Abstract
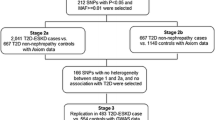
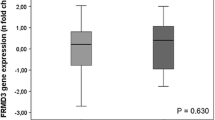
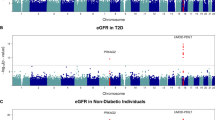
CD2-associated protein (CD2AP) is essential for podocyte function. CD2AP mutations have been found in patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, a disease histologically resembling diabetic nephropathy and often progressing to end-stage renal disease (ESRD). We hypothesised that variations in the CD2AP gene may contribute to susceptibility to glomerular injury in diabetes and investigated if single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in CD2AP are associated with diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes. The discovery cohort consisted of 2,251 Finnish patients with type 1 diabetes. SNPs were selected from the HapMap database to cover the CD2AP gene. The associations between genotyped SNPs and diabetic nephropathy or ESRD were analysed with the chi-squared test and logistic regression. Three SNPs were selected for replication in cohorts from Denmark, Italy, the United Kingdom and Ireland. None of the 15 successfully genotyped SNPs were associated with diabetic nephropathy when compared to patients with normal albumin excretion rate. However, when genotype frequencies in patients with ESRD were compared with all other patients, two CD2AP SNPs, rs9369717 and rs9349417, were found to be associated with ESRD. The meta-analysis of the original and two additional European cohorts resulted in significant p values <0.01 for these SNPs. A third SNP, rs6936632, was suggestively associated with ESRD in the Finnish patients and in the meta-analysis of four cohorts. CD2AP gene variants may contribute to susceptibility to ESRD in patients with type 1 diabetes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim JM, Wu H, Green G, Winkler CA, Kopp JB, Miner JH, Unanue ER, Shaw AS (2003) CD2-associated protein haploinsufficiency is linked to glomerular disease susceptibility. Science 300:1298–1300
Lowik MM, Groenen PJ, Pronk I, Lilien MR, Goldschmeding R, Dijkman HB, Levtchenko EN, Monnens LA, van den Heuvel LP (2007) Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in a patient homozygous for a CD2AP mutation. Kidney Int 72:1198–1203
Gigante M, Pontrelli P, Montemurno E, Roca L, Aucella F, Penza R, Caridi G, Ranieri E, Ghiggeri GM, Gesualdo L (2009) CD2AP mutations are associated with sporadic nephrotic syndrome and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:1858–1864
Barisoni L, Kriz W, Mundel P, D’Agati V (1999) The dysregulated podocyte phenotype: a novel concept in the pathogenesis of collapsing idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and HIV-associated nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:51–61
Schwartz MM (2000) The role of podocyte injury in the pathogenesis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Ren Fail 22:663–684
Boute N, Gribouval O, Roselli S, Benessy F, Lee H, Fuchshuber A, Dahan K, Gubler MC, Niaudet P, Antignac C (2000) NPHS2, encoding the glomerular protein podocin, is mutated in autosomal recessive steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Nat Genet 24:349–354
Kaplan JM, Kim SH, North KN, Rennke H, Correia LA, Tong HQ, Mathis BJ, Rodriguez-Perez JC, Allen PG, Beggs AH, Pollak MR (2000) Mutations in ACTN4, encoding alpha-actinin-4, cause familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet 24:251–256
Winn MP, Conlon PJ, Lynn KL, Farrington MK, Creazzo T, Hawkins AF, Daskalakis N, Kwan SY, Ebersviller S, Burchette JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Howell DN, Vance JM, Rosenberg PB (2005) A mutation in the TRPC6 cation channel causes familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Science 308:1801–1804
Reiser J, Polu KR, Moller CC, Kenlan P, Altintas MM, Wei C, Faul C, Herbert S, Villegas I, Avila-Casado C, McGee M, Sugimoto H, Brown D, Kalluri R, Mundel P, Smith PL, Clapham DE, Pollak MR (2005) TRPC6 is a glomerular slit diaphragm-associated channel required for normal renal function. Nat Genet 37:739–744
