Abstract
Aims
To analyze the serum lipid and inflammatory biomarker profile in the early insulin resistance (e-IR).
Methods
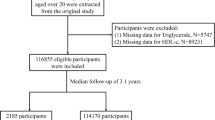
Cross-sectional study of 5943 adults without diabetes, stratified into no IR group (C-peptide <third tertile and glucose <100 mg/dL), e-IR group (C-peptide ≥third tertile and glucose <100 mg/dL) and advanced IR group (glucose ≥100 mg/dL).
Results
E-IR showed significant differences with no IR in the serum concentration of triglycerides (P < 0.001), HDL cholesterol (P < 0.001), LDL cholesterol (P < 0.001), sCD40L (P < 0.001), C-reactive protein (P < 0.004), leptin (P < 0.001) and adiponectin (P < 0.001). Adjusting for age, gender and abdominal obesity, corroborated the association of e-IR with highest quintile of triglycerides (OR 3.88 [3.07–4.89]), HDL cholesterol (OR 0.35 [0.28–0.44]), sCD40L (OR 0.47 [0.24–0.94]), C-reactive protein (OR 2.31 [1.29–4.12]), adiponectin (OR 0.11 [0.04–0.32]), PAI-1 (OR 3.29 [1.29–8.40]) and resistin (OR 1.25 [1.01–1.54]); the same biomarkers were associated with advanced IR although resistin was a protective factor (OR 0.73 [0.58–0.93]).
Conclusions
Euglycemic patients with e-IR present an unfavorable serum lipid and inflammatory biomarker profile. Measuring C-peptide in euglycemic patients with elevated triglycerides identifies e-IR.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pajvani UB, Accili D (2015) The new biology of diabetes. Diabetologia 58:2459–2468
Muniyappa R, Madan R, Quon MJ (2000) Assessing insulin sensitivity and resistance in humans. In: De Groot LJ, Beck-Peccoz P, Chrousos G, et al. (eds) NCBI Bookshelf. Endotext [Internet]. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278954. Last Update: 2 Feb 2015
Weyer C, Tataranni PA, Bogardus C et al(2001) Insulin resistance and insulin secretory dysfunction are independent predictors of worsening of glucose tolerance during each stage of type 2 diabetes development. Diabetes Care 24:89–94
Tabak AG, Jokela M, Akbaraly TN et al (2009) Trajectories of glycemia, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion before diagnosis of type 2 diabetes: an analysis from the Whitehall II study. Lancet 373:2215–2221
Shulman GI (2014) Ectopic fat in insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and cardiometabolic disease. N Engl J Med 371:1131–1141
Samuel VT, Shulman GI (2016) The pathogenesis of insulin resistance: integrating signaling pathways and substrate flux. J Clin Invest 126:12–22
Khodabandehloo H, Gorgani-Firuzjaee S, Panahi G, Meshkani R (2016) Molecular and cellular mechanisms linking inflammation to insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction. Transl Res 167:228–256
Cersosimo E, DeFronzo RA (2006) Insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: the road map for cardiovascular diseases. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 22:423–436
Zhan Y, Tang Z, Yu J (2014) Serum ferritin, diabetes, diabetes control, and insulin resistance. Acta Diabetol 51:991–998
Kharroubi I, Ladriere L, Cardozo AK et al (2004) Free fatty acids and cytokines induce pancreatic beta cell apoptosis by different mechanisms: role of NF-kappa B and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Endocrinology 145:5087–5096
Moran A, Steffen LM, Jacobs DR Jr et al (2005) Relation of C-reactive protein to insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk factors in youth. Diabetes Care 28:1763–1768
Kajimoto Y, Matsuoka T, Kaneto H et al (1999) Induction of glycation suppresses glucokinase gene expression in HIT-T15 cells. Diabetologia 42:1417–1424
Daniele G, Guardado-Mendoza R, Winnier D et al (2014) The inflammatory status score including IL-6, TNF-α, osteopontin, fractalkine, MCP-1 and adiponectin underlies whole-body insulin resistance and hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol 51:123–131
Nwaneri C, Cooper H, Bowen-Jones D (2013) Screening for type 2 diabetes and population mortality over 10 years. Lancet 381:901–912
Salazar MR, Carbajal HA, Espeche WG et al (2016) Insulin resistance: the linchpin between prediabetes and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res 13:157–163
Ariel D, Reaven G (2014) Modulation of coronary heart disease risk by insulin resistance in subjects with normal glucose tolerance or prediabetes. Acta Diabetol 51:1033–1039
