Abstract
Aims
The aims of this study were: to develop new equations for predicting resting energy expenditure (REE) in obese Italian subjects according to body composition parameters; to compare them with predicted values estimated by other REE prediction equations; and to cross-validate our equations using a validation set cohort.
Methods
Four hundred patients were enrolled and divided into three groups. Besides anthropometry and REE (indirect calorimetry), total body fat and lean were evaluated by dual X-ray absorptiometry, and fat mass and fat-free mass by bioelectrical impedance analysis.
Results
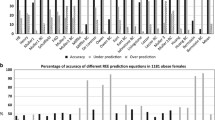
The subjects eligible to participate were 330. Group 1 (n = 174) was used to develop (R 2 = 0.79) and (R 2 = 0.77). Group 2 (n = 115) was used to generate (R 2 = 0.85) and (R 2 = 0.81). Group 3 (n = 41) was used to cross-validate the equations.
Conclusion
Equations 1 and 3 are reliable to measure REE from calorimetry and better than other equations that use anthropometric variables as predictors of REE. Further analysis in different populations is required before it can be applied in clinical practice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deed G, Barlow J, Kawol D, Kilov G, Sharma A, Hwa LY (2015) Diet and diabetes. Aust Fam Phys 44(5):192–196
American Diabetes Association, Bantle JP, Wylie-Rosett J, Albright AL, Apovian CM, Clark NG et al (2008) Nutrition recommendations and interventions for diabetes: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 1:S61–S78. doi:10.2337/dc08-S061
Evert AB, Boucher JL, Cypress M, Dunbar SA, Franz MJ, Mayer-Davis EJ et al (2013) American Diabetes Association: nutrition therapy recommendations for the management of adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care 36(11):3821–3842. doi:10.2337/dc13-2042
Foster GD, McGuckin BG (2001) Estimating resting energy expenditure in obesity. Obes Res 5:367S–372S (discussion 373S–374S)
DeLany JP, Lovejoy JC (1996) Energy expenditure. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 25(4):831–846
Hills AP, Mokhtar N, Byrne NM (2014) Assessment of physical activity and energy expenditure: an overview of objective measures. Front Nutr 16(1):5. doi:10.3389/fnut.2014.00005
Abdel-Hamid TK (2002) Modeling the dynamics of human energy regulation and its implications for obesity treatment. Syst Dyn Rev 18:431–471
Fullmer S, Benson-Davies S, Earthman CP, Frankenfield DC, Gradwell E, Lee PS et al (2015) Evidence analysis library review of best practices for performing indirect calorimetry in healthy and non-critically ill individuals. J Acad Nutr Diet 115(9):1417–1446. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2015.04.003
Lazzer S, Agosti F, Silvestri P, Derumeaux-Burel H, Sartorio A (2007) Prediction of resting energy expenditure in severely obese Italian women. J Endocrinol Investig 30(1):20–27
Madden AM, Mulrooney HM, Shah S (2016) Estimation of energy expenditure using prediction equations in overweight and obese adults: a systematic review. J Hum Nutr Diet 29(4):458–476. doi:10.1111/jhn.12355
Wells JC, Fuller NJ, Dewit O, Fewtrell MS, Elia M, Cole TJ (1999) Four-component model of body composition in children: density and hydration of fat-free mass and comparison with simpler models. Am J Clin Nutr 69(5):904–912
De Lorenzo A, Andreoli A, Bertoli S, Testolin G, Orinani G, Deurenberg P (2000) Resting metabolic rate in Italians: relation with body composition and anthropometric parameters. Acta Diabetol 37(2):77–81
Van der Ploeg GE, Gunn SM, Withers RT, Modra AC, Keeves JP, Chatterton BE (2001) Predicting the resting metabolic rate of young Australian males. Eur J Clin Nutr 55(3):145–152
Roza AM, Shizgal HM (1984) The Harris-Benedict equation revaluated: resting energy requirements and the body cell mass. Am J Clin Nutr 40(1):168–182
De Lorenzo A, Tagliabue A, Andreoli A, Testolin G, Comelli M, Deurenberg P (2001) Measured and predicted resting metabolic rate in Italian males and females, aged 18–59 y. Eur J Clin Nutr 55(3):208–214
Marra M, Cioffi I, Sammarco R, Montagnese C, Naccarato M, Amato V et al (2017) Prediction and evaluation of resting energy expenditure in a large group of obese outpatients. Int J Obes (Lond) 41(5):697–705. doi:10.1038/ijo.2017.34
Ikeda K, Fujimoto S, Goto M, Yamada C, Hamasaki A, Ida M et al (2013) A new equation to estimate basal energy expenditure of patients with diabetes. Clin Nutr 32(5):777–782. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2012.11.017
Müller MJ, Bosy-Westphal A, Kutzner D, Heller M (2003) Metabolically active components of fat free mass (FFM) and resting energy expenditure (REE) in humans. Forum Nutr 56:301–303
Wang Z, Heshka S, Gallagher D, Boozer CN, Kotler DP, Heymsfield SB (2000) Resting energy expenditure-fat-free mass relationship: new insights provided by body composition modeling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 279(3):E539–E545