Dustin ML, Olszowy MW, Holdorf AD, Li J, Bromley S, Desai N, Widder P, Rosenberger F, van der Merwe PA, Allen PM, Shaw AS (1998) A novel adaptor protein orchestrates receptor patterning and cytoskeletal polarity in T-cell contacts. Cell 94:667–677
Kirsch KH, Georgescu MM, Ishimaru S, Hanafusa H (1999) CMS: an adapter molecule involved in cytoskeletal rearrangements. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:6211–6216
Lehtonen S, Ora A, Olkkonen VM, Geng L, Zerial M, Somlo S, Lehtonen E (2000) In vivo interaction of the adapter protein CD2-associated protein with the type 2 polycystic kidney disease protein, polycystin-2. J Biol Chem 275:32888–32893
Huber TB, Hartleben B, Kim J, Schmidts M, Schermer B, Keil A, Egger L, Lecha RL, Borner C, Pavenstadt H, Shaw AS, Walz G, Benzing T (2003) Nephrin and CD2AP associate with phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and stimulate AKT-dependent signaling. Mol Cell Biol 23:4917–4928
Shih NY, Li J, Karpitskii V, Nguyen A, Dustin ML, Kanagawa O, Miner JH, Shaw AS (1999) Congenital nephrotic syndrome in mice lacking CD2-associated protein. Science 286:312–315
Atkins RC, Zimmet P (2010) Diabetic kidney disease: act now or pay later. Acta Diabetol 47:1–4
Groop PH, Thomas MC, Moran JL, Waden J, Thorn LM, Makinen VP, Rosengard-Barlund M, Saraheimo M, Hietala K, Heikkila O, Forsblom C, FinnDiane Study Group (2009) The presence and severity of chronic kidney disease predicts all-cause mortality in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 58:1651–1658
Guo L, Cheng Y, Wang X, Pan Q, Li H, Zhang L, Wang Y (2012) Association between microalbuminuria and cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus of the Beijing Han nationality. Acta Diabetol 49(Suppl 1):S65–S71
Ellis EN, Steffes MW, Chavers B, Mauer SM (1987) Observations of glomerular epithelial cell structure in patients with type I diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int 32:736–741
Chiang ML, Hawkins EP, Berry PL, Barrish J, Hill LL (1988) Diagnostic and prognostic significance of glomerular epithelial cell vacuolization and podocyte effacement in children with minimal lesion nephrotic syndrome and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: an ultrastructural study. Clin Nephrol 30:8–14
Steffes MW, Schmidt D, McCrery R, Basgen JM, International Diabetic Nephropathy Study Group (2001) Glomerular cell number in normal subjects and in type 1 diabetic patients. Kidney Int 59:2104–2113
Meyer TW, Bennett PH, Nelson RG (1999) Podocyte number predicts long-term urinary albumin excretion in Pima Indians with Type II diabetes and microalbuminuria. Diabetologia 42:1341–1344
Susztak K, Raff AC, Schiffer M, Bottinger EP (2006) Glucose-induced reactive oxygen species cause apoptosis of podocytes and podocyte depletion at the onset of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 55:225–233
Ihalmo P, Wessman M, Kaunisto MA, Kilpikari R, Parkkonen M, Forsblom C, Holthofer H, Groop PH, FinnDiane Study Group (2008) Association analysis of podocyte slit diaphragm genes as candidates for diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia 51:86–90
Thorn LM, Forsblom C, Fagerudd J, Thomas MC, Pettersson-Fernholm K, Saraheimo M, Waden J, Ronnback M, Rosengard-Barlund M, Bjorkesten CG, Taskinen MR, Groop PH, FinnDiane Study Group (2005) Metabolic syndrome in type 1 diabetes: association with diabetic nephropathy and glycemic control (the FinnDiane study). Diabetes Care 28:2019–2024
Tolonen N, Forsblom C, Thorn L, Waden J, Rosengard-Barlund M, Saraheimo M, Heikkila O, Pettersson-Fernholm K, Taskinen MR, Groop PH, FinnDiane Study Group (2008) Relationship between lipid profiles and kidney function in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 51:12–20
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF III, Feldman HI, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Greene T, Coresh J, CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) (2009) A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 150:604–612
McKnight AJ, Woodman AM, Parkkonen M, Patterson CC, Savage DA, Forsblom C, Pettigrew KA, Sadlier D, Groop PH, Maxwell AP, Warren 3/UK GoKinD Study Group (2009) Investigation of DNA polymorphisms in SMAD genes for genetic predisposition to diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 52:844–849
