Abstract
Background
Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) is a group of life-threatening complications of organ transplantation, which occurs most frequently in pediatric patients. This retrospective study evaluates a single-institution experience of five cases of PTLD after living-donor liver transplantation (LDLT).
Patients and method
We reviewed the records of 78 pediatric patients (<18 years old) and 54 adult patients, who underwent LDLT between July 1991 and December 2009.
Result
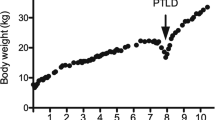
PTLD was diagnosed in five pediatric patients, yielding an overall incidence of 3.8%. There were no significant differences between the pediatric patients with and those without PTLD in terms of their age, sex, reason for transplantation, calcineurin inhibitor, Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) serostatus, ABO compatibility, lymphocyte cross-matching, or episodes of biopsy proven rejection. Two patients with abdominal lymphadenopathy and one with gastrointestinal PTLD responded to a reduction in immunosuppression. Treatment with rituximab was necessary for another gastrointestinal PTLD patient. Diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma was diagnosed in one patient with mediastinal and lung masses. This patient was treated with chemotherapy and rituximab, followed by surgical resection. All patients survived and no evidence of recurrence has been found since.
Conclusion
Although PTLD is potentially life-threatening, it can be managed by appropriate and prompt treatment, with a good outcome.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doak PB, Montgomerie JZ, North JD, Smith F. Reticulum cell sarcoma after renal homotransplantation and azathioprine and prednisone therapy. Br Med J. 1968;4:746–8.
Starzl TE, Nalesnik MA, Porter KA, Ho M, Iwatsuki S, Griffith BP, et al. Reversibility of lymphomas and lymphoproliferative lesions developing under cyclosporin-steroid therapy. Lancet. 1984;1:583–7.
Heslop HE. How I treat EBV lymphoproliferation. Blood. 2009;114:4002–8.
Leblond V, Davi F, Charlotte F, Dorent R, Bitker MO, Sutton L, et al. Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders not associated with Epstein–Barr virus: a distinct entity? J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:2052–9.
Dotti G, Fiocchi R, Motta T, Mammana C, Gotti E, Riva S, et al. Lymphomas occurring late after solid-organ transplantation: influence of treatment on the clinical outcome. Transplantation. 2002;74:1095–102.
Ghobrial IM, Habermann TM, Macon WR, Ristow KM, Larson TS, Walker RC, et al. Differences between early and late posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders in solid organ transplant patients: are they two different diseases? Transplantation. 2005;79:244–7.
Jain A, Nalesnik M, Reyes J, Pokharna R, Mazariegos G, Green M, et al. Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders in liver transplantation: a 20-year experience. Ann Surg. 2002;236:429–36. (discussion 36–7).
Smith JM, Corey L, Healey PJ, Davis CL, McDonald RA. Adolescents are more likely to develop posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder after primary Epstein–Barr virus infection than younger renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2007;83:1423–8.
Opelz G, Dohler B. Lymphomas after solid organ transplantation: a collaborative transplant study report. Am J Transplant. 2004;4:222–30.
Muti G, Cantoni S, Oreste P, Klersy C, Gini G, Rossi V, et al. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders: improved outcome after clinico-pathologically tailored treatment. Haematologica. 2002;87:67–77.
Smets F, Vajro P, Cornu G, Reding R, Otte JB, Sokal E. Indications and results of chemotherapy in children with posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease after liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2000;69:982–4.
Guthery SL, Heubi JE, Bucuvalas JC, Gross TG, Ryckman FC, Alonso MH, et al. Determination of risk factors for Epstein–Barr virus-associated posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in pediatric liver transplant recipients using objective case ascertainment. Transplantation. 2003;75:987–93.
Kataoka K, Seo S, Sugawara Y, Ota S, Imai Y, Takahashi T, et al. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder after adult-to-adult living donor liver transplant: case series and review of literature. Leuk Lymphoma. 2010;51:1494–501.
Shigeta T, Imadome K, Sakamoto S, Fukuda A, Kakiuchi T, Matsuno N, et al. Epstein–Barr virus infection after pediatric living-related liver transplantation—management and risk factors. Transplant Proc. 2010;42:4178–80.
Bakker NA, van Imhoff GW, Verschuuren EA, van Son WJ, Homan van der Heide JJ, Veeger NJ, et al. Early onset post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease is associated with allograft localization. Clin Transplant. 2005;19:327–34.
