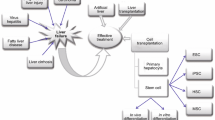
Organ liver transplantation and hepatocyte transplantation are not performed to their full potential because of donor shortage, which could be resolved by identifying new donor sources for the development of hepatocyte-like cells (HLCs). HLCs have been differentiated from some stem cell sources as alternative primary hepatocytes throughout the world; however, the currently available techniques cannot differentiate HLCs to the level of normal adult primary hepatocytes. The outstanding questions are as follows: which stem cells are the best cell sources? which protocol is the best way to differentiate them into HLCs? what is the definition of differentiated HLCs? how can we enforce the function of HLCs? what is the difference between HLCs and primary hepatocytes? what are the problems with HLC transplantation? This review summarizes the current status of HLCs, focusing on stem cell sources, the differentiation protocol for HLCs, the general characterization of HLCs, the generation of more functional HLCs, comparison with primary hepatocytes, and HLCs in cell-transplantation-based liver regeneration.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HLCs:
-
Hepatocyte-like cells
- IPSCs:
-
Induced pluripotent stem cells
- ESCs:
-
Embryonic stem cells
- MSCs:
-
Mesenchymal stem cells
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- GSK3:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factors
- BMP:
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- OsM:
-
Oncostatin M
- Dex:
-
Dexamethasone
- AFP:
-
Alpha fetoprotein
- IGF-1:
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I
- SOX17:
-
SRY-Box 17
- HEX:
-
Hematopoietically expressed homeobox
- HNF:
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor
- FOXA2:
-
Forkhead box A2
- ALB:
-
Albumin
- ATD:
-
AAT deficiency
- LDLR:
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor
- PCSK9:
-
Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9
- FTA:
-
Familial transthyretin amyloidosis
- GSD1A:
-
Glycogen storage disease type 1a
- CN1:
-
Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 1
- PH1:
-
Primary hyperoxaluria-1
- EBiSC:
-
European Bank for induced pluripotent Stem Cells
- FH:
-
Familial hypercholesterolemia
References
Zhang K, Zhang L, Liu W, Ma X, Cen J, Sun Z, et al. In vitro expansion of primary human hepatocytes with efficient liver repopulation capacity. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;23:806–819.e4.
Fu GB, Huang WJ, Zeng M, Zhou X, Wu HP, Liu CC, et al. Expansion and differentiation of human hepatocyte-derived liver progenitor-like cells and their use for the study of hepatotropic pathogens. Cell Res. 2019;29:8–22.
Peng WC, Logan CY, Fish M, Anbarchian T, Aguisanda F, Álvarez-Varela A, et al. Inflammatory cytokine TNFα promotes the long-term expansion of primary hepatocytes in 3D culture. Cell. 2018;175:1607–1619.e15.
Evans MJ, Kaufman MH. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981;292:154–6.
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–7.
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–76.
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007;131(5):861–72.
Saito Y, Shimada M, Utsunomiya T, Ikemoto T, Yamada S, Morine Y, et al. The protective effect of adipose-derived stem cells against liver injury by trophic molecules. J Surg Res. 2013;180(1):162–8.
Saito Y, Shimada M, Utsunomiya T, Ikemoto T, Yamada S, Morine Y, et al. Homing effect of adipose-derived stem cells to the injured liver: the shift of stromal cell-derived factor 1 expressions. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014;21(12):873–80.
Jeong J, Kim KN, Chung MS, Kim HJ. Functional comparison of human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells as sources of hepatocyte-like cells. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;13(6):740–9.
Citro L, Naidu S, Hassan F, Kuppusamy ML, Kuppusamy P, Angelos MG, et al. Comparison of human induced pluripotent stem-cell derived cardiomyocytes with human mesenchymal stem cells following acute myocardial infarction. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(12):e116281.
Yun YI, Park SY, Lee HJ, Ko JH, Kim MK, Wee WR, et al. Comparison of the anti-inflammatory effects of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in a murine model of corneal injury. Cytotherapy. 2017;19(1):28–35.