Barrett JC (2009) Haploview: visualization and analysis of SNP genotype data. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2009: pdb.ip71
de Bakker PI, Yelensky R, Pe’er I, Gabriel SB, Daly MJ, Altshuler D (2005) Efficiency and power in genetic association studies. Nat Genet 37:1217–1223
Purcell S, Cherny SS, Sham PC (2003) Genetic power calculator: design of linkage and association genetic mapping studies of complex traits. Bioinformatics 19:149–150
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PI, Daly MJ, Sham PC (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575
Naj AC, Jun G, Beecham GW, Wang LS, Vardarajan BN, Buros J, Gallins PJ, Buxbaum JD, Jarvik GP, Crane PK, Larson EB, Bird TD, Boeve BF, Graff-Radford NR, De Jager PL, Evans D, Schneider JA, Carrasquillo MM, Ertekin-Taner N, Younkin SG, Cruchaga C, Kauwe JS, Nowotny P, Kramer P, Hardy J, Huentelman MJ, Myers AJ, Barmada MM, Demirci FY, Baldwin CT, Green RC, Rogaeva E, St George-Hyslop P, Arnold SE, Barber R, Beach T, Bigio EH, Bowen JD, Boxer A, Burke JR, Cairns NJ, Carlson CS, Carney RM, Carroll SL, Chui HC, Clark DG, Corneveaux J, Cotman CW, Cummings JL, DeCarli C, DeKosky ST, Diaz-Arrastia R, Dick M, Dickson DW, Ellis WG, Faber KM, Fallon KB, Farlow MR, Ferris S, Frosch MP, Galasko DR, Ganguli M, Gearing M, Geschwind DH, Ghetti B, Gilbert JR, Gilman S, Giordani B, Glass JD, Growdon JH, Hamilton RL, Harrell LE, Head E, Honig LS, Hulette CM, Hyman BT, Jicha GA, Jin LW, Johnson N, Karlawish J, Karydas A, Kaye JA, Kim R, Koo EH, Kowall NW, Lah JJ, Levey AI, Lieberman AP, Lopez OL, Mack WJ, Marson DC, Martiniuk F, Mash DC, Masliah E, McCormick WC, McCurry SM, McDavid AN, McKee AC, Mesulam M, Miller BL, Miller CA, Miller JW, Parisi JE, Perl DP, Peskind E, Petersen RC, Poon WW, Quinn JF, Rajbhandary RA, Raskind M, Reisberg B, Ringman JM, Roberson ED, Rosenberg RN, Sano M, Schneider LS, Seeley W, Shelanski ML, Slifer MA, Smith CD, Sonnen JA, Spina S, Stern RA, Tanzi RE, Trojanowski JQ, Troncoso JC, Van Deerlin VM, Vinters HV, Vonsattel JP, Weintraub S, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Williamson J, Woltjer RL, Cantwell LB, Dombroski BA, Beekly D, Lunetta KL, Martin ER, Kamboh MI, Saykin AJ, Reiman EM, Bennett DA, Morris JC, Montine TJ, Goate AM, Blacker D, Tsuang DW, Hakonarson H, Kukull WA, Foroud TM, Haines JL, Mayeux R, Pericak-Vance MA, Farrer LA, Schellenberg GD (2011) Common variants at MS4A4/MS4A6E, CD2AP, CD33 and EPHA1 are associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 43:436–441
Forsblom C, Harjutsalo V, Thorn LM, Waden J, Tolonen N, Saraheimo M, Gordin D, Moran JL, Thomas MC, Groop PH, FinnDiane Study Group (2011) Competing-risk analysis of ESRD and death among patients with type 1 diabetes and macroalbuminuria. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:537–544
Seaquist ER, Goetz FC, Rich S, Barbosa J (1989) Familial clustering of diabetic kidney disease. Evidence for genetic susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med 320:1161–1165
(1997) Clustering of long-term complications in families with diabetes in the diabetes control and complications trial. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Diabetes 46:1829–1839
Williams WW, Salem RM, McKnight AJ, Sandholm N, Forsblom C, Taylor A, Guiducci C, McAteer JB, McKay GJ, Isakova T, Brennan EP, Sadlier DM, Palmer C, Soderlund J, Fagerholm E, Harjutsalo V, Lithovius R, Gordin D, Hietala K, Kyto J, Parkkonen M, Rosengard-Barlund M, Thorn L, Syreeni A, Tolonen N, Saraheimo M, Waden J, Pitkaniemi J, Sarti C, Tuomilehto J, Tryggvason K, Osterholm AM, He B, Bain S, Martin F, Godson C, Hirschhorn JN, Maxwell AP, Groop PH, Florez JC, for the GENIE Consortium (2012) Association testing of previously reported variants in a large case-control meta-analysis of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 61:2187–2194
Grunkemeyer JA, Kwoh C, Huber TB, Shaw AS (2005) CD2-associated protein (CD2AP) expression in podocytes rescues lethality of CD2AP deficiency. J Biol Chem 280:29677–29681
