Abstract
Purpose
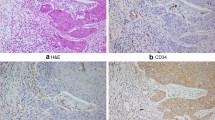
It was recently identified that the vasohibin family may regulate angiogenesis through suppression by the vasohibin-1 gene and promotion by the vasohibin-2 gene. We assessed vasohibin expression in gastric cancer patients and its effect on their prognosis.
Methods
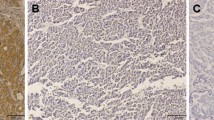
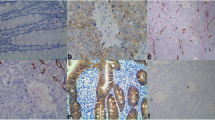
We evaluated vasohibin immunohistochemical expression in 210 patients with gastric cancer, who underwent radical surgery. The patients were divided first into a vasohibin-1-positive group and a vasohibin-1-negative group, and then into groups with high or low vasohibin-2 expression, to allow us to investigate the clinicopathological factors of prognosis retrospectively.
Results
There were 139 patients in the vasohibin-1-positive group and 71 patients in the vasohibin-1-negative group, among which there were and 108 with high vasohibin-2 expression and 102 with low vasohibin-2 expression. Vasohibin-1 was associated with Ly (P = 0.003) and pT (P = 0.037), whereas vasohibin-2 was associated with Ly (P < 0.001), V (P < 0.001) and pStage (P < 0.001). Overall, cancer-specific and relapse-free survival rates were lower in the vasohibin-1-positive (P = 0.034, P < 0.001, P = 0.002, respectively) and high vasohibin-2 expression (P = 0.004, P = 0.003, P < 0.001, respectively) groups. Multivariate analysis revealed that vasohibin-1 expression was associated with cancer-specific (P = 0.014, hazard ratio [HR] 4.454) and relapse-free (P = 0.035, HR 2.557) survival and vasohibin-2 expression tended to influence relapse-free survival (P = 0.051, HR 2.061). Grouping patients by vasohibin expression status combinations showed correlation among their expressions (P = 0.005). Overall, cancer-specific and relapse-free survival rates were lowest in the vasohibin-1-positive and high vasohibin-2 expression group.
Conclusion
Our findings demonstrate that vasohibin-1 and vasohibin-2 could be novel biomarkers for predicting gastric cancer prognosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Cutsem E, Sagaert X, Topal B, Haustermans K, Prenen H. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2016;388:2654–64.
Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V, Harewood R, Matz M, Nikšić M, et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000–14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37513025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet. 2018;391:1023–75.
Gotoda T. Endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2007;10:1–11.
Kitano S, Iso Y, Moriyama M, Sugimachi K. Laparoscopy-assisted Billroth I gastrectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1994;4:146–8.
Bandoh T, Shiraishi N, Yamashita Y, Terachi T, Hashizume M, Akira S, et al. Endoscopic surgery in Japan: the 12th national survey (2012–2013) by the Japan Society for Endoscopic Surgery. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2017;10:345–53.
Katai H, Ishikawa T, Akazawa K, Isobe Y, Miyashiro I, Oda I, et al. Five-year survival analysis of surgically resected gastric cancer cases in Japan: a retrospective analysis of more than 100,000 patients from the nationwide registry of the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association (2001–2007). Gastric Cancer. 2018;21:144–54.
Hofmann M, Stoss O, Shi D, Buttner R, van de Vijver M, Kim W, et al. Assessment of a HER2 scoring system for gastric cancer: results from a validation study. Histopathology. 2008;52:797–805.
Terashima M, Kitada K, Ochiai A, Ichikawa W, Kurahashi I, Sakuramoto S, et al. Impact of expression of human epidermal growth factor receptors EGFR and ERBB2 on survival in stage II/III gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:5992–6000.
Chung HC, Ros W, Delord JP, Perets R, Italiano A, Shapira-Frommer R, et al. Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab in previously treated advanced cervical cancer: results from the Phase II KEYNOTE-158 Study. J Clin Oncol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.18.01265.
Sato Y. Molecular diagnosis of tumor angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic cancer therapy. Int J Clin Oncol. 2008;8:200–6.
Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971;285:1182–6.
Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ. VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:579–91.
Sato Y, Sonoda H. The vasohibin family: a negative regulatory system of angiogenesis genetically programmed in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:37–41.
Watanabe K, Hasegawa Y, Yamashita H, Shimizu K, Ding Y, Abe M, et al. Vasohibin as an endothelium-derived negative feedback regulator of angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:898–907.
Shibuya T, Watanabe K, Yamashita H, Shimizu K, Miyashita H, Abe M, et al. Isolation and characterization of vasohibin-2 as a homologue of VEGF-inducible endothelium-derived angiogenesis inhibitor vasohibin. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:1051–7.
Hosaka T, Kimura H, Heishi T, Suzuki Y, Miyashita H, Ohta H, et al. Vasohibin-1 expression in endothelium of tumor blood vessels regulates angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2009;175:430–9.
Koyanagi T, Saga Y, Takahashi Y, Suzuki Y, Suzuki M, Sato Y. Downregulation of vasohibin-2, a novel angiogenesis regulator, suppresses tumor growth by inhibiting angiogenesis in endometrial cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2013;5:1058–62.