Pourhassan M, Eggeling B, Schautz B, Johannsen M, Kiosz D, Glüer CC et al (2015) Relationship between submaximal oxygen uptake, detailed body composition, and resting energy expenditure in overweight subjects. Am J Hum Biol 27(3):397–406. doi:10.1002/ajhb.22666
Weir JB (1949) New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein metabolism. J Physiol 109:1–9
Horie LM, Gonzalez MC, Torrinhas RS, Cecconello I, Waitzberg DL (2011) New specific equation to estimate resting energy expenditure in severely obese patients. Obesity (Silver Spring) 19(5):1090–1094. doi:10.1038/oby.2010.326
De Lorenzo A, Soldati L, Sarlo F, Calvani M, Di Lorenzo N, Di Renzo L (2016) New obesity classification criteria as a tool for bariatric surgery indication. World J Gastroenterol 22(2):681–703. doi:10.3748/wjg.v22.i2.681.Review
De Lorenzo A, Bianchi A, Maroni P, Iannarelli A, Di Daniele N, Iacopino L et al (2013) Adiposity rather than BMI determines metabolic risk. Int J Cardiol 166:111–117
Bruno E, Alessandrini M, Napolitano B, De Padova A, Di Daniele N, De Lorenzo A (2009) Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry analysis of body composition in patients affected by OSAS. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266(8):1285–1290. doi:10.1007/s00405-008-0844-0
De Lorenzo A, Martinoli R, Carbonelli MG, Monteleone G, Di Lorenzo N, Di Daniele N (2004) Resting metabolic rate incremented by pulsating electrostatic field (PESF) therapy. Diabetes Nutr Metab 17(5):309–312
Cunningham JJ (1990) Calculation of energy expenditure from indirect calorimetry: assessment of the Weir equation. Nutrition 6(3):222–223
Di Renzo L, Carbonelli MG, Bianchi A, Domino E, Migliore MR, Rillo G et al (2012) Impact of the −174 G > C IL-6 polymorphism on bioelectrical parameters in obese subjects after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. J Obes 2012:208953. doi:10.1155/2012/208953
Altman DG (1996) Relation between two continuous variables. Practical statistics for medical research. Chapman & Hall, London, pp 277–324
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1(8476):307–310
Johnstone AM, Murison SD, Duncan JS, Rance KA, Speakman JR (2005) Factors influencing variation in basal metabolic rate include fat-free mass, fat mass, age, and circulating thyroxine but not sex, circulating leptin, or triiodothyronine. Am J Clin Nutr 82(5):941–948
Nelson KM, Weinsier RL, Long CL, Schutz Y (1992) Prediction of resting energy expenditure from fat-free mass and fat mass. Am J Clin Nutr 56(5):848–856
Kyle UG, Bosaeus I, De Lorenzo AD, Deurenberg P, Elia M, Gómez JM et al (2004) Bioelectrical impedance analysis—part I: review of principles and methods. Clin Nutr 23(5):1226–1243
Kyle UG, Bosaeus I, De Lorenzo AD, Deurenberg P, Elia M, Manuel Gómez J et al (2004) Bioelectrical impedance analysis—part II: utilization in clinical practice. Clin Nutr 23(6):1430–1453
Zhu K, Briffa K, Smith A, Mountain J, Briggs AM, Lye S et al (2014) Gender differences in the relationships between lean body mass, fat mass and peak bone mass in young adults. Osteoporos Int 25(5):1563–1570. doi:10.1007/s00198-014-2665-x
Ness-Abramof R, Apovian CM (2006) Diet modification for treatment and prevention of obesity. Endocrine 29(1):5–9
Seidell JC, Halberstadt J (2015) The global burden of obesity and the challenges of prevention. Ann Nutr Metab 66(Suppl 2):7–12. doi:10.1159/000375143
Zoico E, Corzato F, Bambace C, Rossi AP, Micciolo R, Cinti S et al (2013) Myosteatosis and myofibrosis: relationship with aging, inflammation and insulin resistance. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 57(3):411–416. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2013.06.001
Bredella MA, Ghomi RH, Thomas BJ, Torriani M, Brick DJ, Gerweck AV et al (2010) Comparison of DXA and CT in the assessment of body composition in premenopausal women with obesity and anorexia nervosa. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.) 18(11):2227–2233. doi:10.1038/oby.2010.5
Acknowledgements
We are beholden to all the subjects who volunteered in the study. We also thank the entire medical team from the Section of Clinical Nutrition and Nutrigenomic, University of Rome Tor Vergata, Rome. This study was supported by grants from Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Forestry (D.M.; 2017188).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
De Lorenzo A conceived, designed the experiments and drafted the manuscript; Di Renzo L, Morini P, Romano L contributed to the interpretation of the data and drafted the manuscript; Romano L collected the data and performed the experiments; de Miranda RC analyzed the data; Colica C had primary responsibility for the final content. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in this study.
Additional information
Managed by Massimo Federici.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Lorenzo, A., Di Renzo, L., Morini, P. et al. New equations to estimate resting energy expenditure in obese adults from body composition. Acta Diabetol 55, 59–66 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-017-1061-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-017-1061-3