Abstract
Objective
Podocytes are closely related to renal function as an important part of the glomerulus. The reduction and damage of podocytes lead to further decline of renal function and aggravate the progression of DKD. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAS) have recently attracted great attention in improving podocyte dysfunction, but the specific mechanism remains uncertain.
Methods
We used mouse kidney podocyte MPC5 to construct a high-glucose injury model. Cell viability was detected by the MTT method; RT-qPCR and western blotting were used to detect the expressions of NF-κB p65, NLRP3, GSDMD, N-GSDMD, caspase-1 and cleaved-caspase-1, and we used ELISA to detect the expressions of inflammatory factors IL-1β and IL-18.
Results
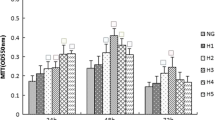
Our results showed that high glucose decreased podocyte survival, while liraglutide and semaglutide increased podocyte survival under high glucose. Liraglutide and semaglutide can inhibit the expression of pyroptosis-related genes and proteins and also inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors IL-1β, IL-18 increase.
Conclusion
The protective effect of liraglutide and semaglutide on podocytes may be achieved by regulating the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway and inhibiting pyroptosis, and there were no significant differences between the two GLP-1RAs (liraglutide and semaglutide) in inhibiting podocyte pyroptosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article (and its additional files).
References
Umanath K, Lewis JB (2018) Update on diabetic nephropathy: core curriculum 2018. Am J Kidney Dis 71:884–895
Al Mamun A, Ara Mimi A, Wu Y et al (2021) Pyroptosis in diabetic nephropathy clinica chimica acta. Int J Clin Chem 523:131–143
Shahzad K, Bock F, Dong W et al (2015) Nlrp3-inflammasome activation in non-myeloid-derived cells aggravates diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 87:74–84
Zhan JF, Huang HW, Huang C, Hu LL, Xu WW (2020) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 regulates pyroptosis in diabetic nephropathy via mediating the miR-34c/NLRP3 axis. Kidney Blood Press Res 45:589–602
An X, Zhang Y, Cao Y, Chen J, Qin H, Yang L (2020) Punicalagin protects diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting pyroptosis based on TXNIP/NLRP3 pathway. Nutrients 12(5):1516
Li F, Chen Y, Li Y, HuangZhao MW (2020) Geniposide alleviates diabetic nephropathy of mice through AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 886:173449
Wen S, Deng F, Li L, Xu L, LiFan XQ (2022) VX-765 ameliorates renal injury and fibrosis in diabetes by regulating caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis and inflammation. J Diabetes Investig 13:22–33
Gao C, Wang B, Chen Q, Wang M, FeiZhao XN (2021) Serum exosomes from diabetic kidney disease patients promote pyroptosis and oxidative stress through the miR-4449/HIC1 pathway. Nutr Diabetes 11:33
Ke R, Wang Y, Hong S, Xiao L (2020) Endoplasmic reticulum stress related factor IRE1α regulates TXNIP/NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis in diabetic nephropathy. Exp Cell Res 396:112293
Gao Y, Ma Y, Xie D, Jiang H (2022) ManNAc protects against podocyte pyroptosis via inhibiting mitochondrial damage and ROS/NLRP3 signaling pathway in diabetic kidney injury model. Int Immunopharmacol 107:108711
El-Lateef AEA, El-Shemi AGA, Alhammady MS, Yuan R, Zhang Y (2022) LncRNA NEAT2 modulates pyroptosis of renal tubular cells induced by high glucose in diabetic nephropathy (DN) by via miR-206 regulation. Biochem Genet 60(5):1733–1747
Zhang Z, Shao X, Jiang N et al (2018) Caspase-11-mediated tubular epithelial pyroptosis underlies contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Cell Death Dis 9:983
Quaggin SE, Kreidberg JA (2008) Development of the renal glomerulus: good neighbors and good fences. Development (Cambridge, England) 135:609–620
Garg P (2018) A review of podocyte biology. Am J Nephrol 47(Suppl 1):3–13
Fu Y, Sun Y, Wang M et al (2020) Elevation of JAML promotes diabetic kidney disease by modulating podocyte lipid metabolism. Cell Metab 32:1052-1062.e1058
Yamazaki T, Mimura I, Tanaka T, Nangaku M (2021) Treatment of diabetic kidney disease: current and future. Diabetes Metab J 45:11–26
Perreault L, Skyler JS, Rosenstock J (2021) Novel therapies with precision mechanisms for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol 17:364–377
Górriz JL, Soler MJ, Navarro-González JF et al (2020) GLP-1 receptor agonists and diabetic kidney disease: a call of attention to nephrologists. J Clin Med 9(4):947
Sattar N, Lee MMY, Kristensen SL et al (2021) Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 9:653–662
Chen A, Chen Z, Xia Y et al (2018) Liraglutide attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis via regulating SIRT1/NOX4/ROS pathway in H9c2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 499:267–272
Yang L, Cheng J, Shi G et al (2022) Liraglutide ameliorates cerebral ischemia in mice via antipyroptotic pathways. Neurochem Res 47:1904–1916
Liu J, Guo S, Li H, Liu XY (2022) Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) on podocytes, inflammation, and oxidative stress in patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN). Pak J Med Sci 38:1170–1174
