Abstract
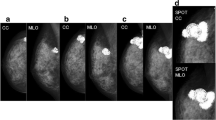
Thoracic radiation in the early years of life is a known risk factor for breast cancer later in life. A 21-year-old woman who had received thoracic radiation therapy for Ewing’s sarcoma of the vertebra 9 years earlier was referred to our hospital for investigation of a palpable mass in her left breast. Ultrasonography and excisional biopsy showed ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) of the left breast, with no detectable pathology in the right breast except that it was more hypoplastic than the left breast. Considering the known risk factors for invasive breast cancer in both breasts, we performed bilateral skin-sparing mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction using subpectoral implants. The final histopathological diagnosis was bilateral DCIS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmichael A, Sami AS, Dixon JM. Breast cancer risk among the survivors of atomic bomb and patients exposed to therapeutic ionizing radiation. Eur J Surg Oncol 2003;29:475–479.
Etkind PR, Sparano JA. What role does radiation exposure play in breast cancer development? In: Roses DF, editor. Breast cancer. 1st ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Harcourt Brace; 1999. p. 59–60.
Cutuli B, Dhermain F, Borel C, de Larochefordiere A, Graic Y, de Lafontan B, et al. Breast cancer in patients treated for Hodgkin’s disease: Clinical and pathologic analysis of 76 cases in 63 patients. Eur J Cancer 1997;33:2315–2320.
Hwang KW, Woo OH, Koo BH, Yong HS, Kim A, Kang EY. Medullary carcinoma of the breast after radiation therapy for Hodgkin’s disease in a young woman: report of a case. Surg Today 2006;36:1105–1107.
Miser JS, Kinsella TJ, Triche TJ, Steis R, Tsokos M, Wesley R, et al. Preliminary results of treatment of Ewing’s sarcoma of bone in children and young adults: Six months of intensive combined modality therapy without maintenance. J Clin Oncol 1988;6:484–490.
Pressman PI. Treatment of bilateral breast cancer. In: Roses DF, editor. Breast Cancer. 1st ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Harcourt Brace; 1999. p. 483–492.
Preston DL, Mattsson A, Holmberg E, Shore R, Hildreth NG, Boice JD Jr. Radiation effects on breast cancer risk: a pooled analysis of eight cohorts. Radiat Res 2002;158:220–235.
Travis LB, Hill DA, Dores GM, Gospodarowicz M, van Leeuwen FE, Holowaty E, et al. Breast cancer following radiotherapy and chemotherapy among young women with Hodgkin disease. JAMA 2003;290:465–475.
Travis LB, Hill DA, Dores GM, Gospodarowicz M, van Leeuwen FE, Holowaty E, et al. Cumulative absolute breast cancer risk for young women treated for Hodgkin lymphoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 2005;97:1428–1437.
Hill DA, Preston-Martin S, Ross RK, Bernstein L. Medical radiation, family history of cancer, and benign breast disease in relation to breast cancer risk in young women, USA. Cancer Causes Control 2002;13:711–718.
Pierce LJ, Levin AM, Rebbeck TR, Ben-David MA, Friedman E, Solin LJ, et al. Ten-year multi-institutional results of breast-conserving surgery and radiotherapy in BRCA1/2-associated stage I/II breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2006;24:2437–2443.
Kirova YM, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Savignoni A, Sigal-Zafrani B, Fabre N, Fourquet A; for the Institut Curie Breast Cancer Study Group. Risk of breast cancer recurrence and contralateral breast cancer in relation to BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation status following breast-conserving surgery and radiotherapy. Eur J Cancer 2005;41:2304–2311.
Clemons M, Loijens L, Goss P. Breast cancer risk following irradiation for Hodgkin’s disease. Cancer Treat Rev 2000;26:291–302.
Yahalom J, Petrek JA, Biddinger PW, Kessler S, Dershaw DD, McCormick B, et al. Breast cancer in patients irradiated for Hodgkin’s disease: a clinical and pathologic analysis of 45 events in 37 patients. J Clin Oncol 1992;10:1674–1681.
Zareba-Szlubowska M, Sas-Korczynska B, Skolyszewski J. The bilateral breast cancer in patient treated for Ewing sarcoma in childhood — the case report. Przegl Lek 2005;62:1568–1569.
Meric F, Robinson EK, Hunt KK. Noninvasive breast cancer. In: Feig BW, Berger DH, Fuhrman GM, editors. The M.D. Anderson Surgical Oncology Handbook. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2003. p. 1–13.
Fisher B, Dignam J, Wolmark N, Wickerham DL, Fisher ER, Mamounas E, et al. Tamoxifen in treatment of intraductal breast cancer: National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-24 randomized controlled trial. Lancet 1999;353:1993–2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keskek, M., Kilic, M., Ertan, T. et al. Bilateral ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast after radiation therapy for Ewing’s sarcoma of the vertebra in a young woman: Report of a case. Surg Today 38, 739–742 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-007-3703-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-007-3703-5