Abazari MF, Nasiri N, Nejati F, Zare Karizi S, Amini Faskhodi M, Saburi E, et al. Comparison of human-induced pluripotent stem cells and mesenchymal stem cell differentiation potential to insulin producing cells in 2D and 3D culture systems in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(5):4239–46.
Takebe T, Sekine K, Enomura M, Koike H, Kimura M, Ogaeri T, et al. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nature. 2013;499:481–4.
Tolosa L, Caron J, Hannoun Z, Antoni M, López S, Burks D, et al. Transplantation of hESC-derived hepatocytes protects mice from liver injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:246.
Yin L, Zhu Y, Yang J, Ni Y, Zhou Z, Chen Y, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiated into hepatocyte-like cells in vivo and in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11:1722–32.
Ishikawa T, Banas A, Hagiwara K, Iwaguro H, Ochiya T. Stem cells for hepatic regeneration: the role of adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010 Jun;5(2):182–9.
Cong Du, Feng Y, Qiu D, Yan Xu, Pang M, Cai N, et al. Highly efficient and expedited hepatic differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells by pure small-molecule cocktails. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9:58.
D'Amour KA, Agulnick AD, Eliazer S, Kelly OG, Kroon E, Baetge EE. Efficient differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to definitive endoderm. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:1534–41.
Hay DC, Fletcher J, Payne C, Terrace JD, Gallagher RC, Snoeys J. Highly efficient differentiation of hESCs to functional hepatic endoderm requires ActivinA and Wnt3a signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:12301–6.
Toivonen S, Lundin K, Balboa D, Ustinov J, Tamminen K, Palgi J, et al. Activin A and Wnt-dependent specification of human definitive endoderm cells. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319:2535–44.
Chen YF, Tseng CY, Wang HW, Kuo HC, Yang VW, Lee OK. Rapid generation of mature hepatocyte-like cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells by an efficient three-step protocol. Hepatology. 2012;55:1193–203.
Touboul T, Hannan NR, Corbineau S, Martinez A, Martinet C, Branchereau S, et al. Generation of functional hepatocytes from human embryonic stem cells under chemically defined conditions that recapitulate liver development. Hepatology. 2010;51:1754–65.
Magner NL, Jung Y, Wu J, Nolta JA, Zern MA, Zhou P. Insulin and IGFs enhance hepatocyte differentiation from human embryonic stem cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Stem Cells. 2013;31:2095–103.
Huang J, Guo X, Li W, Zhang H. Activation of Wnt/β-catenin signalling via GSK3 inhibitors direct differentiation of human adipose stem cells into functional hepatocytes. Sci Rep. 2017;17(7):40716.
Cai J, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Ye F, Song Z, Qin H, et al. Directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into functional hepatic cells. Hepatology. 2007;45:1229–39.
Brolen G, Sivertsson L, Bjorquist P, et al. Hepatocyte-like cells derived from human embryonic stem cells specifically via definitive endoderm and a progenitor stage. J Biotechnol. 2010;145:284–94.
Brolén G, Sivertsson L, Björquist P, Eriksson G, Ek M, Semb H, et al. FGF2 specifies hESC-derived definitive endoderm into foregut/midgut cell lineages in a concentration-dependent manner. Stem Cells. 2010;28:45–56.
Hay DC, Zhao D, Fletcher J, Hewitt ZA, McLean D, Urruticoechea-Uriguen A, et al. Efficient differentiation of hepatocytes from human embryonic stem cells exhibiting markers recapitulating liver development in vivo. Stem Cells. 2008;26:894–902.
Kajiwara M, Aoi T, Okita K, Takahashi R, Inoue H, Takayama N, et al. Donor-dependent variations in hepatic differentiation from human-induced pluripotent stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:12538–43.
Si-Tayeb K, Lemaigre FP, Duncan SA. Organogenesis and development of the liver. Dev Cell. 2010;18:175–89.
Snykers S, De Kock J, Rogiers V, Vanhaecke T. In vitro differentiation of embryonic and adult stem cells into hepatocytes: state of the art. Stem Cells. 2009;27:577–605.
Agarwal S, Holton KL, Lanza R. Efficient differentiation of functional hepatocytes from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2008;26(5):1117–27.
