Abstract
Purpose
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) is detected in lung tissues subjected to ventilator-induced injury and is involved in the process of lung injury. We investigated the immunohistochemical expression of MMP-9 in the bilateral lungs of newborns with congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) during mechanical ventilation and evaluated the degree of damage based on MMP-9 expression.
Methods
Lung tissue samples were obtained during autopsy from six newborns with CDH. Control lung tissue samples were obtained from two of these newborns; one who died of persistent pulmonary hypertension after being ventilated for 2 days, but whose bilateral lungs were not subjected to the compressions of herniation, and one who died of bilateral diaphragmatic hernias soon after birth, but was not subjected to artificial ventilation. The other four newborns with CDH had unilateral Bochdalek hernias. Immunohistochemical detection of MMP-9 expression was done using a wet autoclave antigen retrieval method on sections from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded lung tissue.
Results
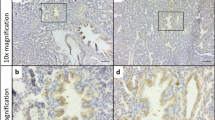
The reaction and distribution of MMP-9 was strongly positive in the alveolar macrophages in thickened alveolar septi and ducts, and in the inflammatory cells around the parenchymal hemorrhage and intra-alveolar spaces. Only the four patients with unilateral Bochdalek hernia had widely positive MMP-9 immunoreactivity in the unaffected side, as well as the affected side.
Conclusions
Based on MMP-9 expression, the lungs of newborns with CDH were damaged bilaterally during mechanical ventilation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
IY Adamson GM King DH Bowden (1998) ArticleTitleCollagen break down during acute lung injury Thorax 43 562–8
MA Swartz DJ Tschumperlin RDDr Kamm (2001) ArticleTitleazen JM. Mechanical stress is communicated between different cell types to elicit matrix remodeling Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98 6180–5 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.111133298 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MzhtlCgsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11353845
MA Attar SM Donn (2002) ArticleTitleMechanisms of ventilator-induced lung injury in premature infants Semin Neonatol 7 353–60 Occurrence Handle10.1053/siny.2002.0129 Occurrence Handle12464497
CC Dos Santos AS Slutsky (2000) ArticleTitleMechanisms of ventilator-induced lung injury: a perspective J Appl Physiol 89 1645–55 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXotlylu70%3D Occurrence Handle11007607
HD Foda EE Rollo M Drews C Conner K Appelt DR Shalinsky et al. (2001) ArticleTitleVentilator-induced lung injury upregulates and activates gelatinases and EMMPRIN Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 25 717–24 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXptlKiu7k%3D Occurrence Handle11726397
Y Gushima K Ichikado M Suga T Okamoto K Iyonaga K Sato et al. (2001) ArticleTitleExpression of matrix metalloproteinases in pigs with hyperoxia- induced acute lung injury Eur Respir J 18 827–37 Occurrence Handle10.1183/09031936.01.00049201 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXpt1Wgs7c%3D Occurrence Handle11757634
A Pardo R Barrios V Maldonado J Melendez J Perez V Ruiz et al. (1998) ArticleTitleGelatinases A and B are upregulated in rat lungs by subacute hyperoxia: pathogenetic implications Am J Pathol 153 833–44 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmtFKnu7c%3D Occurrence Handle9736032
J Pugin I Dunn P Jolliet D Tassaux JL Magnenat LP Nicod et al. (1998) ArticleTitleActivation of human macrophage by mechanical ventilation in vitro Am J Physiol 275 L1040–50 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhs1Sktw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9843840
Y Sakurai K Azarow E Cutz A Messineo R Pearl D Bohn (1999) ArticleTitlePulmonary barotraumas in congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a clinicopathological correlation J Pediatr Surg 34 1813–7 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-3468(99)90319-6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2FptVartQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10626861
W Areechon L Reid (1963) ArticleTitleHypoplasia of lung with congenital diaphragmatic hernia Br Med J 1 230–3
M Kitagawa A Hislop EA Boyden L Reid (1971) ArticleTitleLung hypoplasia in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. A quantitative study of airway, and alveolar development Br J Surg 58 342–6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CS6C1cnmtFM%3D Occurrence Handle5574718
FO Hi (1993) ArticleTitleStudy Group. Randomized study of high-frequency oscillated ventilation in infants with severe respiratory distress syndrome J Pediatr 122 609–19 Occurrence Handle8463913
Y Ogawa K Miyasaka T Kawano S Imura K Inukai K Okuyama et al. (1993) ArticleTitleA multicenter randomized trial of high frequency oscillatory ventilation as compared with conventional mechanical ventilation in preterm infants with respiratory failure Early Hum Dev 32 1–10 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-3782(93)90088-C Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyB3Mrks1M%3D Occurrence Handle8462430
T Sakai H Kakizawa S Aiba R Takahashi T Yoshioka K Iinuma (1999) ArticleTitleEffects of mean and swing pressure on piston-type high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in rabbits with and without acute lung injury Pediatr Pulmonol 27 328–35 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1099-0496(199905)27:5<328::AID-PPUL6>3.0.CO;2-5 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3nsVGjuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10344712
MK Winkler JK Foldes RC Bunn JL Fowlkes (2003) ArticleTitleImplications for matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of pediatric lung disease Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 284 L557–65 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjtlyrs7g%3D Occurrence Handle12456387
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tatekawa, Y., Kemmotsu, H., Joe, K. et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Expression in Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia During Mechanical Ventilation. Surg Today 35, 524–529 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-004-2969-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-004-2969-0