Cabrera de León A, Oliva García JG, Marcelino Rodríguez I et al (2015) C-peptide as a risk factor of coronary artery disease in the general population. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res 12:199–207
Cabrera de León A, Rodríguez Pérez MC, Almeida González D et al (2008) Presentation of the “CDC de Canarias” cohort: objectives, design and preliminary results. Rev Esp Salud Publica 82:519–534
Fernández-Bergés D, Consuegra-Sánchez L, Peñafiel J et al (2014) Perfil inflamatorio y metabólico. Estudio DARIOS Inflamatorio. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed) 67:624–631
Ashwell M, Gunn P, Gibson S (2012) Waist-to-height ratio is a better screening tool than waist circumference and BMI for adult cardiometabolic risk factors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev 13:275–286
Bo S, Gentile L, Castiglione A et al (2012) C-peptide and the risk for incident complications and mortality in type 2 diabetic patients: a retrospective cohort study after a 14-year follow-up. Eur J Endocrinol 167:173–180
Kim ST, Kim BJ, Lim DM et al (2011) Basal C-peptide level as a surrogate marker of subclinical atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab J 35:41–49
Marx N, Silbernagel G, Brandenburg V et al (2013) C-peptide levels are associated with mortality and cardiovascular mortality in patients undergoing angiography: the LURIC study. Diabetes Care 36:708–714
Marx N, Walcher D, Raichle C et al (2004) C-peptide colocalizes with macrophages in early arteriosclerotic lesions of diabetic subjects and induces monocyte chemotaxis in vitro. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:540–545
Kappert K, Meyborg H, Clemenz M et al (2008) Insulin facilitates monocyte migration: a possible link to tissue inflammation in insulin-resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 365:503–508
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N et al (2006) Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 116:1784–1792
Schwartz DR, Lazar MA (2011) Human resistin: found in translation from mouse to man. Trends Endocrinol Metab 22:259–265
Iqbal N, Seshadri P, Stern L et al (2005) Serum resistin is not associated with obesity or insulin resistance in humans. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 9:161–165
Coello Domínguez S, Cabrera de León A, Almeida González D et al (2008) Inverse association between serum resistin and insulin resistance in humans. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 82:256–261
Abbasi F, Okeke Q, Reaven GM (2014) Evaluation of fasting plasma insulin concentration as an estimate of insulin action in nondiabetic individuals: comparison with the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). Acta Diabetol 51:193–197
Noctor E, Crowe C, Carmody LA et al (2015) ATLANTIC-DIP: prevalence of metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus by International Association of Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Groups criteria. Acta Diabetol 52:153–160
Hivert MF, Christophi CA, Franks PW et al (2016) Lifestyle and metformin ameliorate insulin sensitivity independently of the genetic burden of established insulin resistance variants in diabetes prevention program participants. Diabetes 65:520–526
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Karen Shashok for translation of the manuscript into English.
Funding
Canary Islands Health Service. Spanish Government (Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Projects 0901314, PI12/01855, and RD12/0042/0031 and 0013. FEDER).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
This study was approved by the Bioethics Committee of Nuestra Señora de la Candelaria University Hospital, and all participants provided their informed consent in writing.
Human and animal rights
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Additional information
Managed by Antonio Secchi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marcelino Rodríguez, I., Oliva García, J., Alemán Sánchez, J.J. et al. Lipid and inflammatory biomarker profiles in early insulin resistance. Acta Diabetol 53, 905–913 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-016-0885-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-016-0885-6