Takayama K, Hagihara Y, Toba Y, Sekiguchi K, Sakurai F, Mizuguchi H. Enrichment of high-functioning human iPS cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells for pharmaceutical research. Biomaterials. 2018;161:24–322.
Chen AA, Thomas DK, Ong LL, Schwartz RE, Golub TR, Bhatia SN, et al. Humanized mice with ectopic artificial liver tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(29):11842–7.
Si-Tayeb K. Highly efficient generation of human hepatocyte-like cells from induced pluripotent stem cells. Hepatology. 2010;51(1):297–305.
Cayo MA, Cai J, DeLaForest A, Noto FK, Nagaoka M, Clark BS, et al. ‘JD’ iPS cell-derived hepatocytes faithfully recapitulate the pathophysiology of familial hypercholesterolemia. Hepatology. 2012;56(6):2163–71.
Khetani SR, Bhatia SN. Microscale culture of human liver cells for drug development. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26(1):120–6.
Tada K, Roy-Chowdhury N, Prasad V, Kim BH, Manchikalapudi P, Fox IJ, et al. Long-term amelioration of bilirubin glucuronidation defect in Gunn rats by transplanting genetically modified immortalized autologous hepatocytes. Cell Transplant. 1998;7(6):607–16.
Murray JW, Thosani AJ, Wang P, Wolkoff AW. Heterogeneous accumulation of fluorescent bile acids in primary rat hepatocytes does not correlate with their homogenous expression of ntcp. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011;301(1):G60–G6868.
Yu Y, Liu H, Ikeda Y, Amiot BP, Rinaldo P, Duncan SA, et al. Hepatocyte-like cells differentiated from human induced pluripotent stem cells: relevance to cellular therapies. Stem Cell Res. 2012;9:196e207.
Baxter M, Withey S, Harrison S, Segeritz CP, Zhang F, Atkinson-Dell R, et al. Phenotypic and functional analyses show stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells better mimic fetal rather than adult hepatocytes. J Hepatol. 2015;62:581e9.
Ogawa S, Surapisitchat J, Virtanen C, Ogawa M, Niapour M, Sugamori KS, et al. Three-dimensional culture and cAMP signaling promote the maturation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes. Development. 3285e;140:3285e96.
Kotaka M, Toyoda T, Yasuda K, Kitano Y, Okada C, Ohta A, et al. Adrenergic receptor agonists induce the differentiation of pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatoblasts into hepatocyte-like cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16734.
Kondo Y, Iwao T, Yoshihashi S, Mimori K, Ogihara R, Nagata K, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid promotes the differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e104010.
Shabani Azandaryani Z, Davoodian N, Samiei A, Rouzbehan S. Insulin-like growth factor-I promotes hepatic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Cell Biol Int. 2019;43(5):476–85.
Shan J, Schwartz RE, Ross NT, Logan DJ, Thomas D, Duncan SA, et al. Identification of small molecules for human hepatocyte expansion and iPS differentiation. Nat Chem Biol. 2013;9:514e20.
Takayama K, Inamura M, Kawabata K, Tashiro K, Katayama K, Sakurai F, et al. Efficient and directive generation of two distinct endoderm lineages from human ESCs and iPSCs by differentiation stage-specific SOX17 transduction. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e21780.
Inamura M, Kawabata K, Takayama K, Tashiro K, Sakurai F, Katayama K, et al. Efficient generation of hepatoblasts from human ES cells and iPS cells by transient overexpression of homeobox gene HEX. Mol Ther. 2011;19:400e7.
Takayama K, Inamura M, Kawabata K, Katayama K, Higuchi M, Tashiro K, et al. Efficient generation of functional hepatocytes from human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells by HNF4alpha transduction. Mol Ther. 2012;20:127e37.
Takayama K, Inamura M, Kawabata K, Sugawara M, Kikuchi K, Higuchi M, et al. Generation of metabolically functioning hepatocytes from human pluripotent stem cells by FOXA2 and HNF1alpha transduction. J Hepatol. 2012;57:628e36.
Sasaki T, Takahashi S, Numata Y, Narita M, Tanaka Y, Kumagai T, et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 activates the transcription of CYP3A4 in hepatocytelike cells differentiated from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2013;28:250e9.
