Abstract
Purpose
The activation of hedgehog (Hh) pathways has been studied extensively in many malignant tumors to elucidate their clinical diagnostic and prognostic utilities. However, their roles in primary gallbladder carcinoma (GBC) remain poorly understood. This study was conducted to clarify the immunoreactivity and prognostic value of Hh pathway components in GBC.
Methods
Levels of sonic hedgehog (Shh), its receptor, Patched (Ptch1), and its downstream transcription factor, Gli1 protein, were measured by immunohistochemistry in 93 specimens from patients with GBC. We analyzed the correlations between the expression of these factors and clinicopathological features, including prognosis.
Results
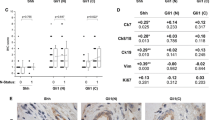
Among the 93 GBC specimens, 76 (81.7%), 70 (75.3%) and 66 (70.0%) were positive for Shh, Ptch1 and Gli1 expression, respectively. Expressions were significantly correlated with stage, lymph node metastasis, venous invasion, hepatic infiltration and lymphatic invasion (all P < 0.05). Patients with positive staining for Shh, Ptch1 and Gli1 had significantly lower survival rates than patients with negative staining. The expression patterns of Shh, Ptch1 and Gli1 were all associated with a malignant behavior risk category in GBC.
Conclusions
To our knowledge, this is the first report to define the role of the Hh pathway in GBC. Shh, Ptch1 and Gli1 are frequently expressed in GBC and associated with poorer survival. Thus, high expressions of Shh, Ptch1 and Gli1 proteins could serve as auxiliary parameters for predicting the malignant behavior of GBC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Misra S, Chaturvedi A, Misra NC, Sharma ID. Carcinoma of the gallbladder. Lancet Oncol. 2003;4:167–76.
Fujikawa T, Tanaka A, Abe T, Yoshimoto H, Tokumitsu Y, Tada S, et al. Undifferentiated carcinoma of the common bile duct with intraductal tumor thrombi: report of a case. Surg Today. 2011;41:579–84.
Roa I, De Aretxabala X, Araya JC, Roa J. Preneoplastic lesions in gallbladder cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2006;93:615–23.
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Maitra A. Widespread requirement for Hedgehog ligand stimulation in growth of digestive tract tumours. Nature. 2003;425:846–51.
Pasca di Magliano M, Hebrok M. Hedgehog signalling in cancer formation and maintenance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:903–11.
Ma X, Chen K, Huang S. Frequent activation of the hedgehog pathway in advanced gastric adenocarcinomas. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:1698–705.
Kameda C, Tanaka H, Yamasaki A. The Hedgehog pathway is a possible therapeutic target for patients with estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:871–9.
Lauth M, Toftgrd R. The Hedgehog pathway as a drug target in cancer therapy. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2007;8:457–61.
Walter K, Omura N, Hong SM. Overexpression of smoothened activates the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer-associated fibroblasts. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:1781–9.
Laurendeau I, Ferrer M, Garrido D. Gene expression profiling of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in human meningiomas. Mol Med. 2010;16:262–70.
Thayer SP, di Magliano MP, Heiser PW. Hedgehog is an early and late mediator of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature. 2003;425:851–6.
Han ME, Lee YS, Baek SY, Kim BS, Kim JB, Oh SO. Hedgehog signaling regulates the survival of gastric cancer cells by regulating the expression of Bcl-2. Int J Mol Sci. 2009;10:3033–43.
Chen G, Goto Y, Sakamoto R, Tanaka K, Matsubara E, Nakamura M, et al. GLI1, a crucial mediator of sonic hedgehog signaling in prostate cancer, functions as a negative modulator for androgen receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;404:809–15.
Kelleher FC. Hedgehog signalling and therapeutics in pancreatic cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2010 (in press).
Ingham PW, McMahon AP. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 2001;15:3059–87.
Ju B, Spitsbergen J, Eden CJ, Taylor MR, Chen W. Co-activation of hedgehog and AKT pathways promote tumorigenesis in zebrafish. Mol Cancer. 2009;8:40.
Saqui-Salces M, Merchant JL. Hedgehog signaling and gastrointestinal cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1803:786–95.
Wistuba II, Gazdar AF. Gallbladder cancer: lessons from a rare tumour. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:695–706.
Misra S, Chaturvedi A, Misra NC. Gallbladder cancer. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2006;9:95–106.
Yanai K, Nagai S, Wada J, Yamanaka N, Nakamura M, Torata N, et al. Hedgehog signaling pathway is a possible therapeutic target for gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2007;95:55–62.
Oue T, Yoneda A, Uehara S, Yamanaka H, Fukuzawa M. Increased expression of the hedgehog signaling pathway in pediatric solid malignancies. J Pediatr Surg. 2010;45:387–92.
Wu WK, Cho CH, Lee CW, Fan D, Wu K, Yu J, et al. Dysregulation of cellular signaling in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2010;295:144–53.
Epstein EH. Basal cell carcinomas: attack of the hedgehog. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:743–54.
Yang Y, Tian X, Xie X, Zhuang Y, Wu W, Wang W. Expression and regulation of hedgehog signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2010;395:515–25.
Liao X, Siu MK, Au CW, Wong ES, Chan HY, Ip PP, et al. Aberrant activation of hedgehog signaling pathway in ovarian cancers: effect on prognosis, cell invasion and differentiation. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:131–40.
Rush SZ, Abel TW, Valadez JG, Pearson M, Cooper MK. Activation of the Hedgehog pathway in pilocytic astrocytomas. Neuro Oncol. 2010;12:790–8.
Li YC, Deng YH, Guo ZH, Zhang MM, Zhu J, Pu CL, et al. Prognostic value of hedgehog signal component expressions in hepatoblastoma patients. Eur J Med Res. 2010;15:468–74.
Beauchamp EM, Ringer L, Bulut G, Sajwan KP, Hall MD, Lee YC, et al. Arsenic trioxide inhibits human cancer cell growth and tumor development in mice by blocking Hedgehog/GLI pathway. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:148–60.
Katoh Y, Katoh M. Hedgehog target genes: mechanisms of carcinogenesis induced by aberrant hedgehog signaling activation. Curr Mol Med. 2009;9:873–86.
Morton JP, Mongeau ME, Klimstra DS. Sonic hedgehog acts at multiple stages during pancreatic tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:5103–8.
Merchant JL, Saqui-Salces M, El-Zaatari M. Hedgehog signaling in gastric physiology and cancer. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2010;96:133–56.
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (#81172287).
Conflict of interest
Jinmao Li and his co-authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. Li and T. Wu contributed to this work equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Wu, T., Lu, J. et al. Immunohistochemical evidence of the prognostic value of hedgehog pathway components in primary gallbladder carcinoma. Surg Today 42, 770–775 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-012-0157-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-012-0157-1