Miyazaki Y, Kosaka T, Mikami S, Kikuchi E, Tanaka N, Maeda T, et al. The prognostic significance of vasohibin-1 expression in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:4145–53.
Ninomiya Y, Ozawa S, Oguma J, Kazuno A, Nitta M, Kajiwara H, et al. Expression of vasohibin-1 and -2 predicts poor prognosis among patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Oncol Lett. 2018;16:5265–74.
Gullo I, Carneiro F, Oliveira C, Almeida GM. Heterogeneity in gastric cancer: from pure morphology to molecular classifications. Pathobiology. 2018;85:50–63.
Remmele W, Stegner HE. Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue. Pathologe. 1987;8:138–40.
Kim JC, Kim KT, Park JT, Kim HJ, Sato Y, Kim HS. Expression of vasohibin-2 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma promotes tumor progression and is associated with a poor clinical outcome. Hepatogastroenterology. 2015;62:251–6.
Tamaki K, Moriya T, Sato Y, Ishida T, Maruo Y, Yoshinaga K, et al. Vasohibin-1 in human breast carcinoma: a potential negative feedback regulator of angiogenesis. Cancer Sci. 2009;100:88–94.
Yoshinaga K, Ito K, Moriya T, Nagase S, Takano T, Niikura H, et al. Expression of vasohibin as a novel endothelium-derived angiogenesis inhibitor in endometrial cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:914–9.
Yoshinaga K, Ito K, Moriya T, Nagase S, Takano T, Niikura H, et al. Roles of intrinsic angiogenesis inhibitor, vasohibin, in cervical carcinomas. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:446–51.
Murakami K, Kasajima A, Kawagishi N, Sekiguchi S, Fujishima F, Watanabe M, et al. The prognostic significance of vasohibin 1-associated angiogenesis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2014;45:589–97.
Kitajima T, Toiyama Y, Tanaka K, Saigusa S, Kobayashi M, Inoue Y, et al. Vasohibin-1 increases the malignant potential of colorectal cancer and is a biomarker of poor prognosis. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:5321–9.
Zhang T, Yu TT, Zhang DM, Hou XM, Liu XJ, Zhao D, et al. Vasohibin-1 expression detected by immunohistochemistry correlates with prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Med Oncol. 2014;31:963.
Mikami S, Oya M, Kosaka T, Mizuno R, Miyazaki Y, Sato Y, et al. Increased vasohibin-1 expression is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis of renal cell carcinoma patients. Lab Invest. 2017;97:854–62.
Torii C, Hida Y, Shindoh M, Akiyama K, Ohga N, Maishi N, et al. Vasohibin-1 as a novel prognostic factor for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2017;37:1219–25.
Kobayashi H, Kosaka T, Mikami S, Miyazaki Y, Matsumoto K, Kikuchi E, et al. Vasohibin-1 as a novel microenvironmental biomarker for patient risk reclassification in low-risk prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;9:10203–100.
Kosaka T, Miyazaki Y, Miyajima A, Mikami S, Hayashi Y, Tanaka N, et al. The prognostic significance of vasohibin-1 expression in patients with prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;108:2123–9.
Sano R, Kanomata N, Suzuki S, Shimoya K, Sato Y, Moriya T, et al. Vasohibin-1 is a poor prognostic factor of ovarian carcinoma. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2017;243:107–14.
Takahashi Y, Koyanagi T, Suzuki Y, Saga Y, Kanomata N, Moriya T, et al. Vasohibin-2 expressed in human serous ovarian adenocarcinoma accelerates tumor growth by promoting angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 2012;10:1135–46.
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis—correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1–8.
Norita R, Suzuki Y, Furutani Y, Takahashi K, Yoshimatsu Y, Podyma-Inoue KA, et al. Vasohibin-2 is required for epithelial–mesenchymal transition of ovarian cancer cells by modulating transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Cancer Sci. 2017;108:419–26.
Suzuki Y, Kitahara S, Suematsu T, Oshima M, Sato Y. Requisite role of vasohibin-2 in spontaneous gastric cancer formation and accumulation of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Sci. 2017;108:2342–51.
Shen Z, Kauttu T, Seppänen H, Vainionpää S, Ye Y, Wang S, et al. Vasohibin-1 and vasohibin-2 expression in gastric cancer cells and TAMs. Med Oncol. 2012;29:2718–26.
Olivera-Severo D, Uberti AF, Marques MS, Pinto MT, Gomez-Lazaro M, Figueiredo C, et al. A new role for helicobacter pylori urease: contributions to angiogenesis. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:398–407.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Noboru Kawabe, Ms. Maki Niioka, and Ms. Izu Inada for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hara, H., Ozawa, S., Ninomiya, Y. et al. Prognostic significance of vasohibin-1 and vasohibin-2 immunohistochemical expression in gastric cancer. Surg Today 50, 1530–1543 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-020-02040-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-020-02040-4