Miki T, Ring A, Gerlach J. Hepatic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells is promoted by three-dimensional dynamic perfusion culture conditions. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011;17:557e68.
Takayama K, Kawabata K, Nagamoto Y, Kishimoto K, Tashiro K, Sakurai F, et al. 3D spheroid culture of hESC/hiPSC-derived hepatocyte-like cells for drug toxicity testing. Biomaterials. 1781e;34:1781e9.
Park Y, Chen Y, Ordovas L, Verfaillie CM. Hepatic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells on microcarriers. J Biotechnol. 2014;174:39e48.
Yao R, Wang J, Li X, Jung Jung D, Qi H, Kee KK, et al. Hepatic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells as microscaled multilayered colonies leading to enhanced homogeneity and maturation. Small. 4311e;10:4311e23.
Gieseck RL 3rd, Hannan NR, Bort R, Hanley NA, Drake RA, Cameron GW, et al. Maturation of induced pluripotent stem cell derived hepatocytes by 3D-culture. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e86372.
Mun SJ, Ryu JS, Lee MO, Son YS, Oh SJ, Cho HS, et al. Generation of expandable human pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like liver organoids. J Hepatol. 2019;71(5):970–85.
Pettinato G, Lehoux S, Ramanathan R, Salem MM, He LX, Muse O, et al. Generation of fully functional hepatocyte-like organoids from human induced pluripotent stem cells mixed with endothelial Cells. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):8920.
Nagamoto Y, Tashiro K, Takayama K, Ohashi K, Kawabata K, Sakurai F, et al. The promotion of hepatic maturation of human pluripotent stem cells in 3D co-culture using type I collagen and Swiss 3T3 cell sheets. Biomaterials. 4526e;33:4526e34.
Du C, Narayanan K, Leong MF, Wan AC. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes and endothelial cells in multi-component hydrogel fibers for liver tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 6006e;35:6006e14.
Berger DR, Ware BR, Davidson MD, et al. Enhancing the functional maturity of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived human hepatocytes by controlled presentation of cell-cell interactions in vitro. Hepatology. 1370e;61:1370e81.
Berger DR, Ware BR, Davidson MD, Allsup SR, Khetani SR. Deterministically patterned biomimetic human iPSC-derived hepatic model via rapid 3D bioprinting. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2206e;113:2206e11.
Xing Q, Luo Y, Gao Y, Zhang S, Zhu Z, Wang Y, et al. Hepatectomised patient sera promote hepatocyte differentiation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells. Dig Liver Dis. 2014;46:731e7.
Ikemoto T, Feng R, Iwahashi SI, Yamada S, Saito Y, Morine Y, et al. In vitro and in vivo effects of insulin-producing cells generated by xeno-antigen free 3D culture with RCP piece. Sci Rep. 2019;9:10759.
Nakamura K, Cell SA. Cell aggregate-like technology using recombinant peptide pieces for MSC transplantation. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14:52–6.
Iwazawa R, Kozakai S, Kitahashi T, Nakamura K, Hata K. The therapeutic effects of adipose-derived stem cells and recombinant peptide pieces on mouse model of DSS colitis. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(9):1390–400.
Ronaldson-Bouchard K, Ma SP, Yeager K, Chen T, Song L, Sirabella D, et al. Advanced maturation of human cardiac tissue grown from pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 2018;556(7700):239–43.
Saito Y, Morine Y, Shimada M. Mechanism of Impairment on Liver Regeneration in Elderly Patients: Role of Hepatic Stellate Cell Function. Hepatol Res. 2017;47(6):505–13.
Yoshizato K, Tateno C. In vivo modeling of human liver for pharmacological study using humanized mouse. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2009;5(11):1435–46.
Carpentier A, Tesfaye A, Chu V, Nimgaonkar I, Zhang F, Lee SB, et al. Engrafted human stem cell-derived hepatocytes establish an infectious HCV murine model. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:4953–64.
Nagamoto Y, Takayama K, Tashiro K, Tateno C, Sakurai F, Tachibana M, et al. Efficient engraftment of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells in uPA/SCID mice by overexpression of FNK, a Bcl-xL mutant gene. Cell Transplant. 2015;24:1127–38.
