Abstract
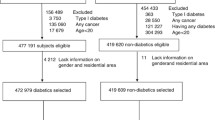
The aim of the study was to evaluate the link between diabetes and pancreatic cancer (PC) mortality and the joint effect of smoking and insulin use on PC mortality. A total of 39,988 men and 46,909 women with type 2 diabetes, aged ≥25 years and recruited in 1995–1998, were followed to 2006 for PC mortality. Age–sex-specific mortality rate ratios for diabetic patients versus the general population were calculated. Cox regression was used to evaluate hazard ratios for PC mortality for covariates including age, sex, diabetes duration, body mass index, smoking, insulin use, and area of residence. The interaction and joint effect of smoking and insulin use were also evaluated. A total of 89 men and 63 women died of PC. The mortality rate ratios (95 % CI) showed a significantly higher risk in diabetic patients with a magnitude most remarkable at the youngest age: 1.51 (1.15, 1.98), 2.02 (1.35, 3.03), and 8.36 (5.39, 12.98) for ≥65, 55–64, and 25–54 years old, respectively, for men; and 1.16 (0.84, 1.59), 2.12 (1.39, 3.23) and 3.33 (1.14, 9.68), respectively, for women. In multivariable Cox regression analysis, only age was significantly predictive for PC mortality. Although smoking and insulin use might be associated with a 50 % higher risk when analyzed as individual risk factors, they did not reach statistical significance. The interaction term of smoking and insulin use was also not statistically significant in additional modeling. However, smoking and insulin use jointly increased the risk with an adjusted hazard ratio (95 % CI) of 3.04 (1.37, 6.73) when compared to patients who did not smoke and did not use insulin. Diabetic patients have a significantly higher risk of PC mortality. In patients with type 2 diabetes, smoking and insulin use may jointly increase the risk by threefold.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicolucci A (2010) Epidemiological aspects of neoplasms in diabetes. Acta Diabetol 47:87–95
Onishi S, Takemoto M, Ishikawa T, Okabe E, Ishibashi R, He P, Kobayashi K, Fujimoto M, Kawamura H, Yokote K (2012) Japanese diabetic patients with Werner syndrome exhibit high incidence of cancer. Acta Diabetol 49(Suppl 1):S259–S260
Lauper JM, Monnat RJ Jr. Diabetes mellitus and cancer in Werner syndrome. Acta Diabetol. 2013 Feb 6. [Epub ahead of print]
Tseng CH, Chong CK, Tai TY (2009) Secular trend for mortality from breast cancer and the association between diabetes and breast cancer in Taiwan between 1995 and 2006. Diabetologia 52:240–246
Tseng CH, Chong CK, Tseng CP, Chan TT (2009) Age-related risk of mortality from bladder cancer in diabetic patients: a 12-year follow-up of a national cohort in Taiwan. Ann Med 41:371–379
Tseng CH (2011) Diabetes and risk of bladder cancer: a study using the National Health Insurance database in Taiwan. Diabetologia 54:2009–2015
Tseng CH (2012) Diabetes and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: analyses of prevalence and annual incidence in 2005 using the National Health Insurance database in Taiwan. Ann Oncol 23:153–158
Arcidiacono B, Iiritano S, Nocera A, Possidente K, Nevolo MT, Ventura V, Foti D, Chiefari E, Brunetti A (2012) Insulin resistance and cancer risk: an overview of the pathogenetic mechanisms. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:789174
Tseng CH (2012) Diabetes, metformin use, and colon cancer: a population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Eur J Endocrinol 167:409–416
Zhang F, Yang Y, Skrip L, Hu D, Wang Y, Wong C, Qiu J, Lei H (2012) Diabetes mellitus and risk of prostate cancer: an updated meta-analysis based on 12 case–control and 25 cohort studies. Acta Diabetol 49(Suppl 1):S235–S246
Tseng CH (2011) Prostate cancer mortality in Taiwanese men: increasing age-standardized trend in general population and increased risk in diabetic men. Ann Med 43:142–150
Tseng CH (2011) Diabetes and risk of prostate cancer: a study using the National Health Insurance. Diabetes Care 34:616–621
Lee MY, Lin KD, Hsiao PJ, Shin SJ (2012) The association of diabetes mellitus with liver, colon, lung, and prostate cancer is independent of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and gout in Taiwanese patients. Metabolism 61:242–249
Hsieh MC, Lee TC, Cheng SM, Tu ST, Yen MH, Tseng CH (2012) The influence of type 2 diabetes and glucose-lowering therapies on cancer risk in the Taiwanese. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:413782
Perseghin G, Calori G, Lattuada G, Ragogna F, Dugnani E, Garancini MP, Crosignani P, Villa M, Bosi E, Ruotolo G, Piemonti L (2012) Insulin resistance/hyperinsulinemia and cancer mortality: the Cremona study at the 15th year of follow-up. Acta Diabetol 49:421–428
Viollet B, Guigas B, Sanz Garcia N, Leclerc J, Foretz M, Andreelli F (2012) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: an overview. Clin Sci (Lond) 122:253–270
Chiu WY, Shih SR, Tseng CH (2012) A review on the association between glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and thyroid cancer. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:924168