Ghobrial IM, Habermann TM, Maurer MJ, Geyer SM, Ristow KM, Larson TS, et al. Prognostic analysis for survival in adult solid organ transplant recipients with post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7574–82.
Beynet DP, Wee SA, Horwitz SS, Kohler S, Horning S, Hoppe R, et al. Clinical and pathological features of posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorders presenting with skin involvement in 4 patients. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:1140–6.
Phan TG, O’Neill BP, Kurtin PJ. Posttransplant primary CNS lymphoma. Neuro Oncol. 2000;2:229–38.
Dote H, Ohta K, Nishimura R, Teramoto N, Asagi A, Nadano S, et al. Primary extranodal non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the common bile duct manifesting as obstructive jaundice: report of a case. Surg Today. 2009;39:448–51.
Tsai DE, Hardy CL, Tomaszewski JE, Kotloff RM, Oltoff KM, Somer BG, et al. Reduction in immunosuppression as initial therapy for posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder: analysis of prognostic variables and long-term follow-up of 42 adult patients. Transplantation. 2001;71:1076–88.
Orii T, Ohkohchi N, Satomi S, Hoshino Y, Kimura H. Decreasing the Epstein–Barr virus load by adjusting the FK506 blood level. Transpl Int. 2002;15:529–34.
Svoboda J, Kotloff R, Tsai DE. Management of patients with post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder: the role of rituximab. Transpl Int. 2006;19:259–69.
Choquet S, Leblond V, Herbrecht R, Socie G, Stoppa AM, Vandenberghe P, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in B-cell post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders: results of a prospective multicenter phase 2 study. Blood. 2006;107:3053–7.
Nakanishi C, Kawagishi N, Sekiguchi S, Akamatsu Y, Sato K, Miyagi S, et al. Steroid-resistant late acute rejection after a living donor liver transplantation: case report and review of the literature. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2007;211:195–200.
Orii T, Ohkohchi N, Kikuchi H, Koyamada N, Chubachi S, Satomi S, et al. Usefulness of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in following up patients with Epstein–Barr virus infection after liver transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2000;14:308–17.
Bakker NA, van Imhoff GW, Verschuuren EA, van Son WJ. Presentation and early detection of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder after solid organ transplantation. Transpl Int. 2007;20:207–18.
Caillard S, Dharnidharka V, Agodoa L, Bohen E, Abbott K. Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders after renal transplantation in the United States in era of modern immunosuppression. Transplantation. 2005;80:1233–43.
Swinnen LJ, Costanzo-Nordin MR, Fisher SG, O’Sullivan EJ, Johnson MR, Heroux AL, et al. Increased incidence of lymphoproliferative disorder after immunosuppression with the monoclonal antibody OKT3 in cardiac-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:1723–8.
Duvoux C, Pageaux GP, Vanlemmens C, Roudot-Thoraval F, Vincens-Rolland AL, Hezode C, et al. Risk factors for lymphoproliferative disorders after liver transplantation in adults: an analysis of 480 patients. Transplantation. 2002;74:1103–9.
Cherikh WS, Kauffman HM, McBride MA, Maghirang J, Swinnen LJ, Hanto DW. Association of the type of induction immunosuppression with posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder, graft survival, and patient survival after primary kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2003;76:1289–93.
Marino IR, Doria C, Scott VL, Foglieni CS, Lauro A, Piazza T, et al. Efficacy and safety of basiliximab with a tacrolimus-based regimen in liver transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2004;78:886–91.
Pirsch JD. Cytomegalovirus infection and posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease in renal transplant recipients: results of the U.S. multicenter FK506 Kidney Transplant Study Group. Transplantation. 1999;68:1203–5.
Wiesner RH. A long-term comparison of tacrolimus (FK506) versus cyclosporine in liver transplantation: a report of the United States FK506 Study Group. Transplantation. 1998;66:493–9.
Armitage JM, Kormos RL, Stuart RS, Fricker FJ, Griffith BP, Nalesnik M, et al. Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease in thoracic organ transplant patients: ten years of cyclosporine-based immunosuppression. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1991;10:877–86. (discussion 86–7).
Walker RC, Marshall WF, Strickler JG, Wiesner RH, Velosa JA, Habermann TM, et al. Pretransplantation assessment of the risk of lymphoproliferative disorder. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:1346–53.
Shahinian VB, Muirhead N, Jevnikar AM, Leckie SH, Khakhar AK, Luke PP, et al. Epstein–Barr virus seronegativity is a risk factor for late-onset posttransplant lymphoroliferative disorder in adult renal allograft recipients. Transplantation. 2003;75:851–6.