Liu Y, Xu Z, Ma F, Jia Y, Wang G (2018) Knockdown of TLR4 attenuates high glucose-induced podocyte injury via the NALP3/ASC/Caspase-1 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 107:1393–1401
Abais JM, Zhang C, Xia M et al (2013) NADPH oxidase-mediated triggering of inflammasome activation in mouse podocytes and glomeruli during hyperhomocysteinemia. Antioxid Redox Signal 18:1537–1548
Hong J, Li G, Zhang Q, Ritter J, Li W, LI PL (2019) D-Ribose induces podocyte nlrp3 inflammasome activation and glomerular injury via AGEs/RAGE pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol 7:259
Kornelius E, Tsou SH, Chang CC et al (2022) Liraglutide attenuates glucolipotoxicity-induced RSC96 Schwann cellsʼ inflammation and dysfunction. Biomolecules 12(10):1338
Liu DX, Zhao CS, Wei XN, Ma YP, Wu JK (2022) Semaglutide protects against 6-OHDA toxicity by enhancing autophagy and inhibiting oxidative stress. Parkinsons Dis 2022:6813017
Li X, Xiao GY, Guo T, SongLi YJQM (2022) Potential therapeutic role of pyroptosis mediated by the NLRP3 inflammasome in type 2 diabetes and its complications. Front Endocrinol 13:986565
He Y, Zeng MY, Yang D, Motro B, NúñEZ G (2016) NEK7 is an essential mediator of NLRP3 activation downstream of potassium efflux. Nature 530:354–357
Schroder K, Zhou R, Tschopp J (2010) The NLRP3 inflammasome: a sensor for metabolic danger? Science (New York, NY) 327:296–300
Wen H, Gris D, Lei Y et al (2011) Fatty acid-induced NLRP3-ASC inflammasome activation interferes with insulin signaling. Nat Immunol 12:408–415
Chen C, Ma X, Yang C et al (2018) Hypoxia potentiates LPS-induced inflammatory response and increases cell death by promoting NLRP3 inflammasome activation in pancreatic β cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495:2512–2518
Lin CF, Kuo YT, Chen TY, Chien CT (2016) Quercetin-rich guava (Psidium guajava) juice in combination with trehalose reduces autophagy, apoptosis and pyroptosis formation in the kidney and pancreas of type II diabetic rats. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 21:334
Zuo Y, Chen L, Gu H et al (2021) GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis: a critical mechanism of diabetic nephropathy. Expert Rev Mol Med 23:e23
Cheng Q, Pan J, Zhou ZL et al (2021) Caspase-11/4 and gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis contributes to podocyte injury in mouse diabetic nephropathy. Acta Pharmacol Sin 42:954–963
Dai H, Liu Q, Liu B (2017) Research progress on mechanism of podocyte depletion in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Res 2017:2615286
Shao S, Zhang X, Xu Q, Pan R, Chen Y (2022) Emerging roles of Glucagon like peptide-1 in the management of autoimmune diseases and diabetes-associated comorbidities. Pharmacol Ther 239:108270
Draznin B, Aroda VR, Bakris G et al (2022) 9 Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 45:S125–S143
Li X, Song Y, Guo T, Xiao G, Li Q (2022) Effect of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists on the renal protection in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab 48:101366
Elbert A, Castellaro C, Litwak L, Inserra F, Wassermann A, Sinay I (2022) Renal effects of GLP-1 agonists in type 2 diabetes. Medicina (B Aires) 82:576–590
Muskiet MHA, Tonneijck L, Smits MM et al (2017) GLP-1 and the kidney: from physiology to pharmacology and outcomes in diabetes. Nat Rev Nephrol 13:605–628
Zhang Z, Wang X, Yang L, Yang L, Ma H (2021) Liraglutide ameliorates myocardial damage in experimental diabetic rats by inhibiting pyroptosis via Sirt1/AMPK signaling. Iran J Basic Med Sci 24:1358–1365
Song S, Guo R, Mehmood A et al (2022) Liraglutide attenuate central nervous inflammation and demyelination through AMPK and pyroptosis-related NLRP3 pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther 28:422–434
Yu X, Hao M, Liu Y et al (2019) Liraglutide ameliorates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis activation via mitophagy. Eur J Pharmacol 864:172715
Takahashi Y, Nomoto H, Yokoyama H et al (2023) Improvement of glycaemic control and treatment satisfaction by switching from liraglutide or dulaglutide to subcutaneous semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: a multicentre, prospective, randomized, open-label, parallel-group comparison study (SWITCH-SEMA 1 study). Diabetes Obes Metab 25(6):1503–1511
Funding
This research was supported by the Medical Research Project Fund of Dalian Municipal Medical and Health Institutions:2211041.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Q-ML conceived and designed the study. XL and XJ conducted most of the experiments and data analysis, and wrote the manuscript. MJ, Z-FW, TZ, and S-MC participated in collecting data and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of research that does not involve humans formal consent is not required.
Additional information
This article belongs to the Topical Collection “Diabetic Nephropathy”, managed by: Giuseppe Pugliese.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Jiang, X., Jiang, M. et al. GLP-1RAs inhibit the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway to regulate mouse renal podocyte pyroptosis. Acta Diabetol 61, 225–234 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-023-02184-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-023-02184-y