Liu H, Kim Y, Sharkis S, Marchionni L, Jang YY. In vivo liver regeneration potential of human induced pluripotent stem cells from diverse origins. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:82ra39.
Asgari S, Moslem M, Bagheri-Lankarani K, Pournasr B, Miryounesi M, Baharvand H. Differentiation and transplantation of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells. Stem Cell Rev. 2013;9:493–504.
Song Z, Cai J, Liu Y, Zhao D, Yong J, Duo S, et al. Efficient generation of hepatocyte-like cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Res. 2009;19:1233–42.
Nagamoto Y, Takayama K, Ohashi K, Okamoto R, Sakurai F, Tachibana M, et al. Transplantation of a human iPSC-derived hepatocyte sheet increases survival in mice with acute liver failure. J Hepatol. 2016;64:1068–75.
Rashid ST, Corbineau S, Hannan N, Marciniak SJ, Miranda E, Alexander G, et al. Modeling inherited metabolic disorders of the liver using human induced pluripotent stem cells. J Clin Investig. 2010;120(9):3127–36.
Tafaleng EN, Chakraborty S, Han B, Hale P, Wu W, Soto-Gutierrez A, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cells model personalized variations in liver disease resulting from alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency. Hepatology. 2015;62(1):147–57.
Choi SM, Kim Y, Shim JS, Park JT, Wang RH, Leach SD, et al. Efficient drug screening and gene correction for treating liver disease using patient-specific stem cells. Hepatology. 2013;57(6):2458–68.
Zhang S, Chen S, Li W, Guo X, Zhao P, Xu J, et al. Rescue of ATP7B function in hepatocyte-like cells from Wilson’s disease induced pluripotent stem cells using gene therapy or the chaperone drug curcumin. Hum Mol Genet. 2011;20(16):3176–87.
Brown MS, Goldstein JL. Biomedicine lowering LDL—not only how low, but how long? Science. 2006;311(5768):1721–3.
Cayo MA, Cai J, DeLaForest A, Noto FK, Nagaoka M, Clark BS, et al. JD induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes faithfully recapitulate the pathophysiology of familial hypercholesterolemia. Hepatology. 2012;56(6):2163–71.
Seidah NG, Awan Z, Chretien M, Mbikay M. PCSK9: a key modulator of cardiovascular health. Circ Res. 2014;114:1022–36.
Leung A, Nah SK, Reid W, Ebata A, Koch CM, Monti S, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell modeling of multisystemic, hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. Stem Cell Rep. 2013;1(5):451–63.
Smets F, Dobbelaere D, McKiernan P, Dionisi-Vici C, Broué P, Jacquemin E, et al. Phase I/II trial of liver-derived mesenchymal stem cells in pediatric liver-based metabolic disorders: a prospective, open label, multicenter, partially randomized, safety study of one cycle of heterologous human adult liver-derived progenitor cells (hepastem) in urea cycle disorders and crigler-najjar syndrome patients. Transplantation. 2019 Sep;103(9):1903–15.
Wen-Xiong Xu, He H-L, Pan S-W, Chen Y-L, Zhang M-L, Zhu S, et al. Combination treatments of plasma exchange and umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure: a clinical trial in China. Stem Cells Int. 2019;4(2019):4130757.
Lin BL, Chen JF, Qiu WH, Wang KW, Xie DY, Chen XY, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure: A randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 2017;66(1):209–19.
Mohamadnejad M, Pournasr B, Bagheri M, Aghdami N, Shahsavani M, Hosseini LA, et al. Transplantation of allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(4):566–8.
Amer M-E, El-Sayed SZ, El-Kheir WA, Gabr H, Gomaa AA, El-Noomani N, et al. Clinical and laboratory evaluation of patients with end-stage liver cell failure injected with bone marrow-derived hepatocyte-like cells. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;10:936–41.
Funding
No funding
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
Yu Saito and the other co-authors have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, Y., Ikemoto, T., Morine, Y. et al. Current status of hepatocyte-like cell therapy from stem cells. Surg Today 51, 340–349 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-020-02092-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-020-02092-6