Yaddanapudi S, Altintas MM, Kistler AD, Fernandez I, Moller CC, Wei C, Peev V, Flesche JB, Forst AL, Li J, Patrakka J, Xiao Z, Grahammer F, Schiffer M, Lohmuller T, Reinheckel T, Gu C, Huber TB, Ju W, Bitzer M, Rastaldi MP, Ruiz P, Tryggvason K, Shaw AS, Faul C, Sever S, Reiser J (2011) CD2AP in mouse and human podocytes controls a proteolytic program that regulates cytoskeletal structure and cellular survival. J Clin Invest 121:3965–3980
Shankland SJ, Scholey JW, Ly H, Thai K (1994) Expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 during diabetic renal hypertrophy. Kidney Int 46:430–442
Iwano M, Kubo A, Nishino T, Sato H, Nishioka H, Akai Y, Kurioka H, Fujii Y, Kanauchi M, Shiiki H, Dohi K (1996) Quantification of glomerular TGF-beta 1 mRNA in patients with diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int 49:1120–1126
Sever S, Altintas MM, Nankoe SR, Moller CC, Ko D, Wei C, Henderson J, del Re EC, Hsing L, Erickson A, Cohen CD, Kretzler M, Kerjaschki D, Rudensky A, Nikolic B, Reiser J (2007) Proteolytic processing of dynamin by cytoplasmic cathepsin L is a mechanism for proteinuric kidney disease. J Clin Invest 117:2095–2104
Lowik M, Levtchenko E, Westra D, Groenen P, Steenbergen E, Weening J, Lilien M, Monnens L, van den Heuvel L (2008) Bigenic heterozygosity and the development of steroid-resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:3146–3151
Huber TB, Kwoh C, Wu H, Asanuma K, Godel M, Hartleben B, Blumer KJ, Miner JH, Mundel P, Shaw AS (2006) Bigenic mouse models of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis involving pairwise interaction of CD2AP, Fyn, and synaptopodin. J Clin Invest 116:1337–1345
Caramori ML, Fioretto P, Mauer M (2003) Low glomerular filtration rate in normoalbuminuric type 1 diabetic patients: an indicator of more advanced glomerular lesions. Diabetes 52:1036–1040
Acknowledgments
We thank Maikki Parkkonen for accomplished technical assistance and advice. We thank all the persons who participated in the study and gratefully acknowledge all the physicians and nurses involved in the recruitment of participants in the FinnDiane study (ESM 3). The Warren 3/U.K. GoKinD Study Group was jointly funded by Diabetes UK and the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation and includes the following individuals: A.P. Maxwell, A.J. McKnight, D.A. Savage (Belfast); J. Walker (Edinburgh); S. Thomas, G.C. Viberti (London); A.J.M. Boulton (Manchester); S. Marshall (Newcastle); A.G. Demaine and B.A. Millward (Plymouth); Professor S.C. Bain (Swansea). This study was financially supported by the Academy of Finland (121248, 131255, 218021, 134379), the European Research Council (242820), the Diabetes Research Foundation, the Foundation for Paediatric Research, the National Graduate School of Clinical Investigation, Folkhälsan Research Foundation, Wilhelm and Else Stockmann Foundation, Kyllikki and Uolevi Lehikoinen Foundation, the Finnish Cultural Foundation, Liv och Hälsa Foundation and Finnish Medical Society (Finska Läkaresällskapet). MS was supported by the Sectoral Operational Programme Human Resources Development (SOP HRD), financed from the European Social Fund and by the Romanian Government under the contract number POSDRU/89/1.5/S/64109. Genotyping of the UK-ROI samples was supported by the Northern Ireland Kidney Research Fund. GL received a PhD studentship jointly funded by Kidney Research UK and Diabetes UK.
Conflict of interest
PHG has received honorariums from Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Genzyme, MSD and Novo Nordisk, research grants from Eli Lilly and Roche and is a member of advisory boards in Boehringer Ingelheim and Novartis. The present study is not financially supported by a pharmaceutical company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Antonio Secchi.
This study is conducted on behalf of the FinnDiane Study Group.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hyvönen, M.E., Ihalmo, P., Sandholm, N. et al. CD2AP is associated with end-stage renal disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 50, 887–897 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-013-0475-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-013-0475-9