Rooney CM, Loftin SK, Holladay MS, Brenner MK, Krance RA, Heslop HE. Early identification of Epstein–Barr virus-associated post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disease. Br J Haematol. 1995;89:98–103.
McDiarmid SV, Jordan S, Kim GS, Toyoda M, Goss JA, Vargas JH, et al. Prevention and preemptive therapy of postransplant lymphoproliferative disease in pediatric liver recipients. Transplantation. 1998;66:1604–11.
Tsai DE, Nearey M, Hardy CL, Tomaszewski JE, Kotloff RM, Grossman RA, et al. Use of EBV PCR for the diagnosis and monitoring of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in adult solid organ transplant patients. Am J Transplant. 2002;2:946–54.
Lee TC, Savoldo B, Barshes NR, Rooney CM, Heslop HE, Gee AP, et al. Use of cytokine polymorphisms and Epstein–Barr virus viral load to predict development of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in paediatric liver transplant recipients. Clin Transplant. 2006;20:389–93.
Tsai DE, Douglas L, Andreadis C, Vogl DT, Arnoldi S, Kotloff R, et al. EBV PCR in the diagnosis and monitoring of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder: results of a two-arm prospective trial. Am J Transplant. 2008;8:1016–24.
Moog F, Bangerter M, Diederichs CG, Guhlmann A, Merkle E, Frickhofen N, et al. Extranodal malignant lymphoma: detection with FDG PET versus CT. Radiology. 1998;206:475–81.
Zijlstra JM, Lindauer-van der Werf G, Hoekstra OS, Hooft L, Riphagen II, Huijgens PC. 18F-fluoro-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography for post-treatment evaluation of malignant lymphoma: a systematic review. Haematologica 2006;91:522–9.
Marom EM, McAdams HP, Butnor KJ, Coleman RE. Positron emission tomography with fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose (FDG-PET) in the staging of post transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in lung transplant recipients. J Thorac Imaging. 2004;19:74–8.
O’Conner AR, Franc BL. FDG PET imaging in the evaluation of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder following renal transplantation. Nucl Med Commun. 2005;26:1107–11.
Bakker NA, Pruim J, de Graaf W, van Son WJ, van der Jagt EJ, van Imhoff GW. PTLD visualization by FDG-PET: improved detection of extranodal localizations. Am J Transplant. 2006;6:1984–5.
Aucejo F, Rofaiel G, Miller C. Who is at risk for post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLD) after liver transplantation? J Hepatol. 2006;44:19–23.
Paya CV, Fung JJ, Nalesnik MA, Kieff E, Green M, Gores G, et al. Epstein–Barr virus-induced posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders. ASTS/ASTP EBV-PTLD Task Force and The Mayo Clinic Organized International Consensus Development Meeting. Transplantation. 1999;68:1517–25.
Savoldo B, Rooney CM, Quiros-Tejeira RE, Caldwell Y, Wagner HJ, Lee T, et al. Cellular immunity to Epstein–Barr virus in liver transplant recipients treated with rituximab for post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease. Am J Transplant. 2005;5:566–72.
Ganne V, Siddiqi N, Kamaplath B, Chang CC, Cohen EP, Bresnahan BA, et al. Humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (Rituximab) treatment for post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Clin Transplant. 2003;17:417–22.
Blaes AH, Peterson BA, Bartlett N, Dunn DL, Morrison VA. Rituximab therapy is effective for posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders after solid organ transplantation: results of a phase II trial. Cancer. 2005;104:1661–7.
Oertel SH, Verschuuren E, Reinke P, Zeidler K, Papp-Vary M, Babel N, et al. Effect of anti-CD 20 antibody rituximab in patients with post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD). Am J Transplant. 2005;5:2901–6.
Trappe R, Riess H, Babel N, Hummel M, Lehmkuhl H, Jonas S, et al. Salvage chemotherapy for refractory and relapsed posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLD) after treatment with single-agent rituximab. Transplantation. 2007;83:912–8.
Gross TG, Bucuvalas JC, Park JR, Greiner TC, Hinrich SH, Kaufman SS, et al. Low-dose chemotherapy for Epstein–Barr virus-positive post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disease in children after solid organ transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6481–8.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakanishi, C., Kawagishi, N., Sekiguchi, S. et al. Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder in living-donor liver transplantation: a single-center experience. Surg Today 42, 741–751 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-012-0127-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-012-0127-7