Abstract
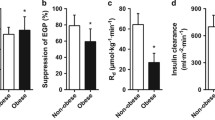
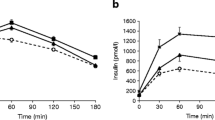
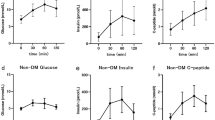
Metabolically healthy obese (MHO) are relatively insulin sensitive and have a favorable cardio-metabolic risk profile compared with metabolically abnormal obese (MAO). To evaluate whether MAO individuals have a decreased insulin clearance compared with MHO individuals, 49 MHO, 147 MAO, and 172 non-obese individuals were analyzed in this cross-sectional study. Insulin clearance and insulin sensitivity were assessed through euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp. MHO subjects exhibited significant lower triglycerides, total cholesterol, 2-h post-challenge glucose, fasting and 2-h post-challenge insulin, steady-state plasma insulin, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and gamma-glutamyltransferase as compared with MAO individuals. Disposition index was higher in MHO subjects as compared with MAO individuals after adjusting for gender and age (P = 0.04). Insulin clearance was significantly lower in MAO individuals as compared with MHO and non-obese individuals. The difference between the two obese subgroups remained significant after adjusting for gender, age, waist circumference, fat mass, and insulin-stimulated glucose disposal (P = 0.03). The hepatic insulin extraction (C-peptide/insulin) in the fasting state was significantly higher in MHO subjects as compared with MAO individuals (P < 0.0001). In univariate analysis adjusted for gender and age, insulin clearance was correlated with hepatic insulin extraction (P = 0.01). In conclusion, insulin clearance differs among obese subjects with different metabolic phenotypes. Impaired insulin clearance may contribute to sustained fasting and post-meal hyperinsulinemia observed in MAO individuals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wildman RP, Muntner P, Reynolds K et al (2008) The obese without cardiometabolic risk factor clustering and the normal weight with cardiometabolic risk factor clustering: prevalence and correlates of 2 phenotypes among the US population (NHANES 1999–2004). Arch Intern Med 168:1617–1624
Messier V, Karelis AD, Prud’homme D et al (2010) Identifying metabolically healthy but obese individuals in sedentary postmenopausal women. Obesity 18:911–917
Brochu M, Tchernof A, Dionne IJ et al (2001) What are the physical characteristics associated with a normal metabolic profile despite a high level of obesity in postmenopausal women? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:1020–1025
Karelis AD, St-Pierre DH, Conus F et al (2004) Metabolic and body composition factors in subgroups of obesity: what do we know? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2569–2575
Karelis AD, Faraj M, Bastard JP et al (2005) The metabolically healthy but obese individual presents a favorable inflammation profile. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:4145–4150
Marini MA, Succurro E, Frontoni S et al (2007) Metabolically healthy but obese women have an intermediate cardiovascular risk profile between healthy non-obese women and obese insulin resistant women. Diabetes Care 30:2145–2147
Stefan N, Kantartzis K, Machann J et al (2008) Identification and characterization of metabolically benign obesity in humans. Arch Intern Med 168:1609–1616
Succurro E, Marini MA, Frontoni S et al (2008) Insulin secretion in metabolically obese, but normal weight, and in metabolically healthy but obese individuals. Obesity 16:1881–1886
Aguilar-Salinas CA, García EG, Robles L et al (2008) High adiponectin concentrations are associated with the metabolically healthy obese phenotype. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:4075–4079
Messier V, Karelis AD, Robillard ME et al (2010) Metabolically healthy but obese individuals: relationship with hepatic enzymes. Metabolism 59:20–24
Sesti G, Folli F, Perego L et al (2011) Effects of weight loss in metabolically healthy obese subjects after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and hypocaloric diet. PLoS One 6(3):e17737
Khan UI, Wang D, Thurston RC et al (2011) Burden of subclinical cardiovascular disease in “metabolically benign” and “at-risk” overweight and obese women: the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN). Atherosclerosis 217:179–186
Sesti G, Succurro E, Arturi F et al (2011) IGF-1 levels link estimated glomerular filtration rate to insulin resistance in obesity: a study in obese, but metabolically healthy, subjects and obese, insulin-resistant subjects. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 21:933–940