Tseng CH, Tseng FH (2012) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists and bladder cancer: lessons from animal studies. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev 30:368–402
Tseng CH (2012) Pioglitazone and bladder cancer in human studies: is it diabetes itself, diabetes drugs, flawed analyses or different ethnicities? J Formos Med Assoc 111:123–131
Tseng CH (2013) Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a significant risk factor for bladder cancer in diabetic patients: a population-based cohort study using the National Health Insurance in Taiwan. BMC Cancer 13:7
Monami M, Lamanna C, Balzi D, Marchionni N, Mannucci E (2009) Sulphonylureas and cancer: a case–control study. Acta Diabetol 46:279–284
Yang X, So WY, Ma RC, Kong AP, Lee HM, Xu G, Ozaki R, Chan JC (2012) Synergistic effects of low LDL cholesterol with other factors for the risk of cancer in type 2 diabetes: the Hong Kong Diabetes Registry. Acta Diabetol 49(Suppl 1):S185–S193
Yang SH, Kuo YH, Tien YW, Hsu C, Hsu CH, Kuo SH, Cheng AL (2011) Inferior survival of advanced pancreatic cancer patients who received gemcitabine-based chemotherapy but did not participate in clinical trials. Oncology 81:143–150
Lowenfels AB, Maisonneuve P (2005) Risk factors for pancreatic cancer. J Cell Biochem 95:649–656
Yeo TP, Lowenfels AB (2012) Demographics and epidemiology of pancreatic cancer. Cancer J 18:477–484
Hariharan D, Saied A, Kocher HM (2008) Analysis of mortality rates for pancreatic cancer across the world. HPB (Oxford) 10:58–62
Ben Q, Xu M, Ning X, Liu J, Hong S, Huang W, Zhang H, Li Z (2011) Diabetes mellitus and risk of pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Eur J Cancer 47:1928–1937
Chen HF, Chen P, Li CY (2011) Risk of malignant neoplasm of the pancreas in relation to diabetes: a population-based study in Taiwan. Diabetes Care 34:1177–1179
Li D, Tang H, Hassan MM, Holly EA, Bracci PM, Silverman DT (2011) Diabetes and risk of pancreatic cancer: a pooled analysis of three large case–control studies. Cancer Causes Control 22:189–197
Tseng CH (2004) Mortality and causes of death in a national sample of diabetic patients in Taiwan. Diabetes Care 27:1605–1609
Tseng CH (2011) Diabetes conveys a higher risk of gastric cancer mortality despite an age-standardised decreasing trend in the general population in Taiwan. Gut 60:774–779
Tseng CH (2006) Prevalence of lower-extremity amputation among patients with diabetes mellitus: is height a factor? CMAJ 174:319–323
Tseng CH (2007) Effect of parental hypertension and/or parental diabetes on hypertension in Taiwanese diabetic patients. Eur J Clin Invest 37:870–877
Michaud DS, Wolpin B, Giovannucci E, Liu S, Cochrane B, Manson JE, Pollak MN, Ma J, Fuchs CS (2007) Prediagnostic plasma C-peptide and pancreatic cancer risk in men and women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16:2101–2109
Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ, Graubard BI, Chari S, Limburg P, Taylor PR, Virtamo J, Albanes D (2005) Insulin, glucose, insulin resistance, and pancreatic cancer in male smokers. JAMA 294:2872–2878
Rieder S, Michalski CW, Friess H, Kleeff J (2011) Insulin-like growth factor signaling as a therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 11:427–433
Pollak M (2012) The insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptor family in neoplasia: an update. Nat Rev Cancer 12:159–169
Kurtzhals P, Schäffer L, Sørensen A, Kristensen C, Jonassen I, Schmid C, Trüb T (2000) Correlations of receptor binding and metabolic and mitogenic potencies of insulin analogs designed for clinical use. Diabetes 49:999–1005
Iodice S, Gandini S, Maisonneuve P, Lowenfels AB (2008) Tobacco and the risk of pancreatic cancer: a review and meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg 393:535–545
Hemkens LG, Grouven U, Bender R, Günster C, Gutschmidt S, Selke GW, Sawicki PT (2009) Risk of malignancies in patients with diabetes treated with human insulin or insulin analogues: a cohort study. Diabetologia 52:1732–1744
Aune D, Greenwood DC, Chan DS, Vieira R, Vieira AR, Navarro Rosenblatt DA, Cade JE, Burley VJ, Norat T (2012) Body mass index, abdominal fatness and pancreatic cancer risk: a systematic review and non-linear dose–response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Ann Oncol 23:843–852
Jee SH, Yun JE, Park EJ, Cho ER, Park IS, Sull JW, Ohrr H, Samet JM (2008) Body mass index and cancer risk in Korean men and women. Int J Cancer 123:1892–1896
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the Department of Health (DOH89-TD-1035; DOH97-TD-D-113-97009) and the National Science Council (NSC 101-2314-B-002-117) of Taiwan. The guarantor of the manuscript is CH Tseng.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Antonio Secchi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tseng, CH. Diabetes, insulin use, smoking, and pancreatic cancer mortality in Taiwan. Acta Diabetol 50, 879–886 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-013-0471-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-013-0471-0