Meigs JB, Wilson PW, Fox CS et al (2006) Body mass index, metabolic syndrome, and risk of type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:2906–2912
Arnlöv J, Ingelsson E, Sundström J et al (2010) Impact of body mass index and the metabolic syndrome on the risk of cardiovascular disease and death in middle-aged men. Circulation 121:230–236
Calori G, Lattuada G, Piemonti L et al (2011) Prevalence, metabolic features, and prognosis of metabolically healthy obese Italian individuals: the Cremona Study. Diabetes Care 34:210–215
Hamer M, Stamatakis E (2012) Metabolically healthy obesity and risk of all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:2482–2488
Ogorodnikova AD, Kim M, McGinn AP et al (2012) Incident cardiovascular disease events in metabolically benign obese individuals. Obesity 20:651–659
Appleton SL, Seaborn CJ, Visvanathan R et al (2013) Diabetes and cardiovascular disease outcomes in the metabolically healthy obese phenotype: a cohort study. Diabetes Care March 14 [Epub ahead of print]
Duckworth WC, Bennett RG, Hamel FG (1997) The significance of intracellular insulin to insulin action. J Investig Med 45:20–27
Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y et al (2003) Insulin degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4162–4167
Abdul-Hay SO, Kang D, McBride M et al (2011) Deletion of insulin-degrading enzyme elicits antipodal, age-dependent effects on glucose and insulin tolerance. PLoS One 6:e20818
Faber OK, Christensen K, Kehlet H et al (1981) Decreased insulin removal contributes to hyperinsulinemia in obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 53:618–621
Bonora E, Zavaroni I, Bruschi F et al (1984) Peripheral hyperinsulinemia of simple obesity: pancreatic hypersecretion or impaired insulin metabolism? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 59:1121–1127
Erdmann J, Mayr M, Oppel U et al (2009) Weight-dependent differential contribution of insulin secretion and clearance to hyperinsulinemia of obesity. Regul Pept 152:1–7
Jones CN, Abbasi F, Carantoni M et al (2000) Roles of insulin resistance and obesity in regulation of plasma insulin concentrations. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278:E501–E508
Peiris AN, Mueller RA, Smith GA et al (1986) Splanchnic insulin metabolism in obesity. Influence of body fat distribution. J Clin Invest 78:1648–1657
Kotronen A, Vehkavaara S, Seppälä-Lindroos A et al (2007) Effect of liver fat on insulin clearance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293:E1709–E1715
Mittelman SD, Van Citters GW, Kim SP et al (2000) Longitudinal compensation for fat-induced insulin resistance includes reduced insulin clearance and enhanced β cell response. Diabetes 49:2116–2125
Laakso M, Zilinskaite J, Hansen T et al (2008) Insulin sensitivity, insulin release and GLP-1 levels in subjects with IFG and/or IGT in the EUGENE2 study. Diabetologia 51:502–511
Marini MA, Frontoni S, Mineo D et al (2003) The Arg972 variant in insulin receptor substrate-1 is associated with an atherogenic profile in offspring of type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:3368–3371
DeFronzo RA, Tobin JD, Andres R (1979) Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab Gastrointest Physiol 237:E214–E223
Kahn SE (2001) The importance of β-cell failure in the development and progression of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:4047–4058
Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM et al (2009) Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 120:1640–1645
Svedberg J, Björntorp P, Smith U, Lönnroth P (1990) Free-fatty acid inhibition of insulin binding, degradation, and action in isolated rat hepatocytes. Diabetes 39:570–574
Wiesenthal SR, Sandhu H, McCall RH et al (1999) Free fatty acids impair hepatic insulin extraction in vivo. Diabetes 48:766–774
Balent B, Goswami G, Goodloe G et al (2002) Acute elevation of NEFA causes hyperinsulinemia without effect on insulin secretion rate in healthy human subjects. Ann NY Acad Sci 967:535–543
Acknowledgments
This work was supported, in part, by Italian Ministry of University grant FIRB/MERIT RBNE08NKH7_002 to G. Sesti.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Massimo Porta.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marini, M.A., Frontoni, S., Succurro, E. et al. Differences in insulin clearance between metabolically healthy and unhealthy obese subjects. Acta Diabetol 51, 257–261 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-013-0511